* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body System Review Name: Date: 1. In humans, the
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
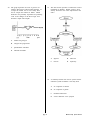
Human Body System Review Name: 1. Date: In humans, the exchange of respiratory gases occurs within the 3. Which sequence correctly indicates the branching pattern of the human respiratory system? A. nose B. trachea A. trachea ! bronchi ! bronchioles ! alveoli C. bronchial tubes D. alveoli B. trachea ! bronchioles ! bronchi ! alveoli C. alveoli ! trachea ! bronchioles ! bronchi D. alveoli ! bronchioles ! trachea ! bronchi 2. Which function of a part of the human respiratory system is represented in the diagram? A. gas exchange B. cellular respiration C. external cyclosis D. active transport page 1 4. The chart shown represents the concentration of gases in inhaled and exhaled air in humans. Inhaled air Exhaled air %O2 %CO2 %N2 14.0 5.60 79.0 20.9 0.04 79.0 What is the reason for the di erence in the O2 and CO2 concentrations of inhaled and exhaled air? A. In cellular respiration, O2 is used and CO2 is produced. B. In cellular respiration, CO2 is used and O2 is produced. C. O2 and CO2 di use easily because they are large molecules. D. O2 and CO2 are actively transported across thin, moist membranes. 5. Which statement best describes the function of the respiratory passageways of a human? A. They permit digestive end-products to make contact with body cells. B. They permit exchange between the external atmosphere and the circulatory system. C. They transport gaseous cellular wastes from body cells to the lungs for excretion. 6. The graph shown represents relative blood pressure in human circulatory structures A through D. Blood pressure drops most drastically within structure D. They regulate the amount of ammonia and salt dissolved in body uids. A. 7. page 2 A B. B C. C D. D What prevents the back ow of blood in structure D ? A. ganglia B. enzymes C. pumps D. valves Human Body System Review 8. The diagram shown represents the human heart, and the direction of blood ow is indicated by arrows. 11. In humans, red bone marrow provides A. structural support for the body B. a source of new blood cells C. an attachment site for muscle tissue D. a site to trap bacteria The aorta is represented by number A. 1 B. 6 C. 8 D. 4 12. 9. 10. Which structure pumps blood directly to the lungs? The maintenance of proper blood sugar level involves the storage of excess sugar in the A. salivary glands B. stomach C. pancreas D. liver A function of human blood is to A. maintain homeostasis B. produce energy C. produce new cells A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 6 D. keep the heart beating page 3 Human Body System Review 13. The removal of a human gallbladder interferes most directly with the A. production of gastric juices B. production of saliva C. storage of pancreatic juices D. storage of bile 14. Chart I shows the percentages of certain materials in the blood entering the kidney and the percentages of the same materials in the urine leaving the body. Chart II shows the number of molecules in the beginning and end of the kidney tubule for every 100 molecules of each substance entering the glomerulus. Chart I Substance Protein % in blood 7.0 % in urine 0.0 Glucose 0.1 0.0 Water 91.5 0.33 0.29 Urea 0.03 2.7 0.02 Number of Molecules Beginning of Tubule 0 End of Tubule Protein in blood entering glomerulus 100 Glucose 100 20 0 Substance 96.0 Sodium Potassium Chart II Water 0.24 Sodium Potassium Urea 100 100 30 30 100 23 100 50 0 1 1 12 90 According to chart I, which substance is more highly concentrated in the urine than in the blood? A. water B. sodium C. page 4 protein D. glucose Human Body System Review 15. Into which parts of the human digestive system are digestive enzymes secreted? 18. A. mouth, esophagus, stomach A. completion of lipid digestion B. stomach, small intestine, large intestine B. absorption of water into the bloodstream C. mouth, stomach, small intestine C. completion of carbohydrate digestion D. esophagus, stomach, large intestine 16. 17. In humans, the large intestine is the major site for the D. storage of nutrients for future use 19. Which process reduces the concentration of urea in the blood of humans? A. excretion B. egestion C. digestion D. synthesis 20. Which part of the digestive system contains structural adaptations called villi that increase the surface area for the absorption of food? 21. A. F B. E C. C D. H page 5 In the human digestive system, most nutrients are absorbed into the blood through the lining of the A. esophagus B. stomach C. small intestine D. large intestine In which organ of the human gastrointestinal tract does most chemical digestion of lipids occur? A. stomach B. esophagus C. large intestine D. small intestine Food is usually kept from entering the trachea by the A. diaphragm B. epiglottis C. villi D. ribs Human Body System Review 22. In humans, chemical digestion is accomplished by enzyme action that begins in the mouth and ends in the A. esophagus B. C. small intestine D. gallbladder 25. stomach In humans, structures that absorb most of the products of digestion are the A. ducts of the pancreas B. cells of the esophagus C. villi of the small intestine D. muscular folds of the gallbladder 23. Which type of digestion occurs in the mouth when an individual chews a piece of bread? A. mechanical digestion, only B. chemical digestion, only C. both mechanical digestion and chemical digestion 26. D. neither mechanical digestion nor chemical digestion 24. The correct pathway for urine to ow out of the human body is A. bladder ! ureter ! kidney ! urethra B. kidney ! ureter ! bladder ! urethra C. urethra ! bladder ! kidney ! ureter D. kidney ! urethra ! bladder ! ureter In humans, the ureter transports urine from the A. blood to the kidney B. liver to the kidney C. kidney to the urinary bladder 27. D. urinary bladder to outside the body page 6 Which gland most directly regulates the metabolism of calcium within the human body? A. adrenal B. parathyroid C. pituitary D. testis Human Body System Review 28. What is the role of sensory organs in the body? 31. Which structures in a human transmit electrochemical messages? A. the transmission of impulses directly to e ectors A. veins B. B. the detection of environmental stimuli C. neurons D. nephrons C. the conduction of impulses from the spinal cord lymphocytes D. the interpretation of impulses from motor neurons 32. 29. 30. Neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, are initially detected by which part of a neuron? A. dendrite B. nucleus C. terminal branch D. mitochondrion visceral muscle and brous tendons B. smooth muscle and ligaments C. skeletal muscle and bones A. neurons located in the brain and spinal cord B. nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord C. interneurons of the central nervous system D. portions of the brain known as the medulla and cerebellum 33. Which two structures are directly involved in locomotion in humans? A. The peripheral nervous system consists of the D. cardiac muscle and immovable joints The muscular nature of the walls of ventricles is most closely associated with their function of A. storing blood from the body B. producing red blood cells C. maintaining pressure lower than that in the atria D. forcing blood to the lungs and body page 7 Human Body System Review 34. 35. In animals, hormones are transported throughout the organism by the A. lysosomes B. C. circulatory system D. excretory system 38. synapses Into which system do endocrine glands secrete hormones? A. circulatory B. C. digestive D. reproductive Which is regulated by thyroxin? A. the rate of metabolism in the body B. the condition of cartilage in the joints of bones C. ACTH production 39. Select the endocrine gland, chosen from the list below, that is best described by the statement shown. This gland is often called the master gland because many of its hormones stimulate the activities of other glands. D. calcium production 36. nervous A. Adrenal B. Pancreas C. Parathyroid D. Pituitary Human ovaries do not function properly unless they receive a stimulating hormone from the A. thyroid B. pituitary gland C. adrenal gland D. pancreas 40. Select the endocrine gland, chosen from the list below, that is best described by the statement shown. This gland produces a hormone that regulates calcium balance in the bloodstream. 37. In humans, glucose is stored in the liver chie y as a polysaccharide known as A. fat B. protein C. maltose D. glycogen page 8 A. Pancreas B. Parathyroid C. Pituitary D. Testis Human Body System Review 41. 43. Select the hormone, chosen from the list below, that is best described by the statement shown. Which ovarian hormone in uences female secondary sexual characteristics? A. Insulin B. Thyroxin C. Estrogen D. Parathormone The chart shown gives incomplete information about various systems of the human body which can fail, causing a speci c malfunction. Malfunction of Human Body A System A ected Chacteristics of Malfunction Endocrine Leukemia B Emphysema Respiratory Not enough insulin produced by the pancreas, causing high levels of sugar in blood and urine; weakness results Cancer of the bone marrow, causing uncontrolled production of white blood cells D C Nervous In ammation of membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord caused by bacterial or viral infection The name of which malfunction should be included in the table at A ? 42. A. gout B. pneumonia C. stroke D. diabetes Select the hormone, chosen from the list below, that is best described by the statement shown. Which hormone regulates the overall rate of metabolism? A. Insulin B. FSH C. Thyroxin D. Parathormone 44. Which endocrine gland would be most responsible for secreting the hormone that accelerates the heart rate? page 9 A. thyroid B. pancreas C. parathyroid D. adrenal Human Body System Review 45. Select the gland, chosen from the list below, that is best described by the statement shown. 48. Select the structure, chosen from the list below, that is best described by the statement shown. A child's heartbeat increases when the child is frightened. A. Islet of Langehans B. C. Testis D. Parathyroid This endocrine gland secrets numerous hormones that directly regulate the activities of several other endocrine glands and body tissues. Adrenal A. Pituitary gland B. Thyroid gland C. Parathyroid gland D. Islets of Langerhans 46. Which hormone aids directly in reducing the sugar level of the blood? A. glucagon B. adrenalin C. insulin D. estrogen 49. 47. For the statement shown, select the endocrine gland that is best described. This gland is responsible for producing a hormone that promotes the conversion of excess glucose to glycogen. Select the malfunction, chosen from the list below, that is best described by the statement shown. This region of the brain functions as an endocrine gland by producing hormones that in uence the activities of the pituitary gland. A. Hypothalamus B. Pituitary gland C. Thyroid gland A. adrenal B. pituitary C. thyroid D. pancreas D. Islets of Langerhans page 10 Human Body System Review 50. The graph represents the level of glucose in a student's blood from 11:00 am until 10:00 pm. At 3:30 pm the student ran in cross-country meet, and at 5:30 pm the student ate dinner. Which hormones were primarily responsible for producing some of the changes in the blood sugar level between 4:30 pm and 8:00 pm? A. insulin and glucagon B. estrogen and progesterone C. parathormone and TSH 51. The chart shown represents a homeostatic control mechanism in humans. Which system is most directly involved in the events represented in the chart? D. adrenalin and FSH 52. A. digestive B. endocrine C. nervous D. respiratory A similarity between the nervous system and the endocrine system in humans is that they both A. are composed of neurons B. are composed of glands C. maintain homeostasis D. secrete chemicals across synapses page 11 Human Body System Review 53. In which part of the human reproductive system does the development of an embryo normally occur? A. scrotum B. C. ovary D. testes 54. Where are the hormones that regulate the human female reproductive cycle produced? uterus A. ovaries, testes, and uterine lining B. hypothalamus, pituitary, and ovaries C. Fallopian tubes, placenta, and ovaries D. ovaries, pituitary, and Fallopian tubes page 12 Human Body System Review Problem-Attic format version 4.4.266 c 2011–2015 EducAide Software _ Licensed for use by Betty Dixon Terms of Use at www.problem-attic.com Human Body System Review 05/17/2016 1. Answer: D 21. Answer: B 2. Answer: A 22. Answer: C 3. Answer: A 23. Answer: C 4. Answer: A 24. Answer: C 5. Answer: B 25. Answer: C 6. Answer: B 26. Answer: B 7. Answer: D 27. Answer: B 8. Answer: B 28. Answer: B 9. Answer: D 29. Answer: A 10. Answer: A 30. Answer: C 11. Answer: B 31. Answer: C 12. Answer: D 32. Answer: B 13. Answer: D 33. Answer: D 14. Answer: A 34. Answer: C 15. Answer: C 35. Answer: A 16. Answer: A 36. Answer: B 17. Answer: D 37. Answer: D 18. Answer: B 38. Answer: A 19. Answer: C 39. Answer: D 20. Answer: D 40. Answer: B Teacher's Key 41. Answer: C 42. Answer: C 43. Answer: D 44. Answer: D 45. Answer: B 46. Answer: C 47. Answer: A 48. Answer: A 49. Answer: D 50. Answer: A 51. Answer: B 52. Answer: C 53. Answer: B 54. Answer: B Page 2