* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tcp/ip
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Hypertext Transfer Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Communication protocol wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
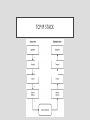
TCP/IP TCP/IP A set of protocols for all TCP/IP network transmissions TCP/IP • Defines the rules about transmission of data packets • IP controls the delivery of packets and TCP keeps track of packets and reassembles them • TCP/IP is made up of a number of layers – a protocol stack • The TCP/IP stack is in with the OSI model • Within each layer there are a number of other protocols THE LAYERS OF TCP/IP Layer 4 - Application layer Layer 3 - Transport layer Layer 2 - Internet layer Layer 1 - Link layer LAYER 4 – APPLICATION LAYER • Handles the Domain Name System + other protocols such as FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, POP3, SMTP and SSH • For example: • incoming and outgoing data are converted from one presentation format to another • presentation formats are standardised so that different types of data (sound, graphics, video, etc) can be understood by receiving device • data that have been compressed or encrypted can be interpreted LAYER 3 – TRANSPORT LAYER • Contains the configurations that ensure that all packets have arrived with no errors • Handles the way connections are made to create a path for data to travel between nodes • Sender and receiver identified and communication is set up, coordinated and terminated in this layer • Network resources are identified to ensure they’re sufficient for the communication LAYER 2 – NETWORK OR INTERNET LAYER • Defines the IP addresses of devices that send and receive data and handles the creation and routing of packets being sent and received LAYER 1 – LINK LAYER • Provides synchronisation of devices so that the receiving device can manage the flow of data being received • Identifies what network topology is being used and controls the physical signals that transmit the strings of bits around the network • Controls physical characteristics such as data transmission rates and physical connections in a network • Handles the CSMA/CA protocol in wireless networks TCP/IP STACK THE TCP/IP STACK • The highest level is closer to the user – processes are usually handled by either the operating system or application software • The lower levels are handled using a combination of hardware and software including the physical or wireless connections between devices • It’s called a stack because of the way the request from the client machine passes down through the layers of the protocol and then back up through the layers on the server side, as shown on the previous slide • This means that the last action that takes place in the Link layer on the client computer becomes the first action in the Link layer in the server – this is an example of the last in first out (LIFO) structure that characterises a stack HTTP AND HTTPS • HTTP is a protocol for transmitting and displaying web pages • Uses the client-server model – the web browser acts as a client, requesting the services of the computer that contains the web page, the server • HTTPS is an extension of the protocol with added security – it works by using either the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol or the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol FTP • File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a protocol for handling file uploads and downloads • Similar to HTTP in that it uses the standard layers of TCP/IP • HTTP tends to be used to transfer viewable content (web pages) whereas FTP is commonly used to transfer program and data files SECURE SHELL (SSH) PROTOCOL • Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol is a protocol for remote access to computers • Uses a command line interface, similar to DOS SIMPLE MAIL TRANSFER PROTOCOL ( SMTP) AND POST OFFICE PROTOCOL (POP3) • SMTP is a protocol for sending emails • POP3 is a protocol for receiving emails EMAIL AND WEB SERVERS • An Email server is a dedicated computer on a network for handling email • A Web server is a dedicated computer on a network for handling web content WEB BROWSERS • A web browser is an application for viewing web pages KEY POINTS • Protocols are sets of rules. There are several protocols that relate to the transmission of data around networks • The TCP/IP stack is a four-layered set of protocols for computer networks, including the Internet • A socket is an endpoint of a communication flow on a computer network that uniquely identifies an application and device • HTTP is the set of rules that govern how multimedia files are transmitted around the Internet • FTP is a set of rules relating to the transfer of files around the Internet • SSH is a set of rules relating to the remote access of computers on a network • SMTP and POP3 are protocols relating to email TASKS 1. What are the four layers of the TCP/IP stack? 2. Explain the need for protocols such as FTP and HTTP 3. What are the key differences between HTTP and HTTPS? 4. How is it possible to complete access to a computer remotely using SSH? 5. Why might a network administrator choose to allocate servers to specific tasks? STUDY / RESEARCH TASKS 1. Describe the process that Nominet uses to allocate domain names 2. The WWW is one service available on the Internet. Identify two other services that are available 3. Identify three browsers that are available and explain why you might choose to use one rather than the others 4. Identify other ways in which information can be downloaded from the Internet without accessing the WWW 5. What is Telnet protocol and why is it no longer in widespread use? 6. Telnet is sometimes associated with hacking. Why is this the case, and what security measures could prevent its use for unauthorised purposes? 7. What are the alternatives to POP3?