* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Statistics AP/GT
Psychometrics wikipedia , lookup
Bootstrapping (statistics) wikipedia , lookup
Inductive probability wikipedia , lookup
Taylor's law wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of statistics wikipedia , lookup
History of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Misuse of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Resampling (statistics) wikipedia , lookup
Math 2311
TEST 1 REVIEW SHEET
Check courseware dates for TEST 1!!!! MAKE SURE
YOU HAVE REGISTERED AND RECORDED YOUR
TIME. IF YOU ARE LATE, THEY WILL NOT ADMIT
YOU.
Math 2311
REVIEW FOR TEST 1
Review for Test 1
7 t/f (4 pts each) and m/c (8 pts each)
3 f/r (either 14 or 16 pts each)
Sections 1.1 – 3.3
Review sheet posted on Homework page
Practice Test under online assignments on CASA
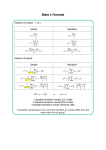
FORMULAS (not necessarily in this order):
n
s2 =
å (x - x )
2
n
i
Pn = n(n -1)(n - 2)...3× 2 ×1 = n!
i=1
s= s
n -1
P =
n r
2
A B c A c B c
P(E) =
P=
n(E)
n(S)
n!
r!s!t!
æ n ö
n!
C
=
ç
÷ = r!(n - r)!
n r
è r ø
P(E c ) = 1 - P(E)
P(E | F) =
n!
(n - r)!
(
)
( ) ( ) (
P EÈF = P E + P F - P EÇF
P(E Ç F)
P(F)
s 2X = Var[X] = ( x1 - m X ) p1 + ( x2 - m X ) p2 +
2
= å ( xi - m X ) pi
2
+ ( xnm-X m
) pn = x1 p1 + x2 p2 +
=XE[X]
2
)
+ xn pn
2
E[X + Y ] = E[ X] + E[Y ]
s 2X+Y = Var[X + Y ] = Var[X] + Var[Y ]
s 2X = Var[X] = E[X 2 ] - ( E[X])
2
E[X - Y ] = E[ X - Y ] = E[X] - E[Y ]
E[W ] = E[aX + b] = aE[X] + b
s 2X-Y = Var[X - Y ] = Var[X] + Var[Y ]
s W2 = Var[W ] = Var[aX + b] = a 2Var[X]
m = E éë X ùû = np
2 np 1 p
1
E[X] = m =
p
1- p
s2 = 2
p
n
P( X k ) p k (1 p) n k
k
P( X ³ k) = 1- P( X £ k -1 )
(
P( X n) (1 p ) n 1 p
P ( X n) (1 p ) n
)
Know the following definitions:
1. Population data
2. Sample data
3. Categorical variables
4. Quantitative variables (know the difference between
discrete and continuous)
5. Mean
6. Median
7. Mode
8. Range
9. Five number summary
10. IQR
11. Outliers
12. Standard deviation
13. Variance
14. Combination
15. Permutation
16. Intersection
17. Union
18. Probability
19. Binomial Distribution
20. Geometric Distribution
Be able to work problems like the following:
21. What kind of variable? Categorical or quantitative?
If quantitative, discrete or continuous?
a. Score on the final exam (out of 100 points) as
recorded on report card.
b. Final grade for the course (A, B, C, D, F).
c. The amount a person grew (in height) in a year.
d. The number of classes a student missed.
22. Twelve people were asked how many movies they
saw last month. The results were:
2 6 1 3 4 2 1 5 3 6 4 5
a. Find the mean and median.
b. Find the variance and the standard deviation.
c.
d. Based on the values you get, what can you say
about the shape of the distribution of the data set?
Explain briefly.
e. Find the five-number summary.
f. Determine the interval for outliers.
23. Suppose that from a group of 9 men and 8 women,
a committee of 5 people is to be chosen.
a. In how many ways can the committee be chosen?
b. In how many ways can the committee be chosen so
that there are exactly 3 men and 2 women?
c. What is the probability that the committee has
exactly 3 men and 2 women?
24. How many different words can be formed from the
letters in the word STATISTICS? (they do not have to
be real words)
25.
Use the following information:
U = {1,2, 3, 4,5, 6, 7,8,9,10}
A = {3, 4,6,8}
B = {1, 2,5,9}
C = {2, 4,6,8,10}
a. A Ç C =
b. B È A =
c
(B È C) =
c
c.
d. Draw a Venn diagram for the information.
26. Suppose that 58% of all customers of a large
insurance agency have automobile policies with the
agency, 42% have homeowner’s policies, and 23%
have both. What is the probability that the customer has
at least one of the policies?
27.
Suppose P(A) = 0.72 , P(B) = 0.46 and
P(A È B) = 0.86
a. Find
P(A Ç B)
b. Find P(A | B)
c. Find
P(B | A)
d. Area A and B independent?
28. Gabelli Partners is planning a major investment.
The amount of profit X is uncertain but a probabilistic
estimate gives the following distribution (in millions of
dollars):
Profit
1 1.5 2 4 10
Probability .1 .2 .4 ?? .1
a. Find
P(X = 4)
b. Find the mean profit and the standard deviation of
the profit.
c. Gabelli Partners owes its source of capital a fee of
$200,000 plus 10% of the profits X. So the firm
actually retains Y = .9X – 0.2 from the investment.
Find the mean and standard deviation of Y.
29. The following table displays the results of a sample
of 99 in which the subjects indicated their favorite sport
of three listed. The data are organized by favorite sport
and age group.
Age Foo Bas So
tball ebal cce
l
r
Over 15 8
7
40
20 – 20 11 15
40
Und 8
7
8
er 20
What is the probability that a person chosen at random
will be over 40 if he or she favors football?
30. The probabilities that a customer selects 1, 2, 3, 4,
or 5 items at a convenience store are 0.32, 0.12, 0.23,
0.18, and 0.15, respectively.
a. Construct a probability distribution for the data
X
P(X)
b. Find P(X > 3.5)
c. Find P(1.0 < X < 3.0)
d. Find P(X < 5)
31. A psychologist interested in right-handedness
versus left-handedness and in IQ scores collected the
following data from a random sample of 2000 high
school students.
High IQ
Normal
IQ
Total
Righthanded
190
1710
Lefthanded
10
90
Total
1900
100
2000
200
1800
a. What is the probability that a student from this
group has a high IQ?
b. What is the probability that a student has a high IQ
given that she is left-handed?
c. Are high IQ and left-handed independent? Why or
why not?
32. What is the expected value of the discrete
probability function given in the table below?
Outc 1 2 3 4 5 6
ome
Proba . . . . 0 .
bility 1 2 3 3 1
33. A headache remedy is said to be 80% effective in
curing headaches caused by simple nervous tension.
An investigator tests this remedy on 100 randomly
selected patients suffering from nervous tension.
a. What kind of distribution does X have? (Binomial
or Geometric?)
b. Calculate the mean and standard deviation of X.
c. Determine the probability that exactly 80 subjects
experience headache relief with this remedy.
d. What is the probability that between 75 and 90
(inclusive) of the patients will obtain relief?
34. A basketball player completes 64% of her freethrows. We want to observe this player during one
game to see how many free-throw attempts she makes
before completing one.
a. What type of distribution is this?
b. What is the probability that the player misses 3
free-throws before she has makes one?
c. How many free-throw attempts can the player
expect to throw before she gets a basket?
d. Determine the probability that it takes more than 5
attempts before she makes a basket.
You need to know the following:
What is the difference between a sample and a population?
What is the difference between continuous and discrete random
variables?
Measures of center?
Measures of spread?
What does it mean to be “resistant to outliers?”
How do you find outlier boundaries?
Counting techniques –
What is the difference between combinations and permuatations?
Sets (intersections, unions, complements)
Probability – What formula to use??
Some extra examples:
Given:
U = {1,2, 3, 4,5,6, 7,8,9,10}
A = {2, 4,6,8,10}
B = {1,2, 3, 4}
C = {4,5,6,9}
Find:
(B È C)C =
A Ç (B È C)C =
(AC Ç C)C =
Suppose P(A) = 0.25 and P(B) = 0.30. If events A and B are
independent then,
P(A Ç B) =
P(A È B) =
P(A | B) =
A distribution of grades in an introductory statistics class (where
A = 4, B = 3, etc) is:
X
0 1 2 3 4
P(X) .10 .15 .35 ?? .05
Find
P(X = 3)
Find
P(1 £ X < 3)
E[X] =
VAR[X] =
Find the lowest grade
X0
such that
P ( X X 0 ) 0.5
Have questions for me to work from the review sheet or practice
test!!!!
Popper 0
1. The test scores of a class of 20 students have a mean grade of
71.6 and the test scores of another class with 14 students has a
mean grade of 78.4. What is the mean of the combined
group?
a. 74.4
b. 75
c. 71.6
d. 78.4
e. none of these
Popper 0
2. If a constant value is added to all data in a sample, the new
variance
a. will be unchanged
b. will be equal to the old variance plus the constant value.
c. will be equal to the old variance plus the square of the
constant value.
d. none of these
3. In how many ways can you select from 7 people, 3 to serve on
a committee?
a. 35
b. 24
c. 56
d. 5040
e. none of these
4. In testing a new drug, researchers found that 6% of all
patients using it will have a mild side effect. A random
sample of 11 patients using the drug is selected. Find the
probability that none will have this mild side effect.
a. 0.3063
b. 0.9400
c. 0.4937
d. 0.0609
e. 0.5063
5. Suppose you have a binomial distribution with n = 20
and p = 0.4. Find P(8 ≤ X ≤ 12).
a. 0.3834
b. 0.5955
c. 0.9790
d. 0.5631
e. 0.9400
6. Which of the following is true?
a. Binomial has a set number of trials
b. Binomial has only success or fail
c. Geometric has only success or fail
d. Geometric does not have a set number of trials (we are
looking for first success)
e. All of the above are true
7. Joe has an 50% probability of passing his statistics quiz 4 each
time he takes it. What is the probability he will take no more
than 5 tries to pass it?
a. 0.9844
b. 0.0156
c. 0.9688
d. 0.0034
e. none of these