* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
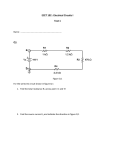
EXAMINATION BRANCH QUESTION BANK Name of the branch: ECE Year & Sem:II-II Name of the subject: PULSE &DIGITAL CIRCUITS Name of the faculty, Designation & Mobile number:G LAXMAN,Asst.Prof,9963933378 Date of Examination: Academic Year: 2016-17 NOTE: All the faculty requested to use Question Style - Calibri and Size - 12 UNIT-I LINEAR WAVE SHAPING S.N0 1 2 3 4 5 6 QUESTION 1. Prove that for any periodic input wave form the average levels of the steady state output signal from RC high pass circuit is always zero 2. (a) Write a short notes on RC low pass circuit (b) Draw the output response of RC low pass circuit for a step input signal and explain in detailed. c)Explain how a low pass RC circuit act as an integrator. 3. (a) Explain about RLC Ringing Circuit (b) Explain RC double differentiator circuit. 4.(a) A symmetrical square wave whose peak-to-peak amplitude is 2V and whose average value is zero is applied to an RC integrating circuit. The time constant is equal to half -period of the square wave. Find the peak to peak value of the output amplitude. (b) Describe the relationship between rise time and RC time constant of a low pass RC circuit. 5. (a) Explain the response of RL circuit when a step input signal is applied (b) In a low pass RC circuit, R=2k and C = 1_ F =1.sv, 2ms, pulse is applied as input to this circuit sketch the output wave form. 6(a) Obtain the response of RC high pass circuit for an exponential i/p signal. APPEARED IN (R05,R07, R09, R13) MARKS Assigned R09 16 R09 6+6+4 R07 8+8 R09 8+8 R07 8+8 R09 8+8 7 (b) A square wave whose peak-to-peak value is 1V, extends _0.5v (0.5V w.r.t.to ground). The half period is 0.1 sec this voltage impressed upon an RC differentiating circuit whose time constant is 0.2 sec. Determine the maximum and minimum values of the O/p voltages in the steady state. 7. (a) The limited ramp is applied to an RC differentiator. Draw to scale, the output wave form for the following cases i. T=RC, ii. T=0.4RC, iii. T=10RC. (b) Derive the expression for the response of RC low pass circuit to which ramp input is applied. 8.a) The output of a high pass RC circuit for a symmetrical square wave input is shown in Figure.1. Derive the expression for percentage tilt in the output. R07 8+8 R05 8+8 R07 8+8 R09 8+8 R09 8+8 R07 8+8 8 9 b) An oscilloscope displays a 5Hz square wave with 6% tilt. The signal input has no tilt and is coupled to the oscilloscope via a 4.7μF capacitor. Calculate the input resistance of the oscilloscope. 9.a) Prove that an RC circuit behaves as a reasonably good integrator if RC > 15T, Where T is the period of an input ‘Em sin ωt′. b) What is the ratio of the rise time of the three sections in cascade to the rise-time of Single section of low pass RC circuit? 10.a) What are the drawbacks of uncompensated attenuators? Prove that the condition to prevent input signal from distortion is R1C1 = R2C2, in an adequately compensated 10 11 12 attenuator. b) An RC differentiator circuit is driven from a 500Hz symmetrical square wave of 10V Peak-to peak. Calculate the output voltage levels under steady state if RC = 1msec. 11.a) Prove that for any periodic input waveform the average level of the steady state output signal from the RC high pass circuit is always Zero. b) Draw the RC low pass circuit. With necessary waveforms and expressions explain its working for a step voltage input 12.a) Derive an expression for the output of a high pass circuit excited by a ramp input. 13 14 15 b) A 1KHz square wave output from an amplifier has rise time tr = 250 ns and tilt = 10%, determine the upper and lower frequencies. 13. (a) Obtain the response of RC high pass circuit for an exponential i/p signal. (b) A square wave whose peak-to-peak value is 1V, extends _0.5v (0.5V w.r.t. to ground. The half period is 0.1 sec this voltage impressed upon an RC differentiating circuit whose time constant is 0.2 sec. Determine the maximum and minimum values. 14. What is the effect of the output resistance of the generator on an attenuator output? values of the O/p voltages in the steady state 15.a) Derive an expression for the output of a high pass circuit excited by a ramp input. b) A 1KHz square wave output from an amplifier has rise time tr = 250 ns and tilt = 10%, determine the upper and lower frequencies. R07 8+8 R09 16 R09 10+6 APPEARED IN (R05,R07, R09, R13) MARKS Assigned R09 10+6 R09 6+10 R09 8+8 R09 8+7 UNIT-II NON LINEAR WAVESHAPING S.N0 1 2 3 4 QUESTION 1(a) Draw the diode comparator circuit and explain the operation of it when ramp input signal is applied. (b) Explain the operation of two level slicer. 2. (a) Draw the basic circuit diagram of negative peak clamper circuit and explain its operation. (b) What is meant by comparator and explain diode differentiator comparator operation with the help of ramp input signal is applied. 3. (a) Draw the basic circuit diagram of a DC restorer circuit and explain its operation. Sketch the output wave form for a sinusoidal input. (b) Draw the basic circuit diagram of positive peak clamper circuit and explain its operation. 4.a)Draw the circuit diagram of an Emitter-Coupled clipping circuit. Explain its operation with its transfer characteristic and necessary expressions b) State and prove clamping circuit theorem. 5 6 7 5(a) What is meant by clipping in wave shaping? (b) Classify different types of clipper circuits. Give their circuits and explain their operation with the aid of transfer characteristics. R09 4+12 R09 8+8 R07 8+8 R07 8+8 R07 8+8 6.a) What is synchronized clamping? Explain. b) Design a diode clamper circuit to clamp the positive peaks of the input signal at zero level. The frequency of the input signal is 500 Hz. 7a) Explain how diode can be used as a Switch. b) In order to operate transistor as a Switch in which operating region it should be biased? Explain why? 8. (a) Design a clipping circuit with ideal components, which can give the waveform shown in figure for a sinusoidal input. 8 (b) State and prove clamping circuit theorem. 9.a) For the clipping circuit shown in figure , make a plot of Vo versus Vi for the range of Vi from 0 to 100 V. Indicate all slopes and voltage levels. Indicate for each region, the diodes which conduct. 9 b) A 100V peak square wave with an average value of 0V and a period of 20 ms is to be negatively clamped at 25V. Draw the circuit diagram necessary for this purpose. Also, draw the input and output waveforms. 10.For the circuit shown in, make a plot of V0 against Vi for the range of Vi from 0 to 50V. Indicate all slopes and voltage levels, and diode conducting region. Assume ideal diodes. 10 R09 16 R05 8+8 (b) For the circuit shown in figure 2b, an input voltage Vi linearly varies from 0 to 150 V is applied. Sketch the output voltage V0 to the same timescale. Assume ideal diodes. R07 12+4 13(a) What is a slicer? Explain with circuit diagram. (b) Sketch the steady state output voltage for the clamper R09 5+10 11 (a) A symmetrical 10 kHz square wave whose peak -to-peak excursion are _10V with respect to ground is impressed upon the diode clamping circuit shown in. The Diodes has Rf = 100 , Rr = _ and V = 0. Sketch the steady state output waveform Indicating clearly the voltage levels. 11 (b) Explain positive peak voltage limiters above and below reference level 12(a) Draw the basic circuit diagram of negative peak clamper circuit and explain its operation. 12 13 circuit shown in and locate the output d.c level and the zero level. The diode used has Rf=1K, Rr=600K, Vr=0. C is arbitrarily large and R=20 K. The input is a _20 Volts square wave with 50% duty cycle. 14(a) In the circuit shown in figure Rf = 1K, Rr = 100K V = 0. Sketch the output waveform V0 indicating all voltage levels and time constants for the given input waveform Vi. 14 (b) Draw the basic circuit diagram of positive peak clamper circuit and explain its operation. R09 10+6 R07 [8+8] 15 The input voltage Vi to the two-level clipper shown in varies linearly from 0 to 200V. Sketch the output voltage V0 to the same scale as the input voltage. 15 b) State and prove the clamping circuit theorem.