* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
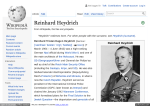
1939-1945 http://www.historyonthenet.com/Lessons/worksheets/ww2.htm Germany used “Blitzkrieg” – or lightening war Planes bombed airfields, factories, towns, etc. Then tanks and troops roared into the country Motorized high speed “keep enemy off balance Poland was conquered within a month Soviet forces took control of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and part of Finland 1939-1945 1939-1945 Two days later Britain & France declared war • So begins the phase of the war called the “phony war” • Coalition Forces wait at the “impenetrable defensive barrier” Maginot Line where all was quiet • Why did the Allied • forces not go on the offensive? Maginot Line http://www.history.com/shows/wwii-in-hd/interactives/inside-wwii-interactive http://www.bbc.co.uk/ history/worldwars/wwt wo/launch_ani_fall_fra nce_campaign.shtml 1) 2) 3) 4) April 1940, launched blitzkrieg against: Norway Denmark Netherlands Belgium http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=FddKPGE19wA&fe ature=relmfu Miracle of Dunkirk Germans pushed all French/British troops to the coastline British sent an improvised armada to rescue trapped soldiers in France Germany heads toward Paris! Benito Mussolini of Italy put his Pact of Steel with Hitler into action Italy declared war against France and Britain on June 10 June 22, 1940 – French surrender a new government formed by Marshal Philippe Petain (France's hero of World War I) requested an armistice France was divided into two zones, one under German military occupation and the other under Petain's government (south) Petain’s government was Hitler’s “puppet” Becomes known as Vichy France Charles de Gaulle – French general, set up a government in exile in London. Committed to reconquering France. Organized Free French military who battled the Nazis until France was liberated in 1944. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gi7mcJCOWp4 Air power takes prominent role Luftwaffe- German air force Parachute troops role increases Tanks were much improved from WWI Deadlier bombs Radar – to detect planes Sonar – to detect submarines Hitler now turned his attention to Britain, invasion (Operation Sea Lion) German planes bombed Britain throughout the summer of 1940 including night raids on London and other industrial centers Known as the “London Blitz” 8/12/1940 – air attacks on southern England Germans bombed London for 57 nights Considered a failure because British did not quit Continued until May 10,1941 The Royal Air Force (RAF) eventually defeated the Luftwaffe (German Air Force) Hitler turns his attention out of Britain onto the Eastern Front Winston Churchill What is Churchill’s prediction if they lose to the Nazi army? -End of the free world Prime Minister who rallied Britain to fight against Nazi aggression “voice of calm” Churchill rallies the British http://www.history.com/shows/wwii-inhd/interactives/inside-wwii-interactive Britain began receiving crucial aid from the U.S. under the Lend-Lease Act, passed by Congress in early 1941. http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/worldwars/wwtwo http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/primaryhistory/world_war2/ Hitler’s goal: continue expanding German property…. East of the Balkans Mediterranean Sea SOVIET UNION Mussolini takes North Africa in September of 1940 while the Battle of Britain was going on. Attacked British controlled Egypt. Egypt’s Suez Canal near Cairo = key to reaching oil fields of the Middle East Britain strikes back in December and by February 1941 Italy needs help… Hitler lends help to Mussolini Germans come in with the Afrika Korps German expeditionary force in Libya and Tunisia its first commander Erwin Rommel “Desert Fox” Seize Tobruk (Libya)= loss for the Allies http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm ?guidAssetId=107BDA7D-6E12-4F41-9E4C7D21F651A6CC The Axis power grows.. Bulgaria Hungary Romania Greece and Yugoslavia had pro-British governments Resist Hitler Hitler invades them These nations mostly devote resources and political alliance to the Nazis • They deport Jews to Poland • The employ secret police forces • They become puppet governments 1941 go get the USSR!!! The Soviet Union was their allies…Why invade? Plentiful Soviet resources! Stalin had the largest army in the world but it wasn’t prepared! 3 million Germans caught Stalin’s 5 million unprepared Soviets retreated Used “torch-earth policy” Nazis invade the Soviet Union Jewish population of 3 million Hitler issues infamous “Commissar Order” SS Einsatzgruppen follow advance of German Army “Liquidate all Communist officials you encounter! SS “Special Action Groups” organized in early years of war by Reinhard Heydrich Heydrich organized 4 large groups (A,B,C,D) in Soviet Union Competition between group leaders to see who could kill the most Jews 1,300,000 Russian Jews killed by end of war by these “mobile killing units” EINSATZ AREA OF OPERATIONS German’s surrounded Leningrad Starved them USSR lost 2.5 million troops Next moved towards Moscow, the capital of the Soviet Union! Germans were halted by Russia’s cold weather October 1941 Germany fails to take Moscow! Germans want oil fields in the Caucuses “Liquidate all Communist officials you encounter! capital oil End of Neutrality Acts Lend-Lease Act (1941) Selling or lending of war materials to countries “Vital to US defense” United States of America supplied Britain, Soviet Union, China, Free France, and other Allied nations Atlantic Charter (Aug. 1941) FDR and Churchill agree on: Free trade and the right of people to CHOOSE their government “Final destruction of Nazi tyranny” 43 min Dunkirk 49 min Pearl Harbor 52 min Afrika Campaign 55 min Battle of Stalingrad 58 min D-day 1 hour France is free 1 hour 4 min The Big Three Meetagree invasion of mainland Japan 1 hour 7 min Germany surrenders 1 hour 11 min – May 13 1945 Churchill proclaims war is over 1 hour 13 min- July 16 1945 Robert Oppenheimer tests atomic bomb 1 hour 19 min- dropping of the atomic bomb in Japan http://player.discovery education.com/index.c fm?guidAssetId=7FA4128 B-D776-4C5E-BC2B91AE1AE844A3 America controlled Philippine Islands and Guam Japan had successfully grabbed Manchuria, China and beyond…plans to take Southeast Asia http://www.history.com/shows/wwii-in-hd/interactives/inside-wwii-interactive Japan invades America sends aid to China 1940 FDR bans the sale of iron, steel and airplanes to Japan Tripartite Pact : Japan joins Axis on September 27, 1940 Japan felt that the US was interfering in their plans to expand Naval strategist Isoroku Yamamoto plans 12/7/1941 – Japan surprise attacks American fleet @ Pearl Harbor (Hawaii) 2,400 deaths US declares war on Japan (12/8/1941) Germany, Italy declare war on US four days later! Pearl Harbor Factories stopped making cars & refrigerators & made planes & tanks Shoes and sugar were rationed Use of propaganda War ended unemployment of the depression Japanese people in US and Canada Lost their jobs and property Forced into internment camps Seen as a security risk Nazi anti-British & American propaganda British anti-Nazi propaganda British anti-Nazi propaganda Strikes Seize Hong Kong Invades Malaysia Singapore surrenders Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia)-- [rich in resources] Burma Other towards the British and Dutch Strikes towards the United States Seize Guam and the Wake Island in western Pacific Attack on the Philippines to march into capital Manila June 1942 Midway Islands= West of Hawaii Home to a key American airfield Japanese secret plan to capture The U.S. would make sure the Japanese Navy would reach no further Over 150 Japanese ships head towards American ships Japan strikes first Marked the beginning of “Island Hopping” The recapture some islands while bypassing others Yamamoto himself on the largest ship U.S. Pacific Fleet took down 332 planes, all 4 aircraft carriers Yamamoto withdraws! retreats http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=C E0D53F2-C9EC-4DAF-A728-0BDFA9355B9D Bypass heavily fortified Concentrate on striking important weaker points “Leapfrogging” Japanese attempt to seize Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands to build large air base Access to Australia Aug 1942 Allied troops with Australia on their side, attack! General MacArthur US Marines captured a huge Japanese Air Force base Japanese lost 24,000 troops Japans goal: Establish a new order in Southeast Asia and the Pacific Puppet governments in Western Europe run by “Aryans” Eastern Europeans “inferior”, shoved aside for more living space Nazis stripped conquered nations of art, factories and resources Used Eastern Europeans as slave laborers; shot and tortured prisoners Battle of El Alamein, Egypt Operation Torch British takes down Rommel Rommel’s army retreats http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=2 C522DC6-BF0F-4430-B520-22282FFFEF25 Allies had regained possession of Tobruk Allies finally brought German Panzers to a halt 107,000 Allied troops invade land in Algeria and Morocco Mussolini orders Italians to invade Egypt Battle of El Alamein October 1942 Egypt – The battle halted the second (and final) advance by the Axis forces going into Egypt ended Axis hopes of occupying Egypt, taking control of the Suez Canal, and gaining access to the Middle Eastern oil fields. Operation Torch 8 November 1942; ended on 11 November. American and British Commonwealth landed in French North Africa under the assumption that there would be little to no resistance British led by Gen. Bernard Montgomery US led by Gen. Douglas MacArthur invasion of northwestern Africa — Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia, African territory was in the hands of Petain’s Vichy French “Nazi puppet” government Successful completion of these operations was to be followed by an advance eastwards into Tunisia. Allies advance into Tunisia Rommel is outflanked, outmanned and outgunned. • Rommel gets the infamous "victory or death" stand-fast order from Hitler • demanded the impossible • virtually ensured the destruction of Panzer Army Africa, • Rommel could not bring himself to disobey a direct order from his Führer Allies trap Rommel’s army and force surrender in May of 1943 led to all Italian colonies in Africa being captured. • Rommel named a “disgrace” • Hitler says face court of people that will scorn your legacy or commit suicide quietly • Rommel takes cyanide pill and dies 1944 Turning Point: Battle of Stalingrad Street by street and house by house battles Nightly bomb raids by the Germans Nov 1942 Germans controlled 90 % of the city ANOTHER RUSSIAN WINTER SETS IN February 1943 Germans surrender ! Stalingrad is now called Volgograd 300,000 killed or injured Over one million Soviet soldiers died City was 99% destroyed Soviets then drive Germans back westward http://player.discoveryedu cation.com/index.cfm?guid AssetId=29091B7E-0A464353-AA49-960E4229AFA1 Turning 9 month campaign for the Allies to regain France D-Day June 6th 1944 To Point in Europe Allied paratroopers and ferried troops (176,000) Fought against heavy gunfire and snipers invade the beaches of Normandy Largest Land and Sea attack in history Battle of Normandy August Allies made their way to Paris By September France was free AND had liberated Belgium, Luxembourg, and much of the Netherlands France named 4th republic and on the road to peace Now Allies push towards Germany!! http://player.discoveryeducation.com/ind ex.cfm?guidAssetId=B94DB811-9CEE-48A9A18B-942CF10F1C6F July 1943 British and American forces land in Sicily and defeat the Italians in 1 month King Victor Emmanuel III fired Mussolini Allied forced landed in Sicily in 1943 Controlled Sicily in one month Italy surrendered within two months Sept 1943 Italy surrenders Hitler uses his control over the North to put Mussolini back in charge http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/worldwars/wwtwo/launch_ani_i taly_campaign.shtml Allies enter Rome in June, pushing Nazis up Although Italy had surrendered, Germany continued to battle the allies in Italy until the end of the war Mussolini is found disguised as a German general in April 1945 He was shot and hung in Milan town square Hitler’s false hope Hitler’s army had been in retreat since D-day Germany launches an attack to break Allied alliances Germany was facing a war on three fronts US to the west (coming from France) Soviet Union to the east US and UK to the south (coming from Italy) Germany on the offensive for the last 85-mile front in the Ardennes Forest time Forest, rolling hills in a mountain range: Belguim, Luxembourg, France Germans able to push into Allied lines (Belgium) Fight over the “Bulge” of land http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=E D5BFEBF-A9D3-478A-A884-A3856DB485ED The Germans experienced great success to start with first 2 days surprise attack, Germans spread misinformation (changed road signs, cutting telephone lines), fog prevented Allied air force Major problem: German military was depleted of supplies Germans running out of fuel, proven by abandonment of the Panzers By December 22nd, the weather started to clear Allies to bring their air power into force The Germans had advanced 60 miles in 2 days but from December 18th on =stalemate. The Battle of the Bulge was the largest battle fought by the Americans in WWII: 600,000 American troops fought Americans lost 81,000 men// Germans lost 100,000 killed wounded and captured Ultimately Allies “push back the Bulge”= success! http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FSxnvwxsAm8 Soviets and allies invade Germany Battle of Berlin, Germany goes on April1945 and ends May 2, 1945 April 27 1945 Mussolini dies April 30 1945 Hitler dies Soviets have control of the capital: Berlin, Germany Hitler had an underground headquarters there Hitler commits suicide in his underground bunker w/ wife Eva Braun May 7th Germany surrenders May 8th surrender was officially signed in Berlin V-E Day or Victory in Europe Day http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cf m?guidAssetId=576912C4-3B93-433D-8E8CC2A439F04877 Surrender in France Surrender in USSR Declaration Regarding the Defeat of Germany and the Assumption of Supreme Authority by Allied Powers was signed by the four Allies on June 5. It included the following: “The Governments of the United States of America, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, the United Kingdom and the Provisional Government of the French Republic, hereby assume supreme authority with respect to Germany, including all the powers possessed by the German Government, the High Command and any state, municipal, or local government or authority. The assumption, for the purposes stated above, of the said authority and powers does not effect the annexation of Germany.” —US Department of State, Treaties and Other International Acts Series, No. 1520. A HOLOCAUST PROGRAM OF MASS MURDER GENOCIDE THE ANNIHILATON OF ENTIRE RACE OF PEOPLE Jews are not allowed to: Marry or have sex hire Aryan women with Aryans as maids have rights of citizenship German Jews are deported to Poland Ghettos of Lodz, Krakow and Warsaw are sealed off. Total of 600,000 Jews These ghettos will be liquidated starting in 1942 German soldiers rounding up Jews to be placed in ghettos Nazis invade the Soviet Union Jewish population of 3 million Hitler issues infamous “Commissar Order” SS Einsatzgruppen follow advance of German Army “Liquidate all Communist officials you encounter! SS “Special Action Groups” organized in early years of war by Reinhard Heydrich Heydrich organized 4 large groups (A,B,C,D) in Soviet Union Competition between group leaders to see who could kill the most Jews 1,300,000 Russian Jews killed by end of war by these “mobile killing units” EINSATZ AREA OF OPERATIONS Heydrich was ordered by Hermann Goering to prepare a “final solution” to the Jewish question Heydrich organized a meeting with 15 top Nazi officials in Berlin = Jan. 20, 1942 Nazis would attempt to exterminate the entire Jewish population of Europe, an estimated 11 million persons Nicknamed “The Blond Beast” and “Hangman Heydrich” second in command of Gestapo and SS principle planner of the Final Solution Brigadier General in SS at the age of 30 “Europe would be combed of Jews from East to West” “Madagascar Plan” ordered Einsatzs to round up and kill Jews in occupied countries leader of RSHA Czech underground agents bombed his car SS hunted down and killed 1000 suspects Czech town of Lidice was liquidated Hilter called him “The man with the iron heart.” 172 men shot in village of Lidice in retaliation. “Now judgement has begun and it will reach its conclusion only when the knowledge of the Jews has been erased from the earth!” Nazi Newspaper there were 3 phases of the Nazi plan to wipe out the Jewish population of Europe Jews were rounded up and told they were to be relocated They were taken to the woods and were shot one by one their bodies were buried in mass graves Again, Jews were rounded up and told they were to be relocated in vans The vans were equipped so that the van’s exhaust was piped back into the van 700,000 Jews killed in Vans The Nazis encountered several problems with the executions and gas vans First, they were both taking to much time Second, resources such as gas and munitions were becoming scarce Third, soldiers involved were beginning to have psychological problems with what they were doing. Nazi leaders decided to drastically speed up the Final Solution there were two different types of camps: CONCENTRATION CAMPS EXTERMINATION CAMPS Jews from all over occupied Europe were to be brought here. 100 of these in Nazi-occupied Europe prisoners used for forced labor prisoners usually lasted less than 1/2 year communists, homosexuals, criminals, socialdemocrats, artists. First camp was opened in 1933, right after Nazis came to power Started out as ordinary concentration camps later modified with gassing installations for use on humans, now “DEATH CAMPS” two sub-groups: 1) Majdanek and Auschwitz, Birkenau 2) Operation Reinhard camps and Chelmno “NAZIS GET CLOSE TO CREATING HELL ON EARTH!!!” CAMPS IN POLAND Started operations in January 1940 (Poland) Himmler chose Auschwitz as the place for the Final Solution had 4 gas chambers/crematories by 1943 mass killings with Zyklon B gas commanded by Rudolph Hoess recorded 12,000 kills in one day ORDERED TO TAKE ALL POSSESSIONS FROM JEWS TEETH WITH GOLD PILES OF GLASSES GAS USED TO KILL VERMIN. IT WAS INEXPENSIVE COMPARED TO GAS. DROPPED FROM CEILINGS Arrived in Auschwitz in May of 1943 SS Doctor who had power of life/death performed medical experiments on Jewish children Introduce himself as Uncle Mengele “ANGEL OF DEATH” Sterilization of men and women endurance of pain to high and low temperatures and pressure experiments on twins to increase number of multiple births to Aryan women injections of phenol to kill patients Dr. Mengele attempted to sew children together to make Siamese twins Mengele's experiments also included attempts to change eye colour by injecting chemicals into children's eyes, various amputations of limbs, and other surgeries. Rena Gelissen's account of her time in Auschwitz details certain experiments performed on female prisoners around October 1943. Mengele would experiment on the chosen girls, performing sterilization and shock treatments. Most of the victims died, because of either the experiments or later infections. Mengele also sought out pregnant women, on whom he would perform vivisections before sending them to the gas chambers. Auschwitz prisoner Alex Dekel has said: "I have never accepted the fact that Mengele himself believed he was doing serious work – not from the slipshod way he went about it. He was only exercising his power. Mengele ran a butcher shop – major surgeries were performed without anesthesia. Once, I witnessed a stomach operation – Mengele was removing pieces from the stomach, but without any anesthetic. Another time, it was a heart that was removed, again without anesthesia. It was horrifying. Mengele was a doctor who became mad because of the power he was given. Nobody ever questioned him – why did this one die? Why did that one perish? The patients did not count. He professed to do what he did in the name of science, but it was a madness on his part." EXTRACTED HUMAN ORGANS EXPERIMENTS ON CHILDREN IN AUSCHWITZ Largest single massacre of Holocaust March 1942-November 1943 Named after Reinhard Heydrich carried out at three camps, run by the SS every Jew that arrived at one of the camps would be dead in 2 hours. Total of 1,700,000 Jews killed November 1943 Most of the staff and guards were then sent to northern Italy for further Aktion against Jews 1,600,000 1,400,000 1,200,000 1,000,000 800,000 killed in camp 600,000 400,000 200,000 0 Auschwitz Belzec Chelmo 3,500,000 3,000,000 2,500,000 2,000,000 BEFORE AFTER 1,500,000 1,000,000 500,000 0 POLAND USSR HUNGARY GERMANY Jewish population before, Jewish population after Holocaust