* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Theory - Courses
Inductive probability wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Confidence interval wikipedia , lookup
History of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Bootstrapping (statistics) wikipedia , lookup
Taylor's law wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
AMS7: MIDTERM
REVIEW
Chapters 1-6
Tuesday May 5, 2015
Introduction
• Important Definitions:
- Data
- Statistic
- A Population
- A census
- A sample
Types of Data
• Parameter (Describing a characteristic of the Population)
• Statistic (Describing a characteristic of the Sample)
-QUALITATIVE DATA (Categorical or Attribute Data)
-QUANTITATIVE DATA:
- Discrete
- Continuous
Levels of Measurement:
- Nominal
- Ordinal
- Interval
- Ratio
Design of Experiments
• An observational study (don’t attempt to modify the
subjects)
• An experiment (treatment group vs. control group)
Types of Observational Studies:
• Cross-sectional
• Retrospective (or case-control)
• Prospective (or longitudinal or cohort)
Problems
• Confounding (confusion of variables effects)
How to solve this problem?:
• Blinding (placebo effect, single-blind, double-blind)
• Blocking
• Randomization:
• Completely randomized design
• Randomized block design
Sampling strategies
• Random sample
• Simple random sample (assumed throughout the book)
• Systematic sampling
• Convenience sampling
• Stratified sampling
• Cluster sampling
• Sampling Error :difference between sampling result and
the true population result
• Non-sampling error: Sample data incorrectly collected
Important characteristics of data
• Center
• Variation
• Distribution
• Outliers
• Time
Frequency distribution
• Counts of data values individually or by groups of
intervals
• Other forms:
• Relative frequency distribution (divide each class frequency by the
total of all frequencies)
• Cumulative frequency distribution (cumulative totals)
• Histogram: Graphical representation of the frequency
distribution
Other graphs
• Relative frequency histogram
• Frequency polygon
• Dotplots
• Steam-Leaf plots
• Pareto chart
• Pie Charts
• Scatter Diagrams
• Time series graphs
Examples: Histogram and Scatter plot
Measures of center
• Sample Mean: ̅ =
∑
• Median: Middle value
• Mode: Most frequent value
• Bimodal
• Multimodal
• No mode
• Midrange=
Skewed distributions
Measures of Variation
• Range= (Maximum value-Minimum value)
• Sample standard deviation: Variation from the mean
=
∑( − ̅ )
−1
• Population standard deviation:
=
∑( − )
• Sample variance:
∑
(
−
̅
)
=
−1
• Population Variance: =
∑()మ
Measures of Variation (Cont.)
• Sample Coefficient of Variation: = . 100%
̅
• Population coefficient of variation: =
. 100%
Range Rule of Thumb
≈
4
• Minimum usual value: (mean)-2 x (standard deviation)
• Maximum usual value: (mean)+2 x (standard deviation)
Rules of data with Bell-Shaped distribution
• About 68% of all values fall within 1 standard deviation of
the mean
• About 95% of all values fall within 2 standard deviations of
the mean
• About 99.7% of all values fall within 3 standard deviations
of the mean
Z Scores
• Sample
• Population
− ̅
=
−
=
Ordinary values: -2≤ z score≤2
Unusual values: z score < -2 or z score> 2
Quartiles and Percentiles
• Quartiles: Separate a data set into four parts
• Q1 (First): Separates bottom 25% of the sorted values from the top
75%
• Q2 (Second): Same as the median
• Q3 (Third): Separates bottom 75% of the sorted values from the top
25%
• Percentiles: Separate the data into 100 parts (P1, P2, …,
P99)
Percentile value of x=
. 100
• Intercuartile range= Q3-Q1
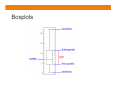
Boxplots
Probability
• Definitions:
• An event
• A simple event
• The Sample Space
• Notation
• P: Probability
• A,B and C: specific events
• P(A): Probability of event A occurring
Definitions of Probability
• Frequency approximation: P(A)=
• Classical Approach: P(A)=
=
• Subjective Probability
• LAW OF LARGE NUMBERS: A procedure is repeated
many times. Relative frequency probability tends to the
actual probability
Properties of probability
• Probability of an impossible event is 0
• Probability of an event that is certain is 1
• For any event A, 0≤P(A)≤1
• P(Complement of event A)=P(̅) = 1 − ()
• Addition Rule:
P(A or B)=P(in a single trial, event A occurs or event B
occurs or they both occur)= P(A)+P(B)-P(A and B)
Or
P(A∪B)= P(A)+P(B)-P(A∩B)
Events A and B are disjoint if P(A∩B)=0
Multiplication Rule
• P(A and B)=P(event A occurs in the first trial and event B
occurs in a second trial)
• = . • Independent events: P(B|A)=P(B)
• If A and B are independent: = . ()
• Conditional probability:
=
()
()
Bayes Theorem
• =
.(|)
. [ ̅ . ̅ ]
Probability distributions
• Definitions:
• Random Variable (x): Numerical value given to an outcome of a
procedure. Example: Number Mountain lions seen at UCSC
campus last year
• Probability distribution (P(x)): Gives the probability to each value of
the random variable.
• Types of random variables:
• Discrete
• Continuous
Requirements of a Probability distribution
• ∑ = 1(Discrete case)
• 0≤P(x)≤1
• Expected value of a discrete random variable
= [. ]
Discrete Distributions:
• Binomial
• Poisson
Binomial distribution
• Requirements:
• Fixed number of trials
• Trials are independent
• Each trial can be a success or a failure
• Probabilities remain constant
• Random variable: x=number of successes among n trials
• =
!
. . !!
(You can also use the Binomial
Table)
• n= number of trials
• p=probability of success in one trial
• q=probability of failure in one trial (q=1-p)
Mean ,Variance and Standard deviation of the
Binomial distribution
• Mean: = • Variance: = • Standard deviation:
• Maximum usual value: + 2
• Minimum usual value: − 2
Poisson distribution
• Requirements:
• Random variable x is the number of occurrences of an event over
some interval
• The occurrences must be random
• The occurrences must be independent
. =
!
The Poisson distribution only depends on (the mean of
the process)
Mean, Variance and Standard deviation of the
Poisson distribution
• Mean: • Variance: • Standard deviation: =
• Maximum usual value: + 2
• Minimum usual value: − 2
Continuous distributions
• Uniform distribution
• Normal distribution
• Density curve: Graph of a continuous distribution
• Properties:
• Area below the curve is equal to 1
• All points in the curve are greater or equal than zero
Uniform and Normal distributions
Sampling distributions
• Variation of the value of a statistics from sample to
sample: Sampling variability
• Sampling distribution of the sample mean
• Sampling distribution of the sample proportion
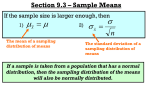
CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM:
• The random variable x has a distribution (normal or not)
with mean and standard deviation • The distribution of the sample means will approach to a
normal distribution as the sample size increases.
Mean and standard deviation of the
sample mean
• Mean: ̅ = • Standard deviation: ̅ =
Normal approximation to the Binomial
• If np≥5 and nq≥5 a Binomial random variable x can be
approximated with a Normal distribution with mean and
standard deviation:
• Mean: = • Use Continuity Correction
• Standard deviation:
Confidence Interval for the Population
Proportion (p)
• p=population proportion
• ̂ =
=
sample proportion of successes
•
= 1- ̂ = sample proportion of failures
Procedure to build a CI of confidence level
(1-ߙ)⨯100% for p
1) Check the normal approximation to the Binomial
distribution (np≥5 and nq≥5 )
2) Get the critical value /
3) Evaluate the margin of error: = / .
4) Confidence Interval:
• ̂ − < < ̂ + • ̂ ± • (̂ − , ̂ + )
5) Interpret results
⁄
Sample size for estimating proportion p
• ̂ is given:
[
/ ] ̂ =
• ̂ is not given: (̂ is assumed = 0.5)
[
/ ] 0.25
=
Finding (point estimate) and E from the
Confidence Interval
Point estimate:
• ̂ =
!
!! ("
!
!!)
Margin of Error:
• E=
!
!! ("
!
!!)
Confidence Interval for the Population
Mean (ߪ known)
• Check Requirements:
• Sample is a simple random sample
• Population standard deviation is known
• Population is normally distributed or n>30
• Procedure
1) Check normality requirements
2) Get the critical value /
Evaluate the margin of error: = / . 4) Confidence Interval:
3)
• ̅ − < < ̅ + • ̅ ± • (̅ − ,̅ + )
5) Interpret results
Sample size for estimating Mean
=
# . Values of , ഀ⁄మ and E are given.
Confidence Interval for the Population
Mean (ߪ unknown)
• In this case we use the Student t distribution with n-1 degrees of
freedom to find the critical value
• Check Requirements:
• Sample is a simple random sample
• Population standard deviation is estimated by s (sample standard dev.)
• Population is normally distributed or n>30
• Procedure
1) Check normality requirements
2) Get the critical value / with n-1 degrees of freedom
3)
4)
Evaluate the margin of error: = / . Confidence Interval:
• ̅ − < < ̅ + • ̅ ± • (̅ − ,̅ + )
5) Interpret results
Finding point estimate and E from Confidence
Interval
Point estimate of ߤ:
!"!#!$ + ("% !"!#!$)
̅ =
2
Margin of Error
• E=
!
!! ("
!
!!)