* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Civilization of the Aztec
Bernardino de Sahagún wikipedia , lookup
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Tepotzotlán wikipedia , lookup
National Palace (Mexico) wikipedia , lookup
Fall of Tenochtitlan wikipedia , lookup
Templo Mayor wikipedia , lookup
Aztec warfare wikipedia , lookup
Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Aztec cuisine wikipedia , lookup
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture wikipedia , lookup
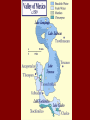
The Civilization of the Aztec Geography / Environment • First established in central Mexico (Mexico City) • The Valley of Mexico has a diverse environment of fertile marshy island filled lakes, a moderately warm climate, and dry desert land to the north. • Expanded to include the Gulf Coast and Pacific Ocean The Aztec Agriculture • Fertile marshlands allowed farmers to harvest crops as many as SEVEN times a year. • Farmers grew maize, beans, red peppers, tomatoes, sweet potatoes, avocados. • Because of the marshy environment, the Aztec also constructed chinampas. Agriculture • Chinampas, or floating islands, were made by sinking logs into the bottom of the lake and filling in the areas with mud, boulders, and reeds. • Eventually the Aztec expanded the city’s land by five square miles Chinampas Urban Centers • The heart of the Aztec civilization was its island capital city, Tenochtitlan. – Plaza, Great Temple, royal palace, marketplace, 3 causeways that connected to the mainland, and fresh water aqueducts • The Aztec empire consisted of a loose union of hundreds of conquered city-states Tenochtitlan (Florentine Codex) Economy • Based on collecting tribute from conquered city-states • Tribute collected: food crops, textiles, jade, emeralds, tortoise shells, jaguar skins, vanilla beans, and cacao. Social / Class Structure Emperor Government Officials, Priests, Military Leaders Merchants, Craftsmen, Artisans, Farmers Peasants Slaves Social Mobility Between Upper Classes Religion • Many gods and practices developed from earlier Mesoamerican cultures • Polytheistic / some nature gods • Aztecs believed in the existence of two worlds material and divine (with heaven and hell) • All male adolescents took religious training at temple schools Aztec Deities • Huitzilopochtli - (sun god and god of war) chief god and symbol of the Aztecs • Quetzalcoatl – (feathered serpent god) represented creation, virtue, learning, and culture – The Aztecs believed that Quetzalcoatl left their homeland promising return in triumph to the Valley of the Mexico Aztec Religion - Human Sacrifice • Aztecs believed that the gods would keep the world going in exchange for sacrifice • Human hearts and blood were presented to Huitzilopochtli • The Aztecs would sacrifice volunteers and captives • Some historians believe the Aztecs might have also used human sacrifices to frighten other city-states into accepting Aztec rule Family Life • Aztec families were patriarchal • Both genders had specific duties in the household • Highest Honor in Life – Men – fight in wars – Women – giving birth Achievements • Medicine and Dentistry - the Aztecs had advanced ways of caring for their health • Calendars – like the Maya the Aztecs also developed an accurate calendar • City Building – the Aztecs built the largest cities in the Americas – over 200,000 people Reasons for Decline • Eventually the Aztecs were conquered by several enemies • This story will be continued in the days to come….