* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation - Fit-ED
Implicit learning wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Problem-based learning wikipedia , lookup
Educational technology wikipedia , lookup
Inquiry-based learning wikipedia , lookup
Learning styles wikipedia , lookup
Learning disability wikipedia , lookup
Concept learning wikipedia , lookup
Classroom management wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Project-based learning wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative education wikipedia , lookup
Autodidacticism wikipedia , lookup
Differentiated instruction wikipedia , lookup
Learning through play wikipedia , lookup
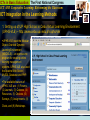
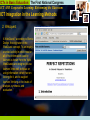
ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND COOPERATIVE LEARNING: REINVENTING THE CLASSROOM Renante P. Manlunas University of the Philippines Cebu College Professional Education Division High School Program ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Introduction This paper presents a case study on the impact of the use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) as a tool, and cooperative learning (CL) as a pedagogical approach to the delivery of curricular content. The main objective of this study was to show that the use of ICT in the classroom should be coupled with sound pedagogical approaches in order to maximize the positive effects of technology integration in the learning process. The effective use of technology in education requires thought, experimentation, and a willingness to spend time needed to develop and refine strategies until they are proven to be effective.” Thus, a successful integration of technology in education requires a rethinking of the ways in which learning is being facilitated together with the readiness and patience to explore new ways of teaching. The education process must be based on a model that is appropriate for an information–driven society. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Traditional Teaching Vs. Cooperative Learning Traditional teaching is a method of learning that views the classroom environment as one where the role of the teacher is to simply give information to students. The goals are predominantly individualistic Cooperative learning (CL) is the instructional use of small groups through which students work together to maximize their own and each others learning. In this type of classroom environment, the students interact with their groups and perform task–oriented activities designed by the teacher. Traditional learning is teacher–centered, a cooperative classroom is student– centered The effectiveness of cooperative learning lies in the core concepts being promoted: positive interdependence, individual accountability, equal opportunities for success and improvement of social skills. The role of the teacher is that of a facilitator and ensures that learning activities are carried out by each of the cooperative learning groups. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Cooperative Learning w/ TGT In this study, the experimental group (CLM) used the Teams–Games– Tournaments cooperative learning method. TGT, originally developed by David DeVries and Keith Edwards, was the first and oldest of the Johns Hopkins University cooperative learning methods. TGT provides an added dimension of fun and excitement through the utilization of academic games and tournaments. In TGT, students are assigned to three or four–member teams that are mixed in performance and gender. The teacher presents the lesson and then students work with their teams to ensure that all the members have mastered the lesson. The students then play academic games and tournaments either weekly or at the end of the unit. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Classroom Organization The study was composed of 2 groups – the Non-Cooperative Learning Method (NCLM) group, with 34 students and the Cooperative Learning Method (CLM) group, with 33 students. Both groups used ICT in the Geometry class. The CLM group also used the TGT cooperative learning method. Each group had ten subgroups used to facilitate group–based classroom activities. The criteria for group creation was based on the previous academic performance of the students. A three or four–member SG represents a cross–section of the class in terms of their academic abilities. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom ICT Integration in the Learning Methods 1. Setting up of UP High School in Cebu Virtual Learning Environment (UPHS-VLE) – http://www.cebu.upv.edu.ph/uphs/vle/ UPHS-VLE used the Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment (MOODLE) – an opensource program for creating online learning management systems. UPHS-VLE also used the Apache Web Server, MySQL Database and PHP. The available features of UPHS–VLE are: (1) Forums, (2) Journals, (3) Quizzes, (4) Resources, (5) Choices, (6) Surveys, (7) Assignments, (8) Chats, and (9) Workshops ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom ICT Integration in the Learning Methods 2. Webquest A WebQuest," according to Bernie Dodge, the originator of the WebQuest concept, "is an inquiry– oriented activity in which most or all of the information used by learners is drawn from the Web. WebQuests are designed to use learners' time well, to focus on using information rather than on looking for it, and to support learners' thinking at the levels of analysis, synthesis, and evaluation." ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom ICT Integration in the Learning Methods 3. Use of MS Powerpoint Presentations in Games and Tournaments Implementation of TGT was modified through the use of computers and a presentation program called Microsoft Powerpoint. Instead of creating 400 cards for a 10–table and 20–item game, a presentation was created using the built-in features of the software. After the file was created, the presentation was copied in each of the 10 computers. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom ICT Integration in the Learning Methods 4. Other ICT integration initiatives Online Puzzles Graphing Calculator Software Yahoo Group and e-mail Internet Research ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Survey Results A pre–test and a post–test were administered before and after the study to determine the impact of cooperative learning on student achievement. The two groups in the study were (1)NCLM – students using ICT only and (2)CLM – students using both ICT and TGT cooperative learning method The assessment instrument consisted of 35 standardized multiple choice items in Geometry. Comparison of Mean Scores Obtained by NCLM and CLM Groups in the Pre–Test Groups N Mean NCLM 34 16.94 CLM 33 18.09 Difference Between Means Computed t–value Critical t–value at p=0.05 1.15 1.10 * 1.96 * - not significant Performance of the NCLM and CLM groups in the pre-test are comparable ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Survey Results Comparison of Mean Scores Obtained by NCLM and CLM Groups in the Post–Test Groups NCLM N Mean 34 25.56 Difference Between Means Computed t–value Critical t–value at p=0.05 2.99 2.90** 1.96 CLM 33 28.55 - significant ** Performance of the CLM group is significantly better than the NCLM group in the posttest. Mean Gains in the Pre–Test and Post–Test Obtained by NCLM and CLM Critical Pre–Test Post–Test Mean Std. Computed Groups N t–value at Means Means Gain Deviation t–value p=0.05 NCLM 34 16.94 25.56 8.62 4.71 10.67** 1.96 CLM 33 18.09 28.55 10.45 4.96 12.10** 1.96 ** - significant Performance of the NCLM and CLM groups improved significantly after going through the two learning methods. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Survey Results Comparison of Mean Gains Obtained by NCLM and CLM Groups N Mean Gains NCLM 34 8.62 CLM 33 10.45 * - not significant Difference Between Means Computed t–value Critical t–value at p=0.05 1.84 1.55* 1.96 The mean gains of the CLM group is higher than the NCLM group. This shows that the level of improvement of students using ICT and TGT is better than students who were using ICT only. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Survey Results Comparison of NCLM Pre–Test and Post–Test Mean Scores Against the Passing Score Groups N Pre–Test Means Passing Score Mean Difference Computed t–value Critical t–value at p=0.05 Pre–Test 34 16.94 18 1.06 1.35 1.96 Post–Test 34 25.56 18 7.56 9.46** 1.96 Comparison of CLM Pre–Test and Post–Test Mean Scores Against the Passing Score Groups N Pre–Test Means Passing Score Mean Difference Computed t–value Critical t–value at p=0.05 Pre–Test 33 18.09 18 0.09 0.13 1.96 Post–Test 33 28.55 18 10.55 16.26** 1.96 ** - significant The performance of the students in both learning environments improved significantly. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom Conclusion The study showed a significant improvement in the performance of the students upon completion of the learning activities. In both of these cooperative and non– cooperative environments, ICT has been integrated into the activities of the students. Group–based learning activities were designed to address the prevailing scarcity of computing resources and create an environment that fosters collaboration among the students. ICT–enhanced learning challenges the teachers to develop innovative teaching strategies that can improve student learning. It should be emphasized that reinvention of the classroom and ultimately the school does not end with the provision of ICT resources. Computers alone will not significantly improve learning outcomes. The application of technology in the classroom should be within the framework of applying effective pedagogical approaches. This study has shown that the combination of ICT and cooperative learning methods proved to be more successful in terms of student achievement. ICTs in Basic Education: The First National Congress ICT AND Cooperative Learning: Reinventing the Classroom THANK YOU !!!