* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology I Semester 1 Quarter 1 Exam Study Guide 2014-10
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
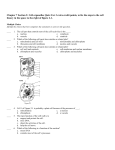
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ Mr. Dennis F. Goode ID: A Biology I Semester One Quarter One Exam Study Guide This Biology I Semester One Quarter One Exam Study Guide is provided to help the Biology learner prepare for a rigorous Biology Exam. Tackle this study guide to prepare yourself to do your best. This Semester One Quarter One Study Guide Practice Exam will assess your knowledge, understanding, and some higher level thinking in the following Biology content areas: The Science Of Life Biochemistry Respiratory System Cell Structure And Functions Chemistry Of Life Circulatory System Nervous System Homeostasis And Cell Transport Prepare the questions below. Print. Bring to the Semester Exam Study Sessions for review. Good Luck!!! Remember: Hard work and smart work pay dividends!!! ============================================================= Completion Complete each statement. 1. ____________________ is the study of the interaction of organisms with their environment and with each other. 2. To function properly, all living things must maintain a constant internal environment through the process of ____________________. 3. An educated guess, or a(n) ____________________, may be tested by experimentation. 4. Stating in advance the result that may be obtained from testing a hypothesis is called ____________________. 5. A unifying explanation for a broad range of observations is a ____________________. 6. A ____________________ experiment is one in which the condition suspected to cause the effect is compared to the same situation without the suspected condition. 7. The base unit for length in the Système International d’Unités (International System of Units) is the ____________________. 8. A ____________________ electron microscope passes a beam of electrons over a specimen’s surface, whereas a ____________________ electron microscope passes a beam of electrons through a thin slice of a specimen. 1 Name: ________________________ ID: A 9. Substances that are changed when they become involved in chemical reactions are called ____________________, while the new substances that are formed are called ____________________. 10. The energy needed to break existing chemical bonds during the initiation of a chemical reaction is called ____________________. 11. Chemical reactions in the body can be speeded up by adding a(n) ____________________, which lowers the amount of activation energy required to start the reaction. 12. The loss of electrons from a molecule is called ____________________, while the gain of electrons by a molecule is called ____________________. 13. A substance that dissolves in another is called a(n) ____________________. 14. ____________________ is the most common solvent in cells. 15. ____________________ and ____________________ ions form when water dissociates. 16. An acidic solution is one that has more ____________________ than ____________________ ions. 17. A solution with a pH of 3 has ____________________ times more hydronium ions than a solution with a pH of 6. 18. Buffers are important because body fluids must be maintained within a relatively narrow range of ____________________. 19. Water is very effective at dissolving other polar substances because of its ____________________. 20. Breaking of ____________________ bonds is the first thing that happens when water is heated, which means that it takes a great deal of thermal energy to raise the temperature of water. 21. Because carbon atoms have four electrons in their outermost energy level, they can form up to ____________________ covalent bonds with other atoms. 22. In the molecule that has the chemical formula C2H4, the carbon atoms are bonded together with a ____________________ bond. 23. In a condensation reaction, two molecules become linked together and a molecule of ____________________ is produced. 24. The formation of polymers from monomers occurs as a result of ____________________ reactions, and the breakdown of polymers into monomers occurs as a result of ____________________ reactions. 25. Lipids are ____________________ molecules because they have no negative and positive poles. 26. A substrate attaches to the ____________________ of an enzyme. 2 Name: ________________________ ID: A 27. In a triple bond, ____________________ pair(s) of electrons is (are) shared between two atoms. 28. ATP contains ____________________ phosphate groups. 29. The statement “Cells are produced only from existing cells” is part of the ____________________. 30. The ratio of surface area to ____________________ puts limitations on a cell’s size. 31. Eukaryotic cells are much larger and have more specialized functions than prokaryotic cells because they contain ____________________, which carry out specialized activities. 32. A cell with a well-defined nucleus and cytoplasm surrounded by a plasma membrane is a(n) ____________________ cell. 33. A plasma membrane is said to be ____________________ permeable because it allows the passage of some solutes and not others. 34. ____________________ molecules have “heads” and “tails” and are found in the plasma membrane. 35. Scientists have discovered that cells contain smaller specialized structures known as ____________________. 36. The spherical organelles that are the site of protein synthesis in a cell are the ____________________. 37. The meshlike network of protein fibers that supports the shape of the cell is called the ____________________. 38. The fluid portion of the cytoplasm is called the ____________________. 39. Photosynthesis takes place in the ____________________ of plant cells. 40. Both plant and animal cells have plasma membranes. In addition, plant cells are surrounded by a(n) ____________________. 3 Name: ________________________ ID: A 41. Refer to the illustration above. The diagram shows the ____________________ that makes up the framework of the plasma membrane. 42. Matthias Schleiden worked with ____________________ cells, and Theodor Schwann worked with ____________________ cells. 43. Some plants produce a _________________________ between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall. 44. Active transport systems are a form of cell transport that requires energy from molecules of ____________________. 45. ____________________ allows a cell to stockpile substances in far greater concentrations than they occur outside the cell. 46. Conduction of nerve impulses is possible because of the _________________________. 47. Refer to the illustration above. The process shown in figure Y is called ____________________. 48. Refer to the illustration above. Cells often trap extracellular particles and fluid. This is shown in figure ____________________. 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A 49. The process in which an amoeba engulfs its prey and takes it in is known as ____________________. 50. The ____________________ system transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, food molecules, hormones, and other material to and from the cells of the body. 51. The ____________________ valve prevents blood from going from the left ventricle to the left atrium. 52. Electrical impulses in the heart are relayed to the ventricles by the _________________________. 53. Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle through the ____________________. 54. ____________________ are the blood vessels that connect the arteries to the veins. 55. Systolic pressure is caused by contraction of the heart’s ____________________. 56. The condition that results when blood pressure is consistently higher than normal is called high blood pressure or ____________________. 57. The flow of blood from the heart to all parts of the body except the lungs is called ____________________ circulation. 58. Excess fluid in the body’s tissues is returned to the blood by a system of vessels called the ____________________ system. 59. The major function of ____________________ is to assist in the blood clotting process. 60. The primary role of hemoglobin in the blood is to carry ____________________. 61. Red blood cells are called ____________________. 62. Defending the body against bacterial infection and invasion by other foreign substances is the function of ____________________ blood cells. 63. Antigens determining blood type are carried on the surface of ____________________. 64. The ____________________ is a long, straight tube that carries air from the back of the throat to the lungs. 65. When you swallow, the ____________________ prevents food from entering the trachea. 66. Hemoglobin in red blood cells binds to both oxygen and ____________________. 67. When the diaphragm and the rib muscles contract, enlarging the chest cavity, ____________________ occurs. 68. Breathing is regulated mainly by response to the level of ____________________ detected in the blood. 5 Name: ________________________ ID: A 69. ____________________ respiration is the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the blood, while ____________________ respiration is the exchange of gases between the blood and the cells of the body. 70. Nerves that control breathing, swallowing, heartbeat, and the diameter of blood vessels are found in the ____________________. 71. The thalamus, the hypothalamus, and cells deep within the gray matter of the brain make up the ____________________ system, which helps regulate emotions. 72. Ventral-root axons carry information to ____________________ and glands, while dorsal-root axons carry information to the ____________________ system. 73. The part of the nervous system that does not include the spinal cord and brain is called the ____________________ nervous system. 74. The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls internal organs is called the ____________________ nervous system. 75. A sudden, involuntary movement in response to a stimulus is called a(n) ____________________. 76. A(n) ____________________ is the basic unit of communication of the nervous system. 77. Cytoplasmic extensions called ____________________ allow a neuron to receive information simultaneously from many different sources. 78. Some axons are surrounded by an insulating structure called a(n) ____________________. 79. A neuron transmits a nerve impulse as a wave of ____________________ charge. 80. The electrical charge across the membrane of a neuron is caused by different concentrations of sodium and ____________________ ions inside and outside the cell. 81. Messages are carried across synapses by _________________________. 82. The junction of a neuron with another neuron or with a muscle cell is called a(n) ____________________. 83. Sensory receptors that respond to tissue damage are called ____________________ receptors. 84. Peripheral nerve cells that receive information from both internal and external stimuli are called ____________________. 85. The ____________________ is the light-sensitive inner layer of the eye. 86. When light enters the eye, it activates photoreceptors called ____________________, which respond to dim light, and ____________________, which respond to bright light and colors. 6 Name: ________________________ ID: A 87. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the ____________________. 88. When light enters the eye, it passes first through the ____________________. 89. The ____________________ is a small, snail-shaped structure lined with hair cells. 90. The specialized hearing receptors found in the cochlea are ____________________ cells. 91. A(n) ____________________ is a globular cluster of cells specialized to detect chemicals found in foods. 92. High concentrations of pain receptors are located in the mouth and ____________________. 93. ____________________ are complex mixtures of chemicals and smoke particles produced by burning tobacco. 94. Drugs that decrease the activity of the central nervous system are known as ____________________. 95. ______________________________ (BAC) is a measurement of the amount of alcohol in the blood. 96. Abuse of psychoactive drugs often leads to a state of uncontrollable physical or psychological dependence called ____________________. 97. Drugs that affect the functioning of the central nervous system are called ____________________ drugs. Problem 98. Some scientists conducted an experiment in which they evaluated various measurements of human health in people who drank at least one cup of coffee a day. They found no significant differences in these health indicators between the subjects who drank only one cup of coffee a day and those who drank as many as 20 cups a day. They concluded that coffee has no adverse effects on human health. Write your answers to the following in the spaces below. a. What were the independent and dependent variables in this experiment? b. Was this a controlled experiment? If so, what were the control and experimental groups? c. Do you agree with the conclusion the scientists drew from their results? Why or why not? 7 Name: ________________________ ID: A 99. Refer to the illustration above. The graph depicts the relative energy levels of the products and reactants for the following chemical reaction: A + B ˆ‡ C + D. Write your answers to the following in the spaces below. a. Which substances, A, B, C, and/or D, are present at point 1 on the graph? b. Which substances, A, B, C, and/or D, are present at point 3 on the graph? c. Why is point 2 at a higher energy level than point 1? d. Why is point 3 at a lower energy level than point 1? e. Draw a dashed line on the graph indicating how the energy level of this reaction over time would be different if the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction were not present. 100. You are given four test tubes containing purified biological macromolecules. The test tubes are unlabeled except for a number between 1 and 4. You are told that one test tube contains a protein, one contains a lipid, one contains a carbohydrate, and one contains a nucleic acid. You then perform some tests on the macromolecules and collect the following information: 1) Test tubes #2 and #4 contain nitrogen, but the other tubes do not. 2) The contents of test tube #3 are not soluble in water, but the contents of the other test tubes are soluble in water. 3) The contents of test tube #1 can be broken down into subunits that are all exactly identical to each other. 4) The macromolecule in test tube #2 is found to have a globular shape. What are the identities of the macromolecules present in the four test tubes? Write your answer in the space below. 101. A living cell has certain characteristics in common with a working factory. In a factory, products are assembled according to specified plans, energy is used in the assembly process, products are packaged and taken out of the factory, and a supervisor directs and oversees all of the activities occurring in the factory. Draw a model of a factory, labeling areas where the following important activities would occur: main office where supervisor keeps the plans and oversees activities, assembly line, electricity generator, packaging center, and factory doors. Next to each of your labels, write the name of the cellular organelle or structure that has a similar function. Choose the cellular organelles and structures from this list: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole. Write your answer in the space below. 8 Name: ________________________ ID: A 102. Organisms in the genus Paramecium are unicellular protists. They have a number of characteristics also found in animals, such as the need to ingest food in order to obtain energy (they are heterotrophs) and the fact that they have a cell membrane but not a rigid cell wall. They have organelles found in animal cells, including nuclei, mitochondria, ribosomes, and cilia. In addition, they have star-shaped organelles called contractile vacuoles, which collect excess water from inside the paramecium and expel it periodically to the outside of the organism. The picture below depicts a paramecium. The data presented in the table below were obtained in an experiment in which paramecia were placed in different salt concentrations and the rate at which the contractile vacuole contracted to pump out excess water was recorded. Salt concentration Very high High Medium Low Very low Rate of contractile vacuole contractions / minute 2 8 15 22 30 Refer to the illustration above. a. How can you explain the observed relationship between salt concentration and rate of contractile vacuole contraction? Write your answer in the space below. b. If something happened to a paramecium that caused its contractile vacuole to stop contracting, what would you expect to happen? Would this result occur more quickly if the paramecium was in water with a high salt concentration or in water with a low salt concentration? Why? Write your answer in the space below. 9 Name: ________________________ ID: A 103. A biologist conducts an experiment designed to determine whether a particular type of molecule is transported into cells by simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport. He collects the following information: 1) The molecule is very small. 2) The molecule is polar. 3) The molecule can accumulate inside cells even when its concentration inside the cell initially is higher than it is outside the cell. 4) Cells use up more energy when the molecule is present in the environment around the cells than when it is not present. The biologist concludes that the molecule moves across cell membranes by facilitated diffusion. Do you agree with his conclusion? Why or why not? Write your answer in the space below. 104. The diagram above shows two human blood vessels, 1 and 2, connected by a capillary bed, 3. Blood pressure is higher in vessel 2 than in vessel 1. The arrows indicate the direction of diffusion of O2 and CO2. Write your answers to the following in the spaces below. a. What type of blood vessel is vessel 1? b. What type of blood vessel is vessel 2? c. Does this diagram show part of the systemic circuit or part of the pulmonary circuit of the human circulatory system? d. In which location, X or Y, will the concentration of O2 in the blood be higher? e. Name one other substance typically found in blood that would move out of a capillary bed into body tissues along with the O2 shown in the diagram. f. Name one other substance typically found in blood that would move into a capillary bed from body tissues along with the CO2 shown in the diagram. 10 Name: ________________________ ID: A 105. Every living cell in the human body must have an energy supply. Cells take up glucose or a related chemical and break it down inside the mitochondria to get ATP. ATP is the form of energy that cells use for their various activities. The breakdown of glucose occurs in the process of aerobic respiration. A summary of this process is shown in the following equation (note that this is not a balanced equation): C6H12O6 + O2 « CO2 + H2O + ATP O2, which is a gas, is consumed in this process, and CO2, also a gas, is produced. Trace the pathway of a molecule of O2 from the location where it enters the human body, across any cell membranes it must pass, until it reaches a muscle cell in the right leg. Then, trace the pathway of a molecule of CO2 from inside that muscle cell, where it is produced in aerobic respiration, until it leaves the body. Write your answer in the space below or on a separate sheet of paper. Essay 106. Briefly discuss some of the major themes in biology that we will examine this year. Write your answer in the space below. 107. Name five characteristics that are considered distinct properties of all living things. Write your answer in the space below. 108. Toads that live in hot, dry regions bury themselves in the soil during the day. How might this be important to the toad? Write your answer in the space below. 109. The results of an experiment do not support the hypothesis that the experiment was designed to test. Was the experiment a waste of time? Explain. Write your answer in the space below. 110. Why is it important to study biology even if you are not planning a career in biology? Write your answer in the space below. 111. Plant growers often use sprinkler irrigation to protect crops they are growing from frost damage. The water that lands on the leaves turns to ice. How does this protect the plants from frost damage? Write your answer in the space below. 112. Define enzyme, and describe how an enzyme can function in speeding up a chemical reaction within a cell. Write your answer in the space below. 113. How does water’s polar nature affect its ability to dissolve different substances? Write your answer in the space below. 114. Explain the relationship between hydrogen bonding and the observation that a full sealed bottle of water breaks when it freezes. Write your answer in the space below. 115. How are the organs of a multicellular organism like the organelles of a single cell? Write your answer in the space below. 11 Name: ________________________ ID: A 116. Why does the addition of a solute with polar molecules to one side of a membrane result in the diffusion of water? Write your answer in the space below. 117. Why is it dangerous for humans to drink ocean water? Write your answer in the space below. 118. Distinguish facilitated diffusion from active transport. Write your answer in the space below. 119. Refer to the illustration above. Identify and explain the processes taking place in Figure X and Figure Y. Write your answer in the space below. 120. Do arteries carry oxygenated blood or deoxygenated blood? Explain. Write your answer in the space below. 121. Describe the antibody-antigen interactions that take place when an Rh– person who has blood type B receives blood from an Rh+ person who has blood type AB. Write your answer in the space below. 122. Describe how oxygen is transported in the blood. Write your answer in the space below. 123. Carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolves poorly in plasma. Although it can bind to hemoglobin, the ability of red blood cells to transport it on hemoglobin is limited. Thus, 70 percent of the CO2 that leaves the body is carried out in a third way. Explain what happens. Write your answer in the space below. 124. How is air moved in and out of the lungs? Write your answer in the space below. 125. Explain why you cannot hold your breath indefinitely. Write your answer in the space below. 126. How is a signal transferred from one neuron to another neuron? Write your answer in the space below. 127. Briefly describe how sensory receptors help you maintain posture and keep your balance. Write your answer in the space below. 128. What are the effects of nicotine on the body? Write your answer in the space below. 12 Name: ________________________ ID: A 129. Explain why addiction to mood-altering drugs is said to have a physiological basis. Write your answer in the space below. 130. Describe the action of cocaine at the synapse and the effects of long-term cocaine use on receptors. Write your answer in the space below. 13 ID: A Biology I Semester One Quarter One Exam Study Guide Answer Section COMPLETION 1. ANS: Ecology PTS: 1 2. ANS: homeostasis DIF: 1 OBJ: 1-2.1 PTS: 1 3. ANS: hypothesis DIF: 1 OBJ: 1-1.5 PTS: 1 4. ANS: predicting prediction DIF: 1 OBJ: 1-3.2 PTS: 1 5. ANS: theory DIF: 1 OBJ: 1-3.1 PTS: 1 6. ANS: controlled DIF: 1 OBJ: 1-3.5 PTS: 1 7. ANS: meter DIF: 1 OBJ: 1-3.3 PTS: 1 8. ANS: scanning, transmission PTS: 1 DIF: 1 9. ANS: reactants, products OBJ: 1-4.2 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 10. ANS: activation energy OBJ: 2-2.2 PTS: 1 11. ANS: enzyme DIF: 1 OBJ: 2-2.3 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 12. ANS: oxidation, reduction OBJ: 2-2.3 PTS: 1 13. ANS: solute DIF: 1 OBJ: 2-2.4 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 2-3.4 1 ID: A 14. ANS: Water PTS: 1 DIF: 1 15. ANS: Hydroxide, hydrogen Hydrogen, hydroxide OBJ: 2-3.4 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 16. ANS: hydronium, hydroxide OBJ: 2-3.2 PTS: 1 17. ANS: 1,000 1000 a thousand one thousand DIF: 1 OBJ: 2-3.5 PTS: 1 18. ANS: pH DIF: 2 OBJ: 2-3.5 PTS: 1 19. ANS: polarity DIF: 1 OBJ: 2-3.5 PTS: 1 20. ANS: hydrogen DIF: 1 OBJ: 2-3.2 PTS: 1 21. ANS: four 4 DIF: 2 OBJ: 2-3.3 PTS: 1 22. ANS: double DIF: 1 OBJ: 3-1.2 PTS: 1 23. ANS: water DIF: 3 OBJ: 3-1.2 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 24. ANS: condensation, hydrolysis OBJ: 3-1.4 PTS: 1 25. ANS: nonpolar DIF: 1 OBJ: 3-1.4 PTS: 1 26. ANS: active site DIF: 1 OBJ: 3-2.4 DIF: 1 OBJ: 3-2.3 PTS: 1 2 ID: A 27. ANS: three 3 PTS: 1 28. ANS: three 3 DIF: 1 OBJ: 3-1.2 PTS: 1 29. ANS: cell theory DIF: 1 OBJ: 3-1.5 PTS: 1 30. ANS: volume DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-1.3 PTS: 1 31. ANS: organelles DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-2.2 PTS: 1 32. ANS: eukaryotic DIF: 2 OBJ: 4-4.5 PTS: 1 33. ANS: selectively DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-2.3 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 34. ANS: Phospholipid OBJ: 4-3.1 PTS: 1 35. ANS: organelles DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-3.1 PTS: 1 36. ANS: ribosomes DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-3.3 PTS: 1 37. ANS: cytoskeleton DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-3.3 PTS: 1 38. ANS: cytosol DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-3.5 PTS: 1 39. ANS: chloroplasts DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-2.3 PTS: 1 40. ANS: cell wall DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-4.4 DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-4.1 PTS: 1 3 ID: A 41. ANS: phospholipid bilayer PTS: 1 DIF: 2 42. ANS: plant, animal OBJ: 4-3.1 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 43. ANS: secondary cell wall OBJ: 4-1.2 PTS: 1 44. ANS: ATP DIF: 1 OBJ: 4-4.2 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 45. ANS: Active transport OBJ: 5-2.1 PTS: 1 DIF: 2 46. ANS: sodium-potassium pump OBJ: 5-2.1 PTS: 1 47. ANS: exocytosis DIF: 1 OBJ: 5-2.2 PTS: 1 48. ANS: X DIF: 2 OBJ: 5-2.3 PTS: 1 DIF: 2 49. ANS: phagocytosis OBJ: 5-2.3 PTS: 1 50. ANS: circulatory DIF: 1 OBJ: 5-2.3 PTS: 1 51. ANS: mitral bicuspid DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-1.5 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 52. ANS: atrioventricular node OBJ: 46-1.1 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 53. ANS: tricuspid valve OBJ: 46-1.2 PTS: 1 54. ANS: Capillaries DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-1.1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-1.3 PTS: 1 4 ID: A 55. ANS: ventricles PTS: 1 DIF: 1 56. ANS: hypertension OBJ: 46-1.3 PTS: 1 57. ANS: systemic DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-1.3 PTS: 1 58. ANS: lymphatic DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-1.4 PTS: 1 59. ANS: platelets DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-1.5 PTS: 1 60. ANS: oxygen DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-2.1 PTS: 1 61. ANS: erythrocytes DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-2.1 PTS: 1 62. ANS: white DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-2.2 PTS: 1 63. ANS: erythrocytes red blood cells DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-2.2 PTS: 1 64. ANS: trachea DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-2.4 PTS: 1 65. ANS: epiglottis DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-3.2 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 66. ANS: carbon dioxide OBJ: 46-3.2 PTS: 1 67. ANS: inspiration DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-3.3 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 68. ANS: carbon dioxide OBJ: 46-3.4 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-3.5 5 ID: A 69. ANS: External, internal PTS: 1 70. ANS: brain stem DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-3.1 PTS: 1 71. ANS: limbic DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-2.2 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 72. ANS: muscles, central nervous OBJ: 49-2.2 PTS: 1 73. ANS: peripheral DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-2.3 PTS: 1 74. ANS: autonomic DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-2.3 PTS: 1 75. ANS: reflex DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-2.4 PTS: 1 76. ANS: neuron DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-2.4 PTS: 1 77. ANS: dendrites DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-1.1 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 78. ANS: myelin sheath OBJ: 49-1.1 PTS: 1 79. ANS: positive DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-1.1 PTS: 1 80. ANS: potassium DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-1.3 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 81. ANS: neurotransmitters OBJ: 49-1.2 PTS: 1 82. ANS: synapse DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-1.4 PTS: 1 83. ANS: pain DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-1.4 DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.1 PTS: 1 6 ID: A 84. ANS: receptors PTS: 1 85. ANS: retina DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.1 PTS: 1 86. ANS: rods, cones DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.3 PTS: 1 87. ANS: iris DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.3 PTS: 1 88. ANS: cornea DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.3 PTS: 1 89. ANS: cochlea DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.3 PTS: 1 90. ANS: hair DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.2 PTS: 1 91. ANS: taste bud DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.2 PTS: 1 92. ANS: hands DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.4 PTS: 1 93. ANS: Tars DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.5 PTS: 1 94. ANS: depressants DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-4.4 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 95. ANS: Blood alcohol concentration OBJ: 49-4.3 PTS: 1 96. ANS: addiction DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-4.4 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 97. ANS: psychoactive OBJ: 49-4.1 PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-4.3 7 ID: A PROBLEM 98. ANS: a. The independent variable was the number of cups of coffee a subject drank each day; the dependent variables were the indicators of human health measured. b. This was not a controlled experiment because there was no group of subjects who drank zero cups of coffee a day. c. Students should disagree with the scientists’ conclusion because this was not a controlled experiment (there could be something harmful in coffee that would be effective when only one cup of coffee was consumed each day). PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 1-3.4 99. ANS: a. A and B b. C and D c. An input of energy, called the activation energy, is required in order to get the reaction going. d. The products contain less energy than the reactants and energy is given off in the reaction. e. The graph should be the same except that the energy level at point 2 should be higher. PTS: 1 DIF: 3 100. ANS: Test tube #1 contains a carbohydrate. Test tube #2 contains a protein. Test tube #3 contains a lipid. Test tube #4 contains a nucleic acid. OBJ: 2-2.2 PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 3-2.2 101. ANS: The drawing should include the following pairs: main office—nucleus assembly line—endoplasmic reticulum electricity generator—mitochondrion packaging center—Golgi apparatus factory doors—plasma membrane PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 4-3.3 8 ID: A 102. ANS: a. The contractile vacuole maintains water balance by pumping water outside of the cell. When the salt concentration outside the cell is very high, water will move from inside to outside the cell—little or no pumping action is required. When the salt concentration outside the cell is lower than inside, the tendency is for water to move from outside to inside, necessitating increased pumping action by the vacuole to move excess water out of the cell. b. If the contractile vacuole were to stop contracting, the organism would burst open because water would collect in excess inside of it and the cell membrane would not be strong enough to resist rupturing. This result would be expected to occur more quickly if the organism were placed in water with a low salt concentration than it would if the organism were placed in water with a high salt concentration. This is because water accumulates inside the paramecium more rapidly when it is placed in a low salt environment. PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 5-1.2 103. ANS: Disagree. The information that cells can accumulate the molecule against a concentration gradient is compelling evidence that active transport is the mechanism of transport. This is the only mechanism among those named that allows movement against a concentration gradient. Active transport also requires energy consumption, which was also found to be a property of transport of this molecule. PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 5-2.1 104. ANS: a. vein b. artery c. systemic circuit d. Y e. possible answers: food molecule, water, vitamin, ion, hormone, or white blood cell f. possible answers: wastes or ammonia PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 46-1.3 9 ID: A 105. ANS: The O2 molecule would enter the body through one of the nostrils, pass through the pharynx, the trachea, and one of the two bronchi, and then enter a bronchiole in the lung. It would then move into an alveolus and then move across a cell membrane of the alveolus and enter the blood. Once in the blood, the O2 would move across the cell membrane into a red blood cell. It would then be transported through the pulmonary vein, which takes blood from the lungs to the heart. The O2 in the blood would enter the heart in the left atrium, move to the left ventricle, and then be forced out of the heart into the aorta. The O2 in the blood would then be transported into smaller arteries, still smaller arterioles, and finally a capillary bed in the muscle in the right leg. The O2 would then move out of the red blood cell across its cell membrane, and would enter a muscle cell across that cell’s membrane. A CO2 molecule produced by aerobic respiration in this muscle cell would leave the cell by moving across the cell membrane and would enter the blood. In the blood, it might move across the cell membrane of a red blood cell and remain in its cytoplasm. (Alternately, the CO2 might dissolve in the plasma or combine with water to form bicarbonate ions.) The CO2 in blood would then be transported into venules, and then into veins, until it returned to the vena cava. From the vena cava, it would reenter the heart. The CO2 in blood would enter the right atrium of the heart, move to the right ventricle, and then be forced out of the heart into the pulmonary artery. From there, it would be transported to one of the lungs. In a lung, the CO2 would move out of the red blood cell by moving across its cell membrane. It would then move across a cell membrane of an alveolus. From the alveolus, the CO2 would pass through a bronchiole, a bronchus, the trachea, and the pharynx, and would then leave the body through one of the nostrils. PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 46-3.3 ESSAY 106. ANS: Major themes are the diversity and unity of life, the interdependence of organisms, and the evolution of life. Diversity and unity refers to the many different kinds of organisms that share similar characteristics even though the organisms themselves are so different. Interdependence refers to ecology and the interaction of organisms with each other and the environment. Evolution refers to changes in species over time. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 1-2.1 107. ANS: Possible answers include the following: All living things are composed of one or more cells and have a hierarchy of organization. All living things respond to stimuli. All living things maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis). All living things carry out metabolic reactions that involve the use of energy. All living things grow. All living things reproduce and pass on genetic information to offspring. Populations of living things change over time. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 1-1.3 108. ANS: Toads must maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis) in order to function properly. Burying themselves in the soil is an adaptation that keeps their body temperature from rising too high and keeps their bodies from drying out. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 1-2.4 10 ID: A 109. ANS: No, the experiment was not a waste of time. A scientist works by systematically showing that certain hypotheses are not valid when they are not consistent with the results of experiments. The results of experiments are used to evaluate alternative hypotheses. An experiment can be successful if it shows that one or more of the alternative hypotheses are inconsistent with observations. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 1-3.2 110. ANS: By studying biology, you can make informed decisions that impact both you and the society in which you live. Decisions about your health, your food supply, and your environment are only some of these issues. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 1-1.2 111. ANS: Water, like any other form of matter, requires an input of thermal energy to change from a solid to a liquid state. It therefore must also give off thermal energy when it changes from a liquid to a solid state. When liquid water turns to ice on plant leaves, it gives off thermal energy that warms the leaves. PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 2-2.1 112. ANS: Enzymes are biological catalysts. They are protein or RNA molecules that lower the activation energy that would otherwise be required for a reaction to occur. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 2-2.3 113. ANS: A weaker attraction exists between polar and nonpolar molecules than between two polar molecules, so a water molecule cannot pull a nonpolar molecule into solution. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 2-3.2 114. ANS: When water freezes, multiple hydrogen bonds form between the molecules. This hydrogen bonding causes water molecules to form a rigid array with large amounts of open space between the molecules relative to liquid water. Because water molecules move farther apart when they freeze, the ice took up more volume than the liquid water and the bottle broke. PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 2-3.3 115. ANS: The organs of a multicellular organism each carry out specialized tasks that enable the whole organism to survive. Similarly, organelles of a single cell each carry out specialized tasks that enable the whole cell to survive. PTS: 1 DIF: 3 OBJ: 4-2.5 116. ANS: The addition of solutes to one side of a membrane reduces the number of water molecules that can move freely on that side. The water molecules become bound to the polar molecules in the solute. Water then moves by osmosis from the side where water molecule concentration is greatest to the side where concentration is least. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 5-1.2 11 ID: A 117. ANS: The concentration of salt in ocean water is higher than the concentration of salt in the fluids that surround the cells in the human body. Drinking ocean water increases the concentration of salt in the body’s fluids. This causes water to leave the cells by osmosis, and without the proper amount of water the cells will be harmed or will die. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 5-1.2 118. ANS: Protein channels that assist the diffusion of substances through the cell membrane do so by facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion works in two directions. As long as a molecule or ion fits into the channel, it is free to pass through in either direction. Each kind of molecule or ion diffuses toward the side where it is least concentrated, eventually balancing the concentrations. Active transport, on the other hand, allows ions to move through the cell membrane in one direction only, like a turnstile at a subway station. Active transport enables a cell to stockpile certain substances in far greater concentrations than they occur outside the cell. Almost all active transport in cells is carried out by the sodium-potassium pump. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 5-2.1 119. ANS: Endocytosis is the process taking place in Figure X. Endocytosis is the process by which cells engulf substances that are too large to enter the cell by passing through the cell membrane. Exocytosis is the process taking place in Figure Y. Exocytosis is the process by which cellular wastes are discharged from sacs at the cell’s surface. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 5-2.3 120. ANS: An artery is a blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart. Most arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body, but some arteries—the pulmonary arteries, which carry blood from the heart to the lungs—carry deoxygenated blood that has been returned to the heart from the rest of the body. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 46-1.2 121. ANS: An Rh– person who has blood type B has only blood antigen B. A person having this antigen would produce antibodies to antigens A and Rh. An Rh+ person who has blood type AB has blood antigens Rh, A, and B. When these antigens enter the recipient’s blood, antibodies to the A and Rh will produce agglutination. The B antigen of the donor’s blood will not cause agglutination because the recipient does not produce antibodies to this antigen. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 46-2.4 122. ANS: Red blood cells are filled with hemoglobin, which is an iron-containing protein that gives blood its red color. Oxygen easily binds to the hemoglobin, making red blood cells efficient oxygen carriers that circulate throughout the body as they flow with the plasma. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-3.3 12 ID: A 123. ANS: The remaining 70 percent combines with water in the blood to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) inside red blood cells. Because carbonic acid is unstable, hydrogen (H+) and bicarbonate (HCO3–) ions quickly form, and the CO2 is transported through the blood in the form of bicarbonate ions. When the blood reaches the lungs, chemical reactions that reverse the process occur, releasing carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli in the lungs. It is then exhaled with water vapor. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 46-3.3 124. ANS: When the diaphragm and rib muscles contract, the diaphragm moves downward and the rib cage moves up and outward. This expands the chest cavity, lowering the air pressure in the lungs and causing air to flow in. When the diaphragm and the rib muscles relax, the diaphragm moves upward and the rib cage moves down and inward. This reduces the size of the chest cavity, increasing the pressure of the air in the lungs and causing air to flow out. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 46-3.4 125. ANS: The autonomic nervous system, which carries messages to muscles and glands that usually work without our noticing, enables the nervous system to govern homeostasis within the body. We have voluntary control over some functions, such as breathing, that are generally regulated by the autonomic nervous system. Any voluntary control of the autonomic nervous system that endangers life disturbs the homeostasis of the brain tissue, causing unconsciousness. Once the body is unconscious and no longer has voluntary control, the autonomic nervous system takes over and restores normal functioning—in this case, breathing. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-2.4 126. ANS: When a nerve impulse gets to the end of an axon, its message must cross the synapse. Messages are carried across synapses by chemical transmitters called neurotransmitters, which are contained in the axons in vesicles. When a nerve impulse reaches an axon terminal, the vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synapses. The neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapses and bind to receptors in the membrane of the postsynaptic cell. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-1.4 127. ANS: Receptors in the inner ear signal the direction of gravity and the speed and direction of movements to the brain, enabling us to maintain a vertical posture. Pressure receptors in our joints, tendons, and muscles detect movement and degree of stretch. These receptors help control how we move and how we maintain our balance. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-3.1 128. ANS: Nicotine causes an increase in heart rate and blood pressure and a decrease in blood circulation to the hands and feet. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-4.4 13 ID: A 129. ANS: Some drugs cause excessive amounts of neurotransmitter to be present in synapses for long periods of time. This results in a decreased number of receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and a less sensitive nerve pathway. The only way a person who is addicted can maintain normal functioning of the nerve pathway is to continue taking the drug. PTS: 1 DIF: 2 OBJ: 49-4.1 130. ANS: Cocaine prevents the reuptake of neurotransmitters from the synapse. The trapped neurotransmitters repeatedly stimulate neurons. Neurons adjust to the presence of cocaine by decreasing their number of neurotransmitter receptors. This causes neurons to become less and less sensitive, requiring more and more cocaine for stimulation. PTS: 1 DIF: 1 OBJ: 49-4.2 14