* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SIMULATION OF BUCK-BOOST converter
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
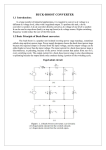
SIMULATION OF BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER AIM To simulate a buck-boost converter using Matlab simulink model. SOFTWARE USED Matlab 2010 SIMULINK LIBRARY BROWSER SL NO. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. COMPONENT DC voltage source MOSFET Series RLC branch Pulse generator Voltage measurement Scope Diode To workspace Display Power gui LIBRARY FILE Simpower system- electrical sources Simpower system- power electronics Simpower system- elements Simulink - sources Simpower system- measurement Simulink - sink Simpower system – power electronics Simulink - sink Simulink - sink Simpower system THEORY A buck converter produce an average output voltage less than the input voltage and a boost converter produce an average output voltage greater than input voltage. In a buck-boost converter an output voltage that may be less or greater than input voltage is produced, hence the name buck-boost converter; the output voltage polarity is opposite to that of input voltage. The circuit operation can be divided into two modes. Continuous mode and discontinuous mode. During mode 1,transistor Q1is turned ON and diode Dm is reverse biased. The input current, which rises, flows through inductor L and transistor Q1. During mode 2, transistor Q1 is switched off and the current which was flowing through inductor L, would flow through L, C, Dm and the load. The energy stored in the inductor L would be transferred to the load and the inductor current would fall until transistor Q1 is switched on again in the next cycle. A buck-boost converter provides output voltage polarity reversal without a transformer. It has high efficiency. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM The ratio of output voltage to input voltage is given by, Vo/Vin= D/(1-D)= I/Io Where Vo & Vin are output & input voltages, I & Io are input and output currents, D is the duty ratio defined as the ratio of ON time of switch to the total switching period. CONTINUOUS MODE OF OPERATION If the current through the inductor never falls to zero during a commutation cycle, the converter is said to operate in continuous mode. The current and voltage waveforms in an ideal converter is shown in figure. From t=0 to t=DT,the converter is in ON state, so the switch S is closed. DISCONTINUOUS MODE OF OPERATION In some cases, the amount of energy required by the load is small enough to be transferred in a time smaller than the whole commutation period. In this case, the current through the inductor falls to zero during part of the period. The only difference in the principle described above is that the inductor is completely discharged at the end of the commutation cycle, in discontinuous operation, the output voltage not only depends on the duty cycle, but also on the inductor value, the input voltage and the output current. SIMULINK MODEL RESULT Buck-boost converter is simulated using MATLAB simulink model.