* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2_part 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
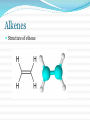
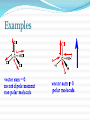
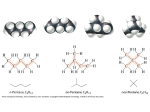
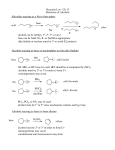
Structure and Functional Groups, Intermolecular Forces and Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy 2.1-2.2 Hydrocarbons: Representative Carbon-carbon formed the most strongest bond in organic molecules Hydrocarbon: molecules that contain only H & C Alkanes Principle sources are natural gas and petroleum Saturated hydrocarbons No double or triple bonds General formula: CnH2n+2 E.g CH4 C 2 H6 C 3 H8 Methane gas Produces carbon dioxide and hydrogen when burning Methane Alkenes Unsaturated hydrocarbons: contain double bonds General formula: CnH2n Used widely in the industry Some occurs as plant hormone Involved in the ripening process Alkenes Structure of ethene Alkynes Unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one triple bond General formula: CnH2n-2 Use for biosynthesis Alkynes Ethyne Benzene Six membered ring with alternating single bonds Polar and NonPolar Molecules Diatomic molecules with different polarity is a polar molecules Vectors cancelled out non polar Dipole moment = charge (in esu) x distance (cm) Must know 3-D structure Examples Examples Examples Using a three dimensional formula, show the direction of the dipole moment of CH3OH. Write ∂and ∂+ signs next to the appropriate atoms Functional Groups Part of a molecule where most of its chemical reaction occur Defined by characteristic arrangements of atoms Determined the compound’s chemical properties 2.5 Alkyl and the symbol R #C N1ame Alkyl (one H has removed) 1 Methane Methyl 2 Ethane Ethyl 3 Propane Propyl 4 Butane Butyl 5 Pentane Pentyl 6 Hexane Hexyl 7 Heptane Heptyl 8 Octane Octyl 9 Nonane Nonyl 10 Decane Decyl Functional groups Alkyl groups are designated as R General formula : R-H Phenyl and Benzyl groups When benzene group is attached to some other groups of atoms in molecule, it is called phenyl Abbreviated as Ar Phenyl and Benzyl groups The combination of a phenyl group and methylene group ( -CH2-) is called benzyl group 2.6 Alkyl Halides or haloalkanes Alkyl halides are compounds in which a halogen atom is replaced with a hydrogen atom from alkane Also known as haloalkanes General formula: R-X X = fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine CH3Cl - chloromethane Alkyl Halides Classified as being Primary (1o) Secondary (2o) Tertiary (3o) Examples Write bond-line structure for a. An alkane with formula C5H12 that has no secondary or tertiary carbon atoms b. A secondary alkyl bromide with formula C4H9Br c. Two constitutionally isomeric primary alky bromide Alcohols Hydrocarbons that contain hydroxyl group (OH) Attached to an sp3-hybridized carbon Alcohols Classified as Primary (1o) Secondary (2o) Tertiary (3o) Examples Write bond-line structure formulas for a. Two primary alcohols b. A secondary alcohols All having the molecular formula C4H10O