* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pseudo Random Number Generation and Random Event Validation
Pattern recognition wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical computer science wikipedia , lookup
Generalized linear model wikipedia , lookup
One-time pad wikipedia , lookup
Recursion (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Corecursion wikipedia , lookup
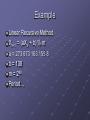
Pseudo Random Number Generation and Random Event Validation through Graphical Analysis What is randomness? A function not affected by any input or state Independent of previous results Example Flipping an unbiased coin Rolling die Quantum effects True vs Pseudo RNG No input criteria PRNG Input initial seed Cannot be predicted usually predictable In the form of a mathematical function The problem Computer systems need random numbers Provided by a PRNG Poor vs Good Good vs Poor R250 Linear recursive method Von Neumann’s Middle Square method Good PRNG using a bad seed Example Linear Recursive Method Xn+1 = (aXn + b) % m a = 273 673 163 155 8 b = 138 m = 248 Period… Approx. 1 year @ 10 000 000 random numbers per second Or 3 x 1014 random numbers Random Event Validation Look at existing PRNG Investigate Lotto numbers Build hardware RNG A graphical view Method of delayed coordinates plotted in a phase space Convert 1-D to 3-D by: X[n] = s[n-2] – s[n-3] Y[n] = s[n-1] – s[n - 2] Z[n] = s[n] – s[n-1] Higher dimensions are possible Acts as a “comb” What to expect True random data set - Random Cloud Random cloud for a good PRNG Poor PRNG will result in attractors True random Poor PRNG ISN’s from Windows 98 SE TPC/IP