* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glossary - Department of Defence
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
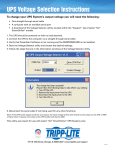
Uninterruptible power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Manual of Infrastructure Engineering Electrical GLOSSARY AC Alternating Current AEMC Australian Energy Market Commission AEMO Australian Energy Market Operator AER Australian Energy Regulator Availability: The ability of an item to perform its intended function at any instant of time. It is usually given as the ratio uptime/(uptime + downtime). Battery: A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy by means of an electrochemical reaction. Usually defined as consisting of two or more cells, but commonly used to refer to one cell. BCA Building Code of Australia. BMS: Building Management System. Building automation system used to control and monitor building services. Brownout: Conditions under which power is available but not sufficient to fully meet the needs (voltage, current) of the load; partial power failure. Capacity (battery): The number of ampere-hours (Ah) a fully charged cell or battery can deliver under specified conditions of discharge. CB Circuit Breaker. CEPS Central Emergency Power Station. A centralised standby power station that supplies power to the Base in the event of power failure. CEP Central Energy Plant. A centralised power station used to offset power purchases from the grid. CFI Capital Facilites & Infrastructure Branch CMS Comprehensive Maintenance Services Controller The device used to automatically process data and control equipment based upon programmable algorithms as either firmware or software (e.g. PLC). CPS Central Power Station. A centralised prime power station that supplies power to the Base. Crest Factor (Fc): Ratio between the peak value to the root mean square (RMS) current value. DALI: Digital Addressable Lighting Interface: a protocol for digital communications between lighting devices. This allows for individual control of each light within a building where each light has its own address. DC Direct Current DEEP Directorate of Estate Engineering Policy Defence Department of Defence MIEE 2011, Amend1 – 1 Feb 2016 GLOSSARY 1 of 7 Manual of Infrastructure Engineering Electrical GLOSSARY DEMS-FM Defence Estate Management System - Facilities Management DEOP-103 Defence Explosive Ordnance Safety Manual DEOS Directorate of Explosive Ordnance Services Design The intent of the works as performed by the Designer and Installer Designer The party engaged to perform a design function for Defence. DESN: Defence Engineering Services Network. A site wide system that usually monitors the electrical power system parameters and other engineering services elements. DEMTR Directorate of Engineering Maintenance & Technical Regulation Distortion (individual): Ratio between the RMS value of an nth order harmonic and the RMS value of the fundamental. Distribution Substation A substation used to directly supply loads (typically at 400/230V) consisting of facilities or processes. The distribution substation typically consists of the following major components: RMU Transformer; and LV Switchboard however either or both of the RMU or LV Switchboard can be located remote to the substation. DNSP Distribution Network Service Provider: The authority providing access to the electricity grid that own, control and/or operate the transmission or distribution systems. DOS Directorate of Ordnance Safety DSRG Defence Support & Reform Group DSI: Digital Serial Interface: A protocol enabling dimming of an electronic ballast EE Environment & Engineering Branch of DSRG – Infrastructure DivisionDSRG-ID ELV Extra Low Voltage. ENA Australian Energy Network Association EO Explosive Ordnance Failure Rate: The number of failures of an item per unit measure of life, where life is expressed cycles, time, events, etc., as applicable for the item. FDB/FRB Functional Design Brief/Functional Requirements Brief FQCC Fuel Quality Control Centre GCB Generator Circuit Breaker MIEE 2011, Amend1 – 1 Feb 2016 GLOSSARY 2 of 7 Manual of Infrastructure Engineering Electrical GLOSSARY GCS Generator Control System. The collective name for the overall system that controls the operation of the CEPS. It generally consists of a network of CONTROLLERs and other control devices. GCS Station The master CONTROLLER in the GCS Controller network. It performs overall power station coordination functions. Harmonic Analysis. Harmonic Analysis is the determination of the harmonic content of the load or supply. Harmonic Distortion (total) THD: Ratio between the RMS value of all harmonics of a nonsinusoidal alternating periodic value and that of the fundamental. Harmonics: Distortions of the sine wave that characterises normal AC current. Harmonics are transmitted into an AC line by non-linear loads (i.e., loads that do not draw power in regular sine waves), such as computers, copiers, FAX machines, and variable-speed motors. Harmonics can cause communication errors and equipment damage. In three-phase systems, they can cause transformers and neutral conductors to overheat creating a possible fire hazard. HAZAN Hazard Analysis HAZOP Hazard Operability HMI Human-Machine Interface. HV High Voltage: Above 1000V AC or 1500V DC. HV Feeders HV cabling from the NSP to the establishment ISS. HV Rings HV cabling on the establishment on which substations and switching stations are connected, but not the Feeders or Interconnectors. HV Switchroom Normally an indoor arrangement provided for HV circuit breakers and HV switchgear panels ID Infrastructure Division Indoor Substations Substations where the various major components are housed within a building, either as a freestanding structure or part of a larger structure. Interconnector A direct intertie HV power cable connection between two (2) PSSs or PSS/ISS/CEPS, that facilitates power flow used to transfer power between them. ISS Intake Switching Station or Intake Substation as appropriate. Kiosk Substations Stand alone, freestanding substations, where the various major components are housed within a metal or composite enclosure. This form of construction is limited to distribution substations. LEG: Local Emergency Generator: An independent standby generator at a facility that supplies power to that facility in the event of power failure. LV Low Voltage: Less than High Voltage but higher than 50V AC or 120V DC. MIEE 2011, Amend1 – 1 Feb 2016 GLOSSARY 3 of 7 Manual of Infrastructure Engineering Electrical GLOSSARY Maintainability: The ability to retain and restore an item to its functional state when maintenance is performed under stated conditions and using prescribed procedures and resources. Measures include probability to repair within a given time, repair rate, and mean time to repair. MEPS: Minimum Energy Performance Standard MFPE Manual of Fire Protection Engineering. Motor-Generator (M-G): Power systems that use a rotating AC generator to generate the needed output power. A motor-generator that is powered by a battery or a diesel or gas-powered engine when utility power is lost, constitutes a rotary or hybrid UPS. MTBF: Mean Time Between Failure. A measure of reliability. As applied to repairable items, the mean value of the length of time between each item’s consecutive failures, calculated as the ratio of OK cumulative time to the total number of failures during the stated period. MTBM: Mean Time Between Maintenance: The interval between scheduled major maintenance activities (i.e. major overhaul), not routine maintenance (i.e. routine servicing). MTTF: Mean Time To Failure. As applied to non-repairable items (i.e. for which a MTBF is not possible), the ratio of the OK cumulative time to the total number of items failed during the stated period. MTTR: Mean Time To Repair. A measure of maintainability. Mathematical calculation (or statistical average if available) of the time required to repair a device. MaxTTR: Maximum Time to Repair. Required maximum time to repair specified as a supportability requirement. MaxTTR is the maximum corrective maintenance downtime within which corrective maintenance actions can be accomplished. NBPS: No Break Power Supply. NEC Neutral earthing contactor NEM National Electricity Market. NER National Electricity Rules NSP Network Service Provider The authority providing access to the electricity grid and the owner/controller of the local sub-transmission and distribution systems. OLA Ordinance Loading Apron or Area On-Line UPS: An UPS that continuously powers the load from the inverter under normal operation. OPSMAN 3 Safety Principles for the Handling of Explosive Ordnance OSC(E)81/1 Operational Safety Committee (Explosives) MIEE 2011, Amend1 – 1 Feb 2016 GLOSSARY 4 of 7 Manual of Infrastructure Engineering Electrical GLOSSARY Outdoor SS Substations where the various major components are outdoors without further enclosure. Output (rated): Apparent power Pn that the UPS can deliver under given load conditions (power factor = 0.8). Oversizing: Increasing the capacity of an UPS beyond that required to exactly meet the needed power requirements. Oversizing allows an UPS to efficiently and effectively handle surges and provides for growth in the power requirements. PCMS Power Control and Monitoring System: A software module on the DESN, which monitors and controls the power distribution system. PELV Protected Extra Low Voltage in accordance with AS/NZS 3000 PLC Programmable Logic Controller. Point of Supply (see AS/NZS 60038) The point where the distribution system of the DNSP and the electrical system of the customer are connected. Power Factor: The power factor is the mathematical relationship between apparent or effective power, measured in kVA, and real or average power, measured in kW. When the current and voltage are in phase, purely resistive load, the power factor is 1. In a purely reactive load in which voltage and current are 90° out of phase, the power factor is 0. Power Failure: See AS 62040.3 Primary Power: See AS 62040.3 PSS Primary Switching Station / Primary Substation as appropriate– Are switching stations/substation that form part of the primary electrical distribution system, to which Incomers and Interconnectors are connected. RCD Residual Current Device (RCD) - see AS/NZS 3000 - A device intended to isolate supply to protected circuits, socket outlets or equipment in the event of a current flow to earth which exceeds a predetermined value. Redundancy (active): Parallel UPS configuration in which several UPS units with equal outputs are parallel connected and share the load. In the event one UPS unit fails, the other units pick up its share without any interruption in the supply of power to the load. Redundancy (standby): UPS configuration in which one or several UPS units operate on standby, with no load or only a partial load, and can immediately back up a faulty UPS unit by no-break transfer of the load, carried out by a static switch. Reliability: The probability that an item will perform as intended for a specified period of time under a stated set of conditions. Usually measured as a probability, a failure rate, or a mean time between failures. MIEE 2011, Amend1 – 1 Feb 2016 GLOSSARY 5 of 7 Manual of Infrastructure Engineering Electrical GLOSSARY Resonance. Resonance results in voltage surges and transients of several times the supply voltage. PFC connected to a supply can cause resonance between the supply and the PFC capacitors or between other equipment and the PFC capacitors. RMU Ring Main Unit, compartmentalised HV switching/protection panels normally switch/fuse switch disconnector unit. Switchgear normally used at substations RTU Remote Terminal Unit Sag: A low-voltage condition in which the voltage on one or more phases of AC power falls below 80 to 85 percent of the nominal value for more than one cycle (1/60th of a second for 60-cycle AC). Can be caused by ground faults, starting large loads, inadequate power supply, utility switching, utility equipment failure, and lightning. Can cause computer crashes and damage equipment. SELV Separated Extra Low Voltage in accordance with AS/NZS 3000. SF6 Sulphur Hexaflouride An electrically insulating gas utilised in HV switchgear equipment. SMS: Site wide Management System. Typically a distributed site wide BMS application Standby Power: See AS 62040 Static Bypass: See AS 62040 Static Switch: Synchronous Bypass Facility. The combination static (semiconductor) and electromagnetic switch that bypasses the UPS to connect the critical load to the bypass power source. Substation (SS) A facility in the electrical distribution system at which voltage transformation occurs, i.e. the voltage is changed from one voltage to another. The typical substation generally comprises as a minimum a power transformer. Substations may also include the associated switchboards, however either or both of these can be located remotely. Support Time: Time during which the UPS can supply the rated load with nominalquality power while the primary power is down. Surge: A high voltage condition in which the voltage on one or more phases of AC power exceeds 100 percent of the nominal value for more than one cycle (1/60th of a second for 60-cycle AC). Can be caused by a rapid load reduction or switching, and can damage equipment. Switching Station (SWS) A facility in the electrical distribution system that is specifically designed for electrical switching. Normally housing HV RMUs. System Control: The control circuits that provides total UPS system control, alarm annunciation and instrumentation metering. MIEE 2011, Amend1 – 1 Feb 2016 GLOSSARY 6 of 7 Manual of Infrastructure Engineering Electrical GLOSSARY Systems Project Office (SPO) Defence agency responsible for the engineering integrity of aircraft systems, subsystems and interfaces Thermal Runaway: A condition that is caused by a battery charging current that produces more internal heat than the battery can dissipate. This condition ultimately causes cell venting and premature failure. Transients: Disturbances to electrical power lasting less than one cycle (1/60th of a second for 60-cycle AC). Also referred to as voltage spikes. Can be caused by lightning strikes, sudden load-shedding on the primary power system, and shutdown of equipment that was drawing an extremely large amount of power, or a general rise in voltage on the primary power system after use by a large number of consumers. Voltage spikes can blow fuses or trigger circuit breakers, destroy electronic circuitry, and corrupt stored data. UPS: Uninterruptible Power System. Refer to AS62640, an electrical device or system providing an interface between the mains power supply and sensitive loads (computer systems, instrumentation, etc.). The UPS supplies sinusoidal AC power free of disturbances and within strict amplitude and frequency tolerances. If input power is removed from the UPS, it will continue to supply the load without interruption. Refer AS62040. UPS, Rotary: An UPS in which a Motor-Generator (M-G) set is used. UPS, Static: A solid-state UPS relying normally on battery power. Useful Life (battery): The time over which a battery can deliver a useful amount of power (normally defined as 80 percent or more of the battery’s capacity). MIEE 2011, Amend1 – 1 Feb 2016 GLOSSARY 7 of 7