* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Maps - Alpine Public School
Iberian cartography, 1400–1600 wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Mercator 1569 world map wikipedia , lookup
History of cartography wikipedia , lookup
Military geography wikipedia , lookup
Map projection wikipedia , lookup
Early world maps wikipedia , lookup
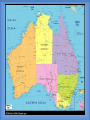
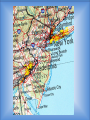
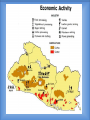
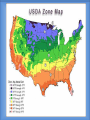
Thursday, September 4, 2014 • Homework: Join Online Textbook (create username and password) • Do Now: In your notes, respond to the following – – Seashore communities have a lot of tourists in the summer. Many businesses depend on serving the needs of the tourists. How does the geography of your area affect the local business? How does it affect your own lifestyle? Monday, September 8, 2014 • No homework • Do Now: Have out completed homework (geography packet) What is Geography? • Geo - geo= land • Graphy= study/ chart • The study of the Earth, including land, places, and people • The study of geography led to the creation of maps Location • Location is a particular place or position. Location can be absolute or it can be relative. • Absolute: is precise, more exact • Relative: gives only a general idea of where something is located Location Examples • Coordinates, street addresses, cities – (40 N, 74W; 100 Main Street, Trenton, NJ; Oahu, Hawaii; Phoenix, Arizona) • Alpine is West of Norwood; Hawaii is an island in the Pacific Ocean Place • A Place has describing characteristics that define a location. These characteristics can be physical or human. • Physical: features that naturally occur on the Earth. This also includes animal and plant life • Human: features that are man-made, such as architecture, or elements of culture Place Examples • Physical: rivers, beaches, mountains, waterfalls, caves, etc. • Human: Eiffel Tower, a straw hut, Stonehenge, your home, etc. Tuesday, September 9, 2014 • Homework: Review all themes and think about how it applies to Alpine • Do Now: Please open to your notes from yesterday and be ready to continue Human-Environment Interaction • Involves how people use, adapt, or modify their environment. This can have positive or negative effects • Adapt vs. Modify: – Adapt- when you change yourself to fit your environment – Modify- when you change your environment to fit you Examples • Adapt- wearing shorts & a t-shirt in hot weather • Modify- using irrigation systems to water crops in areas of dry land/ no rain • Positive- fertilizing crops to feed more people • Negative- polluting clean air and water sources Movement • When people, ideas, goods, fads, etc. are brought from one place to another or are exchanged between places Movement Examples • One Direction first became popular in Britain, then in the US • Internet began in California and is now used globally Regions • A group of places with at least one common characteristic. Regions can be formal or vernacular • Formal: Officially marked boundaries- can be for continents, countries, towns, cities, etc. • Vernacular: No official boundary lines, but instead are understood, or are “perceived” Region Examples • Formal : New York City, the USA, Europe • Vernacular: “The South” or “the Middle East” • In your notes: – Think About It: Which theme do you think is most important? Why? Explain. Types of Maps Political Maps • A political map shows boundaries • Examples: countries, states, counties, etc. Physical Map • A visual representation of an area, usually includes landmarks, cities, major highways, bodies of water, etc. Economic Map • An economic map can show industry, agriculture, or where wealth or poverty are located Topography Map • A topographic map shows elevations or high and low altitudes found in a country or region • Examples- mountains, cliffs, valleys Climate Map • A climate map shows temperatures and climates found within a country or region