* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Yr9_Glowing_Display
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
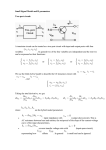
Y Pant School A Glowing Name Plate Year 9 Project 1 Introduction This is a major DESIGN and MAKE Project, but do not let that worry you! During years seven and eight you designed and made things using all sorts of materials and processes. This project will draw on all of the skills and knowledge learned during those projects to help you produce a useable product. The Project We have all seen name plates and signs; they are an everyday part of life. They take various forms and appear in many different places. They all aim to attract us in some way. We are going to design and make a name plate that will be seen by people during the day and during darkness. Your task is to DESIGN a NAME PLATE FOR a CHOSEN ROOM OF YOUR CHOICE. THE NAME PLATE WILL INCORPORATE AN ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT CONTAINING SOME NEW COMPONENTS WHICH YOU WILL LEARN ABOUT LATER IN THIS PROJECT. 2 Organising your Project We are going to use a combination of methods to make an attractive name plate. To do this we will first ANALYSE the problem in class. An important factor for your design is where it will be located. Before we do anything else it is necessary to outline two of the ESSENTIALS in this project: 1. The Name Plate must show up well during the day and when it is dark. 2. It must stand alone to display text clearly. We are going to use a combination of materials to satisfy the requirements. Everyone has use metal, wood, plastics, and electronics in projects. This project is going to extend the skills that you have in a number of these areas. The following pages describe electronic components and their uses. You will be shown how to use them to produce a circuit that will help to illuminate your name plate. There are many new processes to be learned, however, they are commonly used in lots of things you take for granted. E.g. MP3 Players, Televisions, Hi-Fi’s and Computers. To help us produce the most attractive name plate everyone will have the opportunity to use the STIKA-12, Camm-1 and Camm-2. These are computer aided manufacturing tools that can produce accurate making techniques. You will be shown these later in your project. The use of Electronics, Plastics, Timber and CAD/CAM will help you to produce a high quality advertisement. 3 Consider Aesthetics, Typography and the Target Market!! Designing with Electronics Using Electronics to solve design problems is not as difficult as you might think. Most of you will remember the circuit you had to design for your animated display, this circuit has a few more components but is not that much more difficult to understand. Designing Circuits All circuits need three basic blocks: INPUT, CONTROL and OUTPUT. You can use a block diagram to help you design a circuit suitable for our needs. PROBLEM: Design a circuit, which will switch on a light emitting Diode when it begins to get dark? Solution in the form of a block diagram. INPUT Needs to sense when it goes dark. INPUT 4 CONTROL Needs to switch on the output when the input senses dark. CONTROL OUTPUT Needs to light up when the control switches it on. OUTPUT We’ll look at all the individual components to The Resistor The Symbols of components are shown above. understand how each of them work, then put them all together to make our final circuit. Resistors Resistors are very important in electronics because we often have to limit the amount of current flowing in a circuit or parts of it. The most common resistors consist of a thin film of carbon over a ceramic tube, each end of which has a wire connecting leg. The resistance simply depends on the type of carbon used. Carbon Film is in the middle of the Resistor. Resistors are colour coded with four bands that can be read to give their values in ohms. The higher the number in Ohms, the greater the resistance. To read a resistor’s value, look at its first colour band (opposite end to the metallic band) and find this colour on the chart. Now look across the chart to Column 1 and note the number. Do this for the other two colour bands, going across the chart to Column 2 and then to Column 3. If, for example, the resistor’s first colour band is yellow, we note ‘4’ in Column 1 on the chart. If the second band is violet, we go across to Column 2 and note ‘7’. If the third is red, we see two noughts in Column 3, giving a figure of 4,700. This is the value in ohms of the resistor. 5 The Resistor Gold + or – 5% Silver = or – 5% Colour Black Brown Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Violet Grey White Band 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Band 2 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Band 3 Nothing 0 00 000 0000 00000 000000 Work out the resistance values of these resistors Colour 6 Band 1 Band 2 Band 3 Blue Grey Brown Red Red Red Brown Black Red Total The LED Most of the circuits use a light emitting diode (LED) rather than a bulb. LED’s give out less light, but they use less current and cost less. LED’s also come in three colours: red, green and amber. Unlike a bulb, an LED does not have a filament. It is too hard to explain here how it works, but it is easy to use if you follow two simple rules: Examples of different LED’s. Symbol for and LED LED Rule 1 An LED must be used with a resistor in the circuit loop. This restricts current flow and prevents the LED taking more current than is good for it. If an LED takes too much current it will break. LED’s are small in size, they are 39mm. 7 LED Rule 2 An LED must be connected in a circuit with its (-) leg facing towards the (-) terminal of the battery. If you look at they bottom of an LED, there is a small flat edge on the plastic, and the (-) leg is nearest to this. An LED is a diode. This lets current pass only when it is connected in a circuit the right way around. If it is connected backwards, nothing happens and no light. Diagram Shows LED Symbol, Flat side of LED, Shorter and Longer legs. 8 Semiconductor Devices The Transistor This is another device that can be damaged by rough handling. Again it is easy to break off the legs of the Transistor by bending them. The Transistor has three legs called: The Collector (C) The Base (B) The Emitter (E) B C E BC 108 (From underside) 9 Transistor Symbol BFY 51 What Transistors Do! Step 1 If the collector and emitter legs of BC108 are connected as part of an LED circuit, nothing happens. The transistor is acting like a switch turned off. Step 2 To turn the transistor on, a small current has to flow between base and emitter. This can be supplied, for example, by a resistor. A very small base current flowing causes a much larger current to flow between collector and emitter, so that the LED lights up. 10 To be really sure how the transistor works, try following the two current paths around on the diagram with the end of a pencil. You might well ask at his point: why is a transistor needed to turn on an LED? The answer is that it gives us a very sensitive switch because so BC 108 little base current is needed. So little, in fact, you can use your finger in place of the resistor – making the circuit a ‘touch switch’. 11 Finger here. Thumb here. Variable Resistors You can change the resistance of a variable resistor, unlike that of a fixed resistor, by turning the spindle. You can set the resistance from zero up to the value given on the base of the component. The maximum resistance of our variable resistor is 100K, or 100,000 Ohms. If using centre tag and one side tag. If using all three tags. Slider 12 Carbon Track Spindle A Variable Resistor When the spindle rotates, the slider turns with it. If the spindle rotates clockwise the resistance between a and b increases and the resistance between b and c decreases. Light Dependent Res An LDR is really a variable resistor as it changes its resistance with the amount of light that falls on it. In the dark it has a high resistance, and in the light it has a low resistance. An LDR 13 Printed Circuit Boards Modern electronic circuits use only a few wires to connect the main parts together. The components are held together on a printed circuit board called a PCB. Printed circuit board is a thin fibreglass board about 1.5mm thick. On one side of the board is a layer of copper, only about 0.25mm thick. To use the board we must first draw our circuit onto the copper using a special etch resist pen. Take great care at this stage because once the board is placed into the etch tank mistakes cannot be altered. PCB Layout 14 A PCB Board with Components. Etching When you are happy with your circuit, you are ready to place it into the acid (Ferric Chloride). This will eat or etch away all the copper not protected by the special etch resist pen. Take care with this, as it is poisonous and corrosive, don’t get it on your clothes or hands!!! Once all the unwanted copper has been removed you can use the tongs to remove your circuit from the acid and then was it under the cold-water tap. The etch resist pen must now be removed to leave only the copper tracks ready for us to start drilling. Use wire wool to remove the etch pen. An Etching Tank 15 Note the protective gloves that must be worn when using this machine. You can see the PCB in the acid, which is removing the copper, which is not needed. After a circuit board has been placed into an Etching Tank the circuit tracks are left in pen. Once rubbed with wire wool copper is exposed. Drilling You will now need to drill holes in the circuit board for attaching the components. The pins or legs of the components must pass through the board, so they can be soldered to the copper side. To make these small holes you will need a very small drill bit, which is easily broken if not handled with care. Take your time and don’t forget to wear safety glasses!! 16 e-Printed PCB Holes being drilled into a PCB board. The drill bit is very small!!! So, be careful. Soldering Take care when using soldering irons, avoid burning the leads and always replace them in the soldering iron stand when you are not actually using them. Do not leave them lying on a workbench. The component pins and the board should be cleaned with a piece of fine wire wool before soldering. The soldering iron bit is heated and then ‘tinned’ by putting a small amount of multicore solder on it. The solder is hollow and has flux inside. Flux helps to keep the joint clean while it is being heated. It is very important that the work is heated properly, in order to get a good joint, which makes good electrical contact. Hold the tip of the iron on the copper next to the component. Place the solder onto the copper next to the iron. When the work is hot enough the solder will melt and flow. Remove the solder and run the tip of the iron around the pin of the component to make sure it is properly joined to the copper. 17 Example of Soldering Iron Stand, Soldering Iron and Power Source. The power source is used to control current and heat. Always ensure the solder joint is neat and not crossing the tracks. Always solder electronic components correctly to a PCB, if you do not the circuit will not function and the components could break. 18 Remember to follow Health & Safety Rules!!! How does the circuit work? 19 The Light dependent resistor (LDR) reacts to light changes. Its resistance is high in the dark, and low in the light. In our circuit, when it begins to get dark the resistance of the LDR will increase. As it increases the input voltage to the transistor will go above 0.6 volts. When this happens the transistor switches on, so switching on the LED. The circuit also has a variable resistor; this allows you to adjust when the control switches on the output. This variable resistor can be adjusted so the LED comes on just as it begins to get dark, or when it is totally dark. 330 Ohms Resistor Variable Resistor Connection LED Connections Transistor Connection s Battery Connections LDR Connections 20 1K Resistor Connecting Tracks