* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.3-7.4
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Large Hadron Collider wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
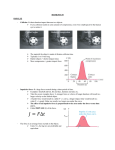
Suppose a cannon is propped against a massive tree to reduce recoil when it fires. Then the range of the cannonball will be 1. increased. 2. decreased. 3. unchanged. Collisions (7-3, 7-4) Elastic Collisions • If we choose our system so there is no net external force on the system, then the momentum of the system will be conserved during the collision. A particle of mass m moving with speed v collides head-on with a second particle of the same mass at rest. What are the speeds of the two particles after the collision, if it is elastic? • Kinetic energy may or may not be conserved What if the second particle has a mass of 100m? • Three kinds of collisions: – Elastic: total kinetic energy is conserved – Inelastic: total kinetic energy not conserved – Completely inelastic: if the objects stick together after colliding Newton's Cradle How does it work? i.e. why do equal numbers of balls bounce on each side? Inelastic Collisions A cart moving at speed v collides with an identical stationary cart on an airtrack, and the two stick together after the collision. What is their velocity after colliding? A. v B. ½ v C. zero D. -½ v E. -v Ballistic Pendulum A ballistic pendulum can be used to measure the speed of a projectile. It consists of a large block of wood hanging from two long cords. The projectile is fired into the block, quickly coming to rest. The block + projectile swing upward and their maximum vertical displacement is measured. If MA = 100 g, MB = 2.733 kg and h=7.9 mm, find the initial speed of the arrow Practice: Compare the initial KE of the bullet and the final KE of the block+bullet. Where did the energy go? Collisions in Two Dimensions (7-4) A marble moving with speed 3 m/s in the +x direction hits an equal-mass marble initially at rest. The two balls move off at 45º, marble 1 above the x axis, and marble 2 below. What are the speeds of the two marbles after the collision?