* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1-15) are True or False (15pts)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
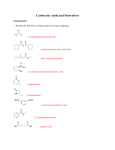
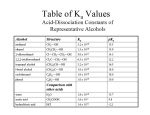
Sp 2011 Organic II Exam #3 Ch 20-21 (100 points) NAME: If you do not wish to have your graded exam script placed outside my office, then please check this box 1-15) are True or False (15pts) 1) Carboxylic acids are proton donors. 2) Carboxylic acids are Lewis acids. 3) Esters undergo SN1 reactions at the C=O bond. 4) Primary amides have an sp hybridized Nitrogen atom. 5) Nitriles have 2 σ and 1 π covalent bonds. 6) Ethanenitrile is more basic than pyridine. 7) Cyclic Esters are called Tone-locs. 8) Carboxylic acids can be reduced to primary alcohols by NH3. 9) The reaction where one ester is transformed into another ester is called cis-esterification. 10) Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions proceed through a linear intermediate. 11) The nucleophilic acyl substitution mechanism is an example of a concerted mechanism. 12) Nitriles can be hydrolyzed to amides. 13) The Carbon/Nitrogen bond lengths decrease from amines to amides to nitriles. 14) Grignard reagents are “organometallic” compounds. 15) Compounds with an amino group, and a carboxylic acid group are known as amino acids. Sp11org2e3.doc Page 1 16) Name the general class of organic compounds that each of these molecules belong to. (15pts) O O R C NR2 O O R C O C R O O R C O-R O R C Br NH R C N O R N R C R O R C NH2 O R C OH 17) Put a cross through the molecule that contains the weakest π bond. (2pts) Sp11org2e3.doc Page 2 18) Circle the stronger acid in the following pairs. (12pts) (a) (b) (c) H3C CO2H NC CO2H CO2H CBrH2CH2 CO2H CH3CBrH CO2H NH2 (d) F (e) F3C CO2H OH F Cl CO2H O (f) Cl CO2H O O OH OH 19) (3pts) Draw a Lewis structure for the most acidic molecule with the molecular formula C4H6O2Br2 Sp11org2e3.doc Page 3 20) Name the following compounds in IUPAC acceptable terms. (18pts) Br F NH2 O O O O O O OH H2N NH O O **BONUS 2 POINTS** for providing the trivial Biological name for the last compound which is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. 21) Circle the most reactive molecule with respect to nucleophilic acyl substitution in the following threesomes. (9pts) O (a) (b) O O H3C C Cl H3C C H O H3C C OH H3C C CH3 O O H3C C O C CH3 O H3C C OCH3 O O (c) H3C O C CH 3 O O Sp11org2e3.doc Page 4 22) Benzoic acid can be made from a wide variety of benzene derivatives. Fill in the missing starting materials. (12pts) - OH/H2O 1) Mg 2) CO2 3) H3O+ CO2H KMnO4, H3O+ Heat Ag2O 23) (2+2 pts) Provide two reasons which explain why amides are less reactive than esters in nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions. Sp11org2e3.doc Page 5 24) Draw in all the curly arrows for the following mechanism of an acid catalyzed esterification. (10pts) O H-X R C O-H + H O R C O-H H O R C O-H + H O R C O-H + :X R'-O-H H + H O R C O-H O R' H-X H O R C O-H O R' H O R C O-H O R' + H :X + R C O-H O R' + R C O-H O R' R C O-H O R' + :X O H-X Sp11org2e3.doc R C O-R' Page 6 *Bonus question* (up to 2pts) Explain why the amide below exists as two observable stereoisomers. O H C NHCH3 Extra bonus Question (2pts) – describe experimentally how you can “observe” these different stereoisomers. Sp11org2e3.doc Page 7