* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Engineering for Design
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Planned obsolescence wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Marketing strategy wikipedia , lookup
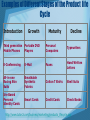
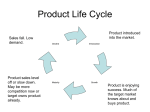
Product Life Cycle 4 Stages of a Product Life Cycle Product life cycles are based on the biological life cycle an example: • Introduction Seed is planted • Growth It sprouts • Maturity Plant puts down roots and grow leaves • Decline After period as an adult plant it dies Graphic Representation of a Product Life Cycle • http://www.marketingteacher.com /Lessons/lesson_plc.htm Introduction Companies seek to develop product awareness and a market for the product through: • Product Branding and Quality Level – intellectual property protection, patents, and trademarks • Pricing – is very competitive to establish a market product • Distribution – Selective until a demand or want is established for product • Promotion – aimed ant innovators and early adopters. Marketing is aimed to educate consumers and build product awareness. http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/product/l ifecycle/ Growth Stage In the Growth Stage Companies try to build brand preference and build market share for their product. • Product quality is maintained • Pricing is maintained as the demand increases with little competition. Profits rise • Distribution channels are added to increase product delivery to market. • Promotion is directed at a wider buying market. http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/pr oduct/lifecycle/ Maturity Stage In the maturity stage sales growth for the product begins to slow. Competitive products begin to appear. Primary objective is to defend market share. • Product features are added to keep the product different from the competition • Pricing is lower because of new competition. Demand starts to ease toward end of this stage. • Distribution is intense and has incentives are offered to maintain market share. • Promotion stresses difference from other products http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/product/ lifecycle/ Decline Stage A the sales of the product continue to decline the company has three options • Maintain the product by adding features to attempt to revive sales. • Harvest the product –reduce the cost and try to maintain product for a niche market of loyal customers. • Discontinue the product, liquidating remaining inventory, or sell to another company that may maintain or continue the product. http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/ product/lifecycle/ Examples of Different Stages of the Product life Cycle Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Third generation Mobile Phones Portable DVD Players Personal Computers Typewriters E-Conferencing E-Mail Faxes Hand Written Letters All-in-one Racing Skin Suits Breathable Synthetic Fabrics Cotton T Shirts Shell Suits Iris-Based Personal Identity Cards Smart Cards Credit Cards Check Books http://www.tutor2u.net/business/marketing/products_lifecycle.asp