* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 4.3.2 Factors influencing growth and development student
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
Uneven and combined development wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
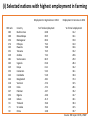
Emerging and developing economies: factors influencing growth and development 4.3.2 Unit content Students should be able to: • Evaluate the impact of economic factors in different countries: primary product dependence, volatility of commodity prices; savings gap: Harrod-Domar model; foreign currency gap, capital flight, demographic factors, debt, access to credit and banking, infrastructure, education/skills, absence of property rights • Evaluate the impact of non-economic factors in different countries What is economic growth? Economic development? • What is economic growth? • What is economic development? • Which is subjective? Which is objective? Draw economic growth on a PPF diagram Developed and Developing Country Growth Source: IMF % growth in real GDP 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 -4 Short run or long run economic growth? • Changes in AD (C+I+G+X-M) • Changes in short run AS • Changes in the labour force • Cyclical changes in real GDP • Investment rates • Potential output / trend growth • Productivity of labour & capital • Short term external shocks to both demand and supply • Short term policy changes e.g. changes in interest rates • Technological progress and strength of enterprise Do these factors affect short run or long run economic growth? • Commodity prices such as oil, gas and foodstuffs • Confidence of businesses and households • Enterprise • Exchange rates • Fiscal policy - government spending and taxation • Innovation • Interest rates set by the central bank • Investment • Labour supply • Productivity • Research • Trading conditions in other countries Benefits of economic growth? Drawbacks of economic growth? Analysing Causes of Economic Growth in Africa 1. Improvement in the terms of trade: higher commodity prices have boosted revenues for countries who rely on _________ exports 2. Improved governance: wider spread of democratic governments & improved institutions so more __________ are able to issue bonds 3. Strongly increasing foreign _______ investment: especially in agriculture, mining, oil and gas, infrastructure, hotels/restaurants 4. Increasing trade including _________ goods with emergence of key African regional trade hubs bolstered by infrastructure spend 5. Improved macroeconomic management: lower_________, more credible central banks and improved fiscal balances 6. Rising per capita ________: growth of consumer markets, extreme poverty rates continue to fall but social progress has been uneven 7. Growing number of African countries less _________ on primary commodities & now more diversified services/manufacturing. countries, dependent, direct, incomes, inflation, manufactured, primary What economic factors influence growth and development? i. primary product dependence and volatility of commodity prices ii. savings gap: Harrod-Domar model iii. foreign currency gap iv. capital flight v. demographic factors vi. debt vii. access to credit and banking viii. infrastructure ix. education/skills x. absence of property rights (i) Primary product dependence and volatility in commodity prices What is primary product dependence? • When an economy depends on: (i) Why might primary product dependence be undesirable? (i) Primary product dependence and volatility in commodity prices Demand for primary products is often income inelastic. What does this mean? • This is the Prebisch-Singer hypothesis. (i) Volatility in commodity prices • What type of elasticity do commodities have (PES and PED)? • What will this do to the revenue of producers and foreign currency earnings of the country? • What might this uncertainty deter? (i) Selected nations with highest employment in farming Employment in Agriculture in 2012 HDI rank 183 180 154 174 163 151 139 181 163 145 153 143 142 116 130 147 152 140 93 73 90 Country Burkina Faso Mozambique Madagascar Ethiopia Rwanda Tanzania Zambia Sierra Leone Uganda Kenya Cameroon Cambodia Bangladesh Vietnam India Pakistan Nigeria Ghana Thailand Sri Lanka China % of total employment 84.8 80.5 80.4 79.3 78.8 76.5 72.2 68.5 65.6 61.1 53.3 51.0 48.1 47.4 47.2 44.7 44.6 41.5 39.6 39.4 34.8 Employment in Services in 2012 % of total employment 12.2 16.1 15.8 13.0 16.6 19.2 20.6 25.0 28.4 32.2 34.1 30.4 37.4 31.5 28.1 35.2 41.7 43.1 39.4 41.5 35.7 Source: HDI report 2015, UNDP (i) Understanding the Prebisch Singer Hypothesis • The Prebisch-Singer Hypothesis suggests that, over the long run, prices of primary goods such as ______ ________ in proportion to prices of manufactured goods such as ______________ • The basic idea: long term _________ in real commodity prices. ___________ terms of trade for primary exporters. The modern reality: labour intensive manufactured goods are now _________. Strong rise in global commodity prices until recently. World commodity prices have started falling again in the last 2 years. Many commodity exporters have seen terms of trade rise (ii) Levels of savings and investment • Why are savings important? • Savings are needed to: • Why is this a problem in many poorer countries? • What does this lead to? • Increases reliance on : • This problem is known as the savings gap. • In Africa for example, savings rates of around 17% of GDP compare to 31% for middle-income countries. (ii) Levels of savings and investment • The Harrod-Domar model suggests that __________ savings lead to _____ investment. This means that capital accumulation will be low, resulting in ________ economic _______ growth, inadequate, low, slow (ii) Deriving the savings gap and foreign exchange gaps • The Harrod-Domar model states that investment, saving and technological change are the key variables in determining __________ growth. • Increased investment in the economy shifts the PPF __________ • Savings is approximately _______ to investment • So to increase economic ______ either savings need to be increased (to fund investment) or technology needs to improve (so more can be produced) economic, equal, growth, outwards (ii) How does investment lead to growth? 1. Injection of demand for capital ___________ benefits those industries 2. ______________ effects 3. More _____________ lifts productivity and hence incomes 4. Economies of ___________ improves competitiveness capital, goods, multiplier, scale (ii) What are the constraints on the Harrod-Domar model? (iii) Foreign currency gap • Why do some developing and emerging economies face a shortage of foreign currency? (iii) The foreign currency gap summary • Many developing countries often face an imbalance between inflows and outflows of foreign currencies • A foreign exchange gap occurs when currency outflows persistently exceed currency inflows for example when: 1. A country is running a persistent ________ account _________________ 2. There is an outflow of capital from investors in money and capital markets (known as capital ________) 3. There is a _______ in the value of inflows of remittances from nationals living and working overseas (iv) Capital flight • Capital flight is the uncertain and rapid movement of large sums of money ______ of a country • Owners of extra income that could be saved and so used for investment, often withdraw their money from the country in search of _________ returns abroad • Why does it matter? (iv) Why might capital flight occur (why are investors unconfident)? • E.g. many Chinese leaders have relatives with offshore companies and so money is taken abroad (iv) Capital Flight from China Capital Outflows from China US$, billions 1000 US$, billions FX reserves-12 month change 4500 FX reserves (RHS) 2000 -200 1500 -400 1000 -600 500 -800 0 2016 0 2014 2500 2012 200 2010 3000 2008 400 2006 3500 2004 600 2002 4000 2000 800 (v) Demographic factors • Many developing and emerging countries are characterised by high birth and death rates. Why does this matter? • Some countries face an ageing population which means that there are _________ workers. This may be as a result of policies followed in the past; for example, ___________ one child policy. (v) Malnutrition as a Barrier to Development • Why do high rates of malnutrition act as a barrier to development? (v) Gender inequality as barrier to growth & development: 10, 50, 70, 80, 232 • ____% of the world’s female population aged 15-64 is in work versus more than ___% men. Proportion of economically active women has declined in the last 20 years • Cultural norms: _____ million women live in economies where they can't get a job without their husband's permission • Less than ____% of credit for small farmers in Africa is directed to women. Without ID, women can’t access a bank account, vote, claim entitlements or inherit property • Women make up ____% of Africa’s farmers but the majority are locked out of land ownership • ______ and Rwanda are the only countries where the share of women in parliament match or exceed their population share • Women often work in the informal economy, working in family businesses, or producing goods for self-consumption. This has irregular/no pay & little access to social security/legal protection (vi) Debt • In the 1970s governments were encouraged to borrow ($) at ______ interest rates to ______ growth. • In the 1980s interest rates rose and the dollar _____________ so countries struggled to repay the interest. • Mexico defaulted in 1982 and banks ________ lending • Poorer countries paid more in ________ than they received in aid. • Some debt was written off or reduced but then the financial ______ exacerbated the problem • Corrupt governments squandered or ______ the money appreciated, crisis, fund, interest, kept, low, stopped (vii) Access to credit and banking • Why does it matter if individuals cannot access credit and banking services? • Who night they turn to and why does this matter? (vii) Inadequate access to basic financial services • According to the World Bank, some 2 billion workingage adults globally do not use formal financial services • These services include: 1. Access to a _______ account for formal savings 2. Access to ________ finance from recognised lenders 3. Access to basic _________ services • Women in developing countries are 20% less likely than men to have an account and 17% less likely to have borrowed from a formal financial institution (viii) Why does poor infrastructure limit economic growth & human development? Why does it matter if infrastructure is inadequate? (ix) Education • Countries which place an emphasis on education and provide some state funding are more likely to: • This improves human capital and shifts the _____ outwards. • What is human capital? (ix) Human Capital Inadequacies • In many countries secondary school enrolment is low and teaching quality / attendance is ______ • There is a _____ gap between expected years of schooling and mean (actual) years of schooling • Lower and middle-income countries may suffer from ______ drains of their younger, more skilled workers • Weak human ________ constrains labour productivity and ability to harness new technologies • Human capital deficiencies are often linked to __________________. Better basic health care and nutrition often improves human capital by avoiding brain impairment big, brain, capital, malnutrition, poor (x) Absence of property rights • Why does absence of property rights matter? Non-economic factors • Non-economic factors include the impact of: corruption, poor governance, wars, political instability and geography. Challenges Facing Landlocked Countries • Land locked economies: without good infrastructure and efficient logistics, it can be _________ and slow to get products to the countries of trade partners • Some landlocked countries such as Ethiopia have been doing _______ especially when they achieve regional economic integration with other landlocked nations. Investment in _____ transport links helps to overcome this development trap Importance of Institutions for Development • What are some of the key institutions that need to function well for development progress to happen? Why is corruption a barrier to growth & development? Brain Drains as a barrier to development • Disadvantages • Advantages