* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System - Weekend Warrior CPR
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
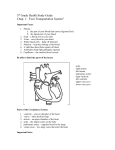
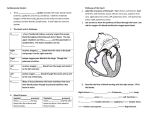
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps 2,000 gallons of blood through 60,000 miles of blood vessels each day Heart Facts A kitchen faucet would need to be turned on all the way for at least 45 years to equal the amount of blood pumped by the heart in an average lifetime Heart Facts The heart begins beating 4 weeks after conception and does not stop until death Heart Facts Newborns have about 1 cup of blood in circulation. Adults have about 4 to 5 quarts The Circulatory System Basic Functions Basic Functions 1. Transports nutrients and waste. Arteries- pick up nutrients and deliver the nutrients to each body cell. Capillaries- nutrient/waste exchange between blood Veins- carry away waste products and excess fluid of each body cell. Basic Functions 2. Transports heat. Regulates heat by distributing heat generated by muscles. 3. Transports oxygen to body cells and carbon dioxide away from body cells. Arteries carry oxygen to cells. Veins take carbon dioxide away from cells. Basic Functions 4. Transports hormones through the blood stream. 5. Transports antibodies. Through the blood stream to help the body fight infection. Structures of the Circulatory System Heart Hollow organ Pumps blood throughout the body Four chambers Major blood vessels Four valves The 4 Chambers of the Heart Right Atrium Receives unoxygenated blood from the veins. Right Ventricle Receives blood from right atrium and pumps to the lungs. Left Atrium Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it into the left ventricle. Left Ventricle Pumps blood into the aorta, which will transport blood through the body. Major Blood Vessels in the Heart Superior Vena Cava-receives blood from upper body. Goes to right atrium Inferior Vena Cava-receives blood from lower limbs. Goes to atrium. Major Blood Vessels in the Heart Pulmonary Arteries- receives deoxygenated blood from left ventricle. Goes to lungs. Pulmonary Veins- carries oxygenated blooded from lungs to left atrium Aorta- sends blood through rest of the body Valves in the Heart Tricuspid Valve- between right atrium & ventricles Pulmonary Valve- between right ventricle & pulmonary artery Mitral (Bicuspid) Valve- between left atrium and ventricle Aortic Valve- between left ventricle & aorta 10. 5. 1. 2. 4. 6. 7. 9. 8. 3. 1. Blood flow through the Heart Superior & Inferior Vena Cava Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right Ventricle Pulmonary Semilunar Valve Pulmonary Arteries Lungs Pulmonary Veins Left Atrium Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve Left Ventricle Aortic Semilunar Valve Aorta Blood Provides vital transportation for the body Four components Red blood cells (transport oxygen & nutrients) White blood cells (protect against against infection) Platelets (start clotting process) Plasma (liquid of blood) • • • • Anemia Heart Attack High Blood Pressure Atherosclerosis Diseases and Disorders Anemia Definition: Blood disorder where capacity of the blood to transport oxygen is decreased. Usually red blood cell count is diminished. Anemia Causes: Internal bleeding, vitamin deficiencies, decreased RBC production, increase in RBC destruction by spleen Symptoms: Fatigue, chest pain, skin paler, increased heart rate, difficulty breathing Anemia Treatment Iron supplements, vitamin supplements, blood transfusions, and erythropoietin (hormone tells bone marrow to make more red blood cells). Heart Attack Definition: Coronary artery or a branch of the coronary artery is blocked. Symptoms: Chest pain Crushing pressure Chest pain Shoulder or left arm pain Nausea Vomiting Difficulty breathing Heart Attack Treatment Oxygen Nitroglycerin pain medications, blood thinning medications Hypertension Definition: (high blood pressure) force of blood pushing against artery walls Cause: narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup Hypertension Symptoms: No major signs or symptoms Headaches Treatments: Medication Low salt diet Exercise Atherosclerosis Definition: hardening of the arteries. Silently and slowly blocks blood flow. Causes: Plaque builds up and arteries lose their elasticity. End Result: Arteries cannot contract and expand. Decrease in blood flow. Atherosclerosis Symptoms: may include chest pain, fainting, pain, and numbness or tingling. Treatment: Medications Diet to reduce fats and cholesterol levels Exercise and weight loss Arrhythmia Definition: an irregular heart beat. Fast, slow, uneven beat Causes: Alcohol, drugs, smoking, stress, hypertension, etc Angina Definition: heart pain due to narrowed arteries. MAJOR WARNING SIGN Cardiac arrest Definition: heart stops completely “clinical death” (0-4 mins) Treatment: CPR, defibrillator (AED). Risk Factors CONTROLLABLE Smoking Drugs Obesity (abdominal fat) Stress (increases blood pressure) Lack of exercise Diet (less fat & salt. More nutrients) Excessive Consumption of Alcohol More than 1 drink for women. More then 2 drinks for men Risk Factors UNCONTROLLABLE Gender (men more likely) Older Age Family History Race (Black, Indians, & Mexicans) Treatment Thrombolysis Definition: a treatment to dissolve dangerous clots in blood vessel. Angioplasty Definition: procedure that pushes plaque against the arterial wall, widening the artery and restores blood flow. Bypass Surgery Definition: taking arteries/veins from other parts of the body to create new passages for blood. Rerouting around clogged artery. Cardiomyoplasty Skeletal muscles are taken from back or abdomen and they're wrapped around an ailing heart. This added muscle, aided by ongoing stimulation from a device similar to a pacemaker, may boost the heart's pumping motion. Atherectomy Similar to angioplasty except that the catheter has a rotating shaver on its tip to cut away plaque from the artery Heart transplant Removes a diseased heart and replaces it with a healthy human heart when a heart is irreversibly damaged. Uses hearts from organ donation.