* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download blue www.ck12.org plain ckfloat!hbptlop[chapter
Survey
Document related concepts
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
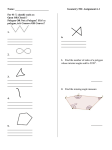
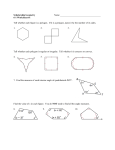
blue www.ck12.org plain ckfloat!hbptlop[chapter] ckfloatCKfloat www.ck12.org 2 Polygons CK-12 Kaitlyn Spong Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based collaborative model termed the FlexBook®, CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning, powered through the FlexBook Platform®. Copyright © 2014 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/terms. Printed: February 25, 2014 AUTHORS CK-12 Kaitlyn Spong www.ck12.org C ONCEPT Concept 1. Polygons 1 Polygons Here you will review the names and basic properties of polygons. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is360◦ . How is this possible? Watch This MEDIA Click image to the left for more content. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dO7zilXORMg James Sousa: Introduction to Polygons MEDIA Click image to the left for more content. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NQp31wZ69fQ James Sousa: Classifying Polygons Guidance A polygon is a flat shape defined by straight lines. A polygon is usually classified by its number of sides, as shown in the table below. TABLE 1.1: Number of Sides 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Name of Polygon Triangle Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon Heptagon Octagon Nonagon (or enneagon) Decagon For a polygon with more than 10 sides, most people prefer to name it by its number of sides and the suffix “gon”. For example, a 40 sided polygon would be a “40-gon”. A diagonal is a line segment that connects any two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon. A polygon is convex if all 1 www.ck12.org diagonals remain inside the polygon. Most polygons that you study in geometry will be convex. If a polygon is not convex then it is concave (or non-convex). The blue pentagon on the left is convex, while the pink quadrilateral on the right is concave. A polygon is equilateral if all of its sides are the same length. A polygon is equiangular if all of its angles are the same measure. A polygon is regular if it is both equilateral and equiangular. The sum of the measures of the three angles in a triangle is 180◦ . You can use this fact to find the sum of the measures of the angles in any polygon. The pentagon above has been divided into three triangles, and its interior angles have been marked. The sum of the measures of the angles of each triangle is 180◦ . Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of the pentagon is 180◦ · 3 = 540◦ . In general, the sum of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is 180(n − 2)◦ . If the polygon is regular (and thus equiangular), you can figure out the measure of each interior angle. Example A Name the regular polygon below and find the sum of its interior angles. 2 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Polygons Solution: This regular polygon has 7 sides, and is therefore a heptagon. To find the sum of the interior angles, imagine dividing the polygon into triangles. There are 5 triangles, each with 180◦ . Therefore, the sum of the interior angles is 180◦ · 5 = 900◦ . Example B Find m6 G in the polygon from Example A. Solution: Because this is a regular polygon, it is equiangular. This means that each of the seven interior angles has the same measure. The sum of the interior angles was 900◦ . This means that each of the seven interior angles is 900◦ ◦ 7 ≈ 128.6 . Example C An exterior angle is the angle between one side of a polygon and the extension of an adjacent side. In the polygon below, an exterior angle has been marked at vertex G. How are exterior angles related to interior angles? What is the measure of the exterior angle at G? 3 www.ck12.org Solution: The exterior angle and interior angle at the same vertex will always be supplementary because together they form a straight angle. In this case, the interior angle at point G was approximately 128.6◦ . Therefore, the exterior angle is 180◦ − 128.6◦ = 51.4◦ . Concept Problem Revisited There are many ways to think about the sum of the exterior angles of a polygon. One way is to first consider that the sum of all the straight angles through the vertices is 180n◦ (where n is the number of sides of the polygon). These angles are marked in green in the sample polygon below. If you only want the sum of the exterior angles, you must subtract the sum of the interior angles. The sum of the interior angles is 180(n − 2)◦ = 180n◦ − 360◦ . Therefore, the sum of the exterior angles is: 180n◦ − (180n◦ − 360◦ ) = 180n◦ − 180n◦ + 360◦ = 360◦ Vocabulary A polygon is a flat shape defined by straight lines. A polygon is usually classified by its number of sides. 4 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Polygons A diagonal is a segment that connects any two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon. A polygon is convex if all diagonals remain inside the polygon. If a polygon is not convex then it is concave (or non-convex). A polygon is equilateral if all of its sides are the same length. A polygon is equiangular if all of its angles are the same measure. A polygon is regular if it is both equilateral and equiangular. Angles inside a polygon at the vertices are called interior angles. An angle between one side of a polygon and the extension of an adjacent side is called an exterior angle. Guided Practice 1. Find the sum of the interior angles of a nonagon. 2. Find the measure of one interior angle of a regular nonagon. 3. Find the measure of one exterior angle of a regular decagon. Answers: 1. A nonagon can be split into 7 triangles. The sum of the interior angles is 180◦ · 7 = 1260◦ . ◦ ◦ 2. The sum of the interior angles is 1260◦ . Therefore, each interior angle is 1260 9 = 140 . ◦ 360 ◦ 3. 10 = 36 Practice 1. What is the measure of an exterior angle of a regular 45-gon? 2. What is the sum of the interior angles of a 35-gon? 3. Draw an example of a convex polygon and a concave polygon. 4. What’s the name of a polygon with 8 sides? 5. What’s the name of a polygon with 10 sides? 6. What’s the name of a polygon with 4 sides? 7. How could you use the dissection shown in the picture below to show why the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon is 720◦ ? 5 www.ck12.org 8. How could you use the dissection shown in the picture below to show why the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon is 720◦ ? 9. A regular polygon has an interior angle of 150◦ . How many sides does the polygon have? 10. How could you use exterior angles to help you find the answer to #9? 11. What is the sum of the exterior angles of an 11-gon? 12. What is the sum of the interior angles of an 11-gon? 13. Solve for x: 14. Solve for x: 6 www.ck12.org Concept 1. Polygons 15. Solve for x: References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. . . . . . . . . . . CC BY-NC-SA CC BY-NC-SA CC BY-NC-SA CC BY-NC-SA CC BY-NC-SA 7