* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concentrate! Key Takeaways of new insulin products
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
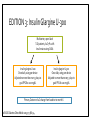
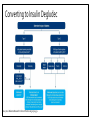
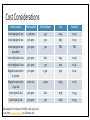
CONCENTRATE! KEY TAKEAWAYS OF NEW INSULIN PRODUCTS Sara Wettergreen, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Professor of Pharmacotherapy University of North Texas System College of Pharmacy Learning Objectives: Pharmacists • Compare and contrast use of insulin pen devices • Identify patients who may benefit from use of new insulin products • Design a patient-specific treatment regimen using new insulin products Learning Objectives: Technicians • Compare and contrast use of insulin pen devices • Define safety considerations related to insulin use • Assist patients with obtaining pricing discounts for new insulin products Diabetes: A Growing Problem • 29.1 million people in the United States have diabetes • About 1 in 4 of these are undiagnosed • 37% of patients treated for diabetes use insulin Center for Disease Control (CDC). National diabetes statistics report, 2014. “Egregious Eleven” Schwartz et al. Dia Care 2016;39:179-186 Role of Insulin American Diabetes Association Dia Care 2016;39:S52-S59 Role of Insulin Reprinted with permission from American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists © 2016 AACE. Endocr Pract.2016;22: 84-113. New Insulin Products • Insulin glargine U-100 equivalent (Basaglar®) • Became available December 15th, 2016 • Insulin glargine U-300 (Toujeo®) • Insulin degludec U-100 and U-200 (Tresiba®) • Regular human insulin u-500 (Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®) • Insulin lispro U-200 (Humalog U-200 KwikPen®) www.accessdata.fda.gov/Scripts/cder/drugsatfda/ . Characteristics of an Ideal Basal Insulin • PK/PD profile that more closely mimics endogenous basal insulin secretion • Low risk of hypoglycemia • Minimal weight gain • Dosing flexibility • Easy for patients to administer Advances with Basal Insulins Detemir Glargine U-100 Glargine U-100 equivalent NPH • • • Peak Shorter duration Risk of hypoglycemia • • • Glargine U-300 Degludec U-100, U-200 • • • Less peak Longer duration Lower risk of hypoglycemia Less peak Longer duration Lower risk of hypoglycemia Insulin Glargine U-100 Equivalent (Basaglar®) • Not considered a “biosimilar” as the Biologic License Application (BLA) pathway was not used, but is a follow-on biologic approved via the New Drug Application (NDA) pathway • Conversion from insulin glargine U-100 (Lantus®) is 1:1 dose • Non-inferior to insulin glargine U-100 (Lantus®) Basaglar [Prescribing Information]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company. Rosenstock J, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(8):734-741. Insulin Glargine U-300 (Toujeo®) Volume • FDA approved February 2015 • Available in disposable, prefilled SoloSTAR pen device • 1/3 of injection volume compared with U-100 • Reduces depot surface area by ½ • Surface Area Allows for a gradual, prolonged rate of absorption • Each pen contains 450 units • Maximum single injection dose = 80 units U-100 TOUJEO® (insulin glargine) injection 300 units/mL [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Sanofi-Aventis. U-300 Insulin (µU/mL) PK/PD of Insulin Glargine U-300 vs. U-100 30 20 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Time (hours) GIR (mg/kg/min) U-100 U-300 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Time (hours) U-100 Becker RHA. Diabetes Care 2015;38:637-43. U-300 EDITION 1: Insulin Glargine U-300 Multicenter, open-label T2D patients, A1C 7%–10% Current basal therapy with ≥ 42 units/day of glargine or NPH + mealtime RAIA ± metformin Insulin glargine U-100 Once daily using pen device Adjusted no more than every 3 days to goal FPG 80–100 mg/dL Insulin glargine U-300 Once daily using pen device Adjusted no more than every 3 days to goal FPG 80–100 mg/dL Primary Outcome: A1C change from baseline to month 6 Riddle MC. Diabetes Care 2014;37:2755-62. EDITION 1: Insulin Glargine U-300 Outcome Glargine U-300 (n=404) Glargine U-100 (n=403) Change in A1C from baseline (%) -0.83 -0.83 Change in weight from baseline (kg) +0.9 +0.9 Daily basal insulin dose at end of study (units) 103 94 Confirmed or severe nocturnal hypoglycemic events (%) 36 46 Met predefined noninferiority criteria. Riddle MC. Diabetes Care 2014;37:2755-62. EDITION 2: Insulin Glargine U-300 Multicenter, open-label T2D patients, A1C 7%–10% Current basal therapy with ≥ 42 units/day of glargine or NPH + OADs Insulin glargine U-100 Once daily using pen device Adjusted no more than every 3 days to goal FPG 80–100 mg/dL Insulin glargine U-300 Once daily using pen device Adjusted no more than every 3 days to goal FPG 80–100 mg/dL Primary Outcome: A1C change from baseline to month 6 Yki-Jarvinen H. Diabetes Care 2014;37:3235-43. EDITION 2: Insulin Glargine U-300 Outcome Glargine U-300 (n=404) Glargine U-100 (n=407) Change in A1C from baseline (%) -0.57 -0.56 Daily basal insulin dose at end of study (units) 91 82 Nocturnal hypoglycemic (%) 30.5 41.6 Confirmed or severe hypoglycemia (%) 21.6 27.9 Met predefined noninferiority criteria. Yki-Jarvinen H. Diabetes Care 2014;37:3235-43. EDITION 3: Insulin Glargine U-300 Multicenter, open-label T2D patients, A1C 7%–11% Insulin naive using OADs Insulin glargine U-100 Once daily using pen device Adjusted no more than every 3 days to goal FPG 80–100 mg/dL Insulin glargine U-300 Once daily using pen device Adjusted no more than every 3 days to goal FPG 80–100 mg/dL Primary Outcome: A1C change from baseline to month 6 Bolli GB. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:386-94. EDITION 3: Insulin Glargine U-300 Outcome Glargine U-300 (n=439) Glargine U-100 (n=439) Change in A1C from baseline (%) -1.42 -1.46 Daily basal insulin dose at end of study (units) 59.4 52 Nocturnal confirmed or severe hypoglycemic (%) 18 24 Met predefined noninferiority criteria. Bolli GB. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:386-94. Insulin Glargine U-300: Summary • Smoother PK/PD profile than glargine U-100 • Full 24-hour coverage; flexibility in dosing time • Less nocturnal hypoglycemia than glargine U-100 • Smaller injection volume • 1:1 conversion recommended when switching from glargine U-100 • Higher doses (~10%) may be needed compared with insulin glargine U-100 TOUJEO® (insulin glargine) injection 300 units/mL [prescribing information]. Bridgewater, NJ: Sanofi-Aventis. Insulin Degludec (Tresiba®) • Approved by FDA September 25, 2015 • U-100 (Tresiba® 100 units/mL) • FlexTouch pen device • 300 units per pen; max single dose = 80 units • Duration of action > 40 hours; allows for flexibility in dosing • Doses are selected in 1 unit increments • U-200 (Tresiba® 200 units/mL) • FlexTouch pen device; low volume • 600 units per pen, max single dose = 160 units • Bioequivalent to degludec U-100; similar glucose lowering • Doses are selected in 2 unit increments Zinman B. Diabetes Care 2012;35:2464-71; Gough SC. Diabetes Care 2013;36:2536-42 Garber AJ. Lancet 2012;379:1498-507. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm464321.htm Insulin Degludec PK/PD • Half life >25 hours • Duration of action: 42 hours • Steady state is reached within 3 days, thus dose titrations should occur on a weekly basis • Similar PK/PD between the U-100 and U-200 concentrations Vora J, et al. Diabetes Research in Clinical Practice 2015;109:19-31. Insulin Degludec Confirmed or Severe Nocturnal Hypoglycemia (per pt-year) Clinical Trial (Duration) Background Therapy Comparator Arms Change in A1C (%) End of Trial Insulin Dose (units/kg) Hypoglycemia (episodes per pt-year) Zinman (52 weeks) Metformin (insulin naive) IDeg U-100 -1.06 0.59 1.52 0.25* Glargine -1.19 0.60 1.85 0.39 IDeg U-100 -1.1 0.75 11.1* 1.4* Glargine -1.2 0.69 13.6 1.8 IDeg U-200 -1.22 0.53* 1.22 0.18 Glargine -1.42 0.60 1.42 0.28 Garber (52 weeks) Insulin ± OADs Gough (26 weeks) Metformin ± DPP-4i (insulin naive) Noninferiority criteria met. *p<0.05. Zinman B. Diabetes Care 2012;35:2464-71; Gough SC. Diabetes Care 2013;36:2536-42; Garber AJ. Lancet 2012;379:1498-507. Converting to Insulin Degludec Vora J, et al. Diabetes Research in Clinical Practice 2015;109:19-31. Patient Considerations with Insulin Degludec • Titration Frequency TITRATE Study: Insulin determir was titrated by 3 units every 3 days • Titrations with insulin degludec should be made on a weekly basis due to the extended duration of action • • Adherence Flexibility in timing between doses with a minimum of 8 hours between doses • Minimal change is safety or efficacy with variability in timing of doses between 8 to 40 hours between doses • Vora J, et al. Diabetes Research in Clinical Practice 2015;109:19-31. Insulin Degludec: Summary • Extended duration of action compared to other basal insulin products • Less nocturnal hypoglycemia with degludec U-100 than glargine U-100 • 1:1 conversion recommended when switching from other basal insulins • • 20% dose reduction may be considered if using twice daily dosing Extended coverage; flexibility in dosing time; weekly titrations Vora J, et al. Diabetes Research in Clinical Practice 2015;109:19-31. Regular Human Insulin U-500 (Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®) • Nothing new about the insulin Five times as concentrated as U-100 insulin • Used for severe insulin resistance (total daily dose >200 units/day) • • The PEN is new! 1500 units per 3 mL pen • Doses are selected in 5 unit increments • No dose-conversions needed (compared to vial use) • Humulin R U-500 KwikPen [Prescribing Information]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company. Regular Human Insulin U-500 • Continues to be available in a 20 mL vial (10,00 units of insulin) • U-500 syringe is recommended for use with the U-500 vial Humulin R U-500 [Prescribing Information]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company. Regular Human Insulin U-500: Dosing Review • Conversion from U-100 products to U-500 • • • A1c ≥ 8%: 1:1 conversion from U-100 to U-500 insulin total daily dose (TDD) May decrease TDD by 10-20% if A1c<8% The TDD is then divided Required TDD (Units) Route and Frequency U-500 Insulin Dosage 150-300 Twice daily 50/50 or 60/40 before breakfast and supper Three times daily 33/33/33 before meals Three times daily 33/33/33 before meals Four times daily 30/30/30/10 (mealtimes and bedtime) Four times daily 30/30/30/10 (mealtimes and bedtime) 300-600 >600 Segal AR, et al. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2010; 67:1526-35 Regular Human Insulin U-500: Dose Titration Ballani P, et al. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29(11):2504-2505. Characteristics of an Ideal Bolus Insulin • Low risk of hypoglycemia • Minimal weight gain • Dosing flexibility • Easy for patients to administer Advances with Bolus Insulins Rapid-acting insulin analogs Regular • • • Slow onset Longer duration Risk of hypoglycemia • • • • Faster onset Shorter duration Clinical outcomes Pen devices Lispro U-200 • Decreased number of pens needed with high doses • Pen device Insulin Lispro U-200 (Humalog U-200 KwikPen®) • The CONCENTRATION is new! Twice as concentrated as U-100 insulin • 1500 units per 3 mL pen • Doses are selected in 1 unit increments • 1:1 unit conversion recommend when switching from insulin lispro U-100 • Benefit is that patients on high bolus doses will use less pens • Humalog [Prescribing Information]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company. http://www.humalog.com/humalog-u200-hcp.aspx Ultra-Rapid Acting Insulin Aspart (NN1218) • Earlier time to 50% maximal concentration • Faster-acting insulin aspart: 20.7 minutes • Insulin aspart: 31.6 minutes • Application submitted to the FDA • October 7, 2016 – FDA response letter issued requesting additional information for the immunogenicity and clinical pharmacology data Heise T, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(7):682-688 http://www.novonordisk.com/media/news-details.2047717.html Discussion Question! What patients may be good candidates for each of these new insulin products? • Insulin glargine U-300 (Toujeo®) • Insulin degludec U-100 and U-200 (Tresiba®) • Regular human insulin u-500 (Humulin R U-500 KwikPen®) • Insulin lispro U-200 (Humalog U-200 KwikPen®) Cost Considerations Insulin product How supplied Total units/pen Cost Cost/unit Insulin glargine U-300 1.5 mL pens 450 $134 $0.30 Insulin glargine U-100 3 mL pens 300 $89 $0.30 Insulin glargine U-100 equivalent 3 mL pens 300 TBD TBD Insulin degludec U-200 3 mL pens 600 $213 $0.36 Insulin degludec U-100 3 mL pens 300 $107 $0.36 Regular human insulin U-500 pen 3 mL pens 1,500 $320 $0.21 Regular human insulin U-500 vial 20 mL vial 10,000 $1655 $0.16 Insulin lispro U-200 3 mL pens 600 $236 $0.39 Insulin lispro U-100 3 mL pens 300 $118 $0.39 Table adapted from: Mospan CM.JAAPA. 2016; 29(6):16-18; Pricing from www.lexicomp.com as of October 2016 Drug Discount Programs Insulin product Insulin glargine U-300 Insulin degludec U-200/U-100 Regular human insulin U-500 pen Insulin lispro U-200 Program Details Discount cards are available • Card can reduce copay to $15, with a maximal discount of $200/pack • Can be used for the first 12 prescription fills Sanofi Patient Connection Program • May be able to decrease drug price to $0 copay Discount cards are available • Can decrease copayment to as low as $15 (maximal discount of $500 for each fill) • Can be used for the first 24 prescription fills Discount cards available • Card can reduce copay to $25, with a maximum of 7 KwikPen packs per prescription fills • Can be used for the first 12 prescription fills Discount cards available • Can decrease copayment to as low as $25 (maximal discount of $100 for each fill) • Can be used for the first 24 prescription fills www.toujeo.com; www.tresiba.com; www.humulin.com; www.humalog.com; Not Just an Outpatient Issue! In the Inpatient Setting: • Insulin pens are preferred by nurses Felt it was easier to teach patients to self-administer insulin using a pen device • Felt that the risk of a dosing error was lower with a pen device vs. syringe • • Reduced waste from using insulin pens instead of vials may reduce cost • One study projected a cost savings of $36 per patient per hospital stay with insulin pen use instead of insulin vials Haines ST, et al. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2016; 73(suppl 5):S4-16. A Risky Situation… • 2009: At a Texas hospital in 2009, 2,114 insulin-dependent patients with diabetes were exposed to disease transmission risk via used insulin pens • 2011: Over 2,000 patients were exposed to used insulin pens at a Wisconsin hospital and outpatient clinic • 2013: Over 700 patients at a New York hospital may have been exposed inadvertently to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B, or hepatitis C because of the reuse of insulin pens on multiple patients http://www.ismp.org/newsletters/acutecare/showarticle.aspx?id=41 Discussion Question! Are insulin pens used at your practice site? If so, how do you decrease the risk of reusing insulin pens? Best Practices for Safe Use of Insulin Pen Devices in Hospitals • Recommendations have been made for each step in the medication-use process • Examples: • “Warning! Confirm patient. Insulin pens are for use in one patient only” • Require all health professionals to pass a competency assessment for insulin pens (at the time of hire and periodically thereafter) • Develop a system to prompt the proper disposal of insulin pens when the order is discontinued Haines ST, et al. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2016; 73(suppl 5):S4-16. Key Takeaways • 37% of patients treated for diabetes use insulin • Many new insulin products are available, each with their own advantages • Cost may be a barrier to patient use, and drug discount programs are one method of assisting patients reduce costs • Addition of new insulin products can lead to further confusion with the various devices available, which has implications for both the inpatient and outpatient settings CONCENTRATE! KEY TAKEAWAYS OF NEW INSULIN PRODUCTS Sara Wettergreen, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Professor of Pharmacotherapy University of North Texas System College of Pharmacy