* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Systems Vocabulary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
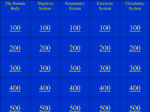
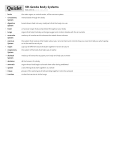
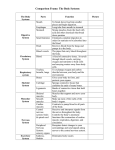
Body Systems Vocabulary 8th Grade Skeletal System – An internal system made up of bones, joints, and connective tissue Marrow – A tissue in the center of some bones Joints – The points at which bones meet Cartilage – Strong, flexible tissue that provides cushioning at your joints Ligaments -- Strong cords of tissue that connect the bones in each joint Tendons -- Tough bands of tissue that attach your muscles to bones Muscular System – The group of structures that make your body parts move Skeletal Muscle – Muscle attached to bones that enables you to move your body Smooth Muscle – Muscle found in organs, (stomach and intestines ) and in blood vessels and glands. Cardiac Muscle – Muscle found only in the walls of your heart Circulatory System – Organs and tissues that transport essential materials to body cells and remove their waste products Cardiovascular System – Another name for circulatory system Pulmonary Circulation – The flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart Systemic Circulation – The flow of blood to all the body tissues except the lungs Arteries – Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to other parts of the body Veins – Blood vessels that carry blood from the body back to the heart Capillaries – Tiny tubes that carry blood from the arteries to the body’s cells, and then back to the veins Respiratory System – The organs that provide the body with a continuous supply of oxygen and rid the body of carbon dioxide Epiglottis – A flap of tissue that closes over the trachea when you swallow Larynx – The upper part of the respiratory system which contains the vocal cords Trachea – A windpipe that directs air to the lungs Bronchi – passages through which air enters the lungs Diaphragm – A dome-shaped muscle that separates the lungs from the abdomen Alveoli – Microscopic air sacs in the lungs where oxygen passes into the capillaries and into the blood Nervous System – The body control center Neurons – Specialized cells that make up the nervous system Central Nervous System (CNS) – Part of the nervous system that includes the spinal cord and brain Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – Part of the nervous system that includes the nerves that connect the CNS to all parts of the body Somatic System – A system dealing with actions you control (part of the PNS) Autonomic System -- A system dealing with actions you do not usually control, ie. breathing and digestion (part of the PNS) Digestive System – An organ system that converts food to a form useful to the body Digestion – The changing of food you eat into substances the body can use Saliva – Fluid produced by the salivary glands that softens and moistens food Small Intestine – A coiled, tubelike organ that is about 20 feet long that absorbs digested nutrients Liver – A large gland that has many digestive functions. It produces bile, a substance that aids in the digestion of fats Gallbladder – A small saclike organ that stores bile and releases it as needed Pancreas – An organ that produces enzymes that assist in digestion Excretory System – A system that removes wastes from the body Excretion – is the process of removing wastes from the body Colon – The large intestine Kidneys – Organs that filter water and dissolves wastes from the blood and help maintain proper levels of water and salts in the body Endocrine System – A chemical communication system that regulates many body functions Gland – A group of cells, or an organ, that secretes a chemical substance Pituitary Gland – A gland signaling other endocrine glands to produce hormones when needed Reproductive System – The organs that make possible the production of offspring Sperm – The male reproductive cells Egg cell – The female reproductive cells Ovulation -- The release of one mature egg cell each month Menstruation – The flow of the uterine lining out of the body Menstrual Cycle – The sequence of events in the reproductive system that occurs from one menstruation to another Menopause – A period marking the end of a female’s reproductive years