* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 5 Temperature, Pressure, and Moisture
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
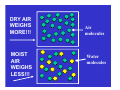
COPY Temperature, Pressure, and Moisture Mr. Rocco COPY Temperature • As air warms, its density decreases and it gets pushed up higher into the atmosphere. • As it does, pressure falls and temperature decreases ***The water vapor in this air cools and condenses to form CLOUDS!! • Clouds need condensation nuclei for water droplets to stick to! Cold Air COPY (ALOFT) • Cold air higher up in atmosphere is more dense and starts to sink • As it does, pressure increases and temperature warms up.( bike tire pump) Latent Heat COPY As water vapor changes from gas to liquid, heat is released into the air. What’s Latent heat used for? • The fact that supercells (thunderstorms) occur where warm, moist air meets cold, dry air suggests the source of energy for both t-storm and tornado: • latent heat is in the warm, moist air. Latent heat is heat you can't detect with a thermometer. COPY Moisture • When more moisture(water vapor) is added to air, the density and pressure of the air decreases. (You would think adding water would make the air heavier like a wet sponge, right?) BUT……….. • For each molecule of dry air ( N or O) that gets replaced by a water molecule, the air actually becomes less dense. • Why? • An N(28) or O(32) dry air molecule weighs 1.5 to 2x as much as a water molecule.(Atomic Weight=18) • So moist air weighs less!!! DRY AIR WEIGHS MORE!!! MOIST AIR WEIGHS LESS!!! Air molecules Water molecules COPY **Weather Differences** LOW Pressure: HIGH Pressure: • Warm/Hot air • Moist air • Stormy!!!! • Cool/Cold air • Dry air • Clear,sunny conditions COPY Summing up…….. • As altitude increases, air density and pressure decrease • As temperature and moisture increase, air density and pressure decrease