* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Epoch (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
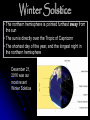
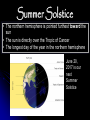
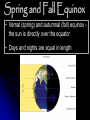
Solstices and Equinoxes TEK 8.7A – the student knows the effects resulting from cyclical movements of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. The student is expected to model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the sun causing changes in seasons. The Earth in Space How the Earth moves: Rotates on an axis Revolves around a star We have named several phenomenon beyond seasons. However, these also occur in predictable cycles. What is a Solstice? At two points throughout the year, the tilt of the Earth’s axis reaches its maximum angle compared to the Sun, and then begins to move back the other direction. This usually happens around June 21st and December 21st. These days are known as solstices. Solstice These two times in the year, the summer solstice and the winter solstice, The sun reaches its highest (summer) or lowest point (winter) in the sky at noon, marked by the longest and shortest days. Make a quick T chart in your notes Winter Solstice Summer Solstice Winter Solstice • The northern hemisphere is pointed furthest away from the sun • The sun is directly over the Tropic of Capricorn • The shortest day of the year, and the longest night in the northern hemisphere December 21, 2016 was our most recent Winter Solstice Winter Solstice for Northern Hemisphere Summer Solstice for Southern Hemisphere Summer Solstice • The northern hemisphere is pointed furthest toward the sun • The sun is directly over the Tropic of Cancer • The longest day of the year in the northern hemisphere June 20, 2017 is our next Summer Solstice Summer Solstice for Northern Hemisphere Winter Solstice for Southern Hemisphere Solstices On two days each year, the noon sun is overhead at either 23.5° S or 23.5° N – solstices. Winter Solstice 23.5° S in the northern hemisphere December 21st shortest day of the year Summer Solstice 23.5° N in the northern hemisphere June 21st Longest day of the year Equinox Equinox: the date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the equator The equinoxes are half-way between the solstices Therefore, they occur in the spring and fall Equinoxes The word Equinox is derived from latin - aequus (equal) and nox (plural: noctis) (night). During the Spring and Fall equinox the length of day versus night is equal. Make a quick T chart in your notes Spring Equinox Fall Equinox Spring and Fall Equinox • Vernal (spring) and autumnal (fall) equinox the sun is directly over the equator • Days and nights are equal in length Vernal (Spring) Equinox Occurs on or around March 21st Marks the beginning of spring in the northern hemisphere Autumnal (Fall) Equinox Occurs on or around September 23rd Marks the beginning of fall in the northern hemisphere Equinox Video Click on picture Activity