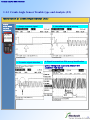
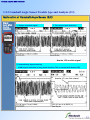
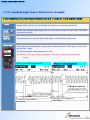
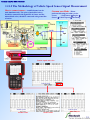
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EMS Professor - AE Tools & Computers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor Carman scan for EMS professor 1 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor Contents 1. Scope Meter Utilization 2. Application of Ignition Secondary Wave 3. Multi-meter Utilization 4. Application of Simulation Function 5. Application of Special Maintenance 6. Carman scan Utilization Chart 2 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1. Scope Meter Utilization 1.1 Crank Angle Sensor Signal Analysis 1.2 CAM Angle Sensor Signal Analysis 1.3 TPS Signal Analysis 1.4 Air Flow Sensor Signal Analysis 1.5 O2 Sensor Signal Analysis 1.6 Injector Signal Analysis 1.7 Ignition System Analysis 1.8 ISC Valve Signal Analysis 1.9 Air Temp. Sensor Signal Analysis 1.10 Knock Sensor Signal Analysis 1.11 Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal Analysis 1.12 EGR Valve Signal Analysis 1.13 Purge Valve Signal Analysis 1.14 O2 Sensor Heater Signal Analysis 3 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.1 Crank angle sensor signal analysis 1.1.1 Introduction of crank angle sensor and principle (1/2) About Sensor Crank angle sensor is a sensor for locating piston by ECU and necessary to find ignition time . If the signal of the crank angle sensor keeps its consistency, then it is hard to find starting and ending point. Therefore, two teeth are taken out from the crank and it is called Long Tooth and the rest are called Short Tooth. By using long Tooth, TDC ( Top Dead Center ) is found. Contents shown by signal of crank sensor. 1. Ignition time = 360deg * Number of tooth before TDC / Number of tooth at one revolution of engine. Ignition time is calculated by number of tooth between the long tooth and peak voltage. Peak voltage is obtained by measuring signal of crank angle sensor and primary ignition wave simultaneously. 2. Engine speed (RPM) = 60 / ( Time between long tooth * Number of long tooth at one revolution of engine) RPM is calculated by number of long tooth at one revolution of engine. 4 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.1.1 Introduction of crank angle sensor and principle (2/2) Sensor type Three mostly used crank angle sensor. 1. Optical Sensor : The sensor is used on a single-bodied cam shaft with a hole on the disk. The signal is recognized when the signal passes through the hole while the disk is revolving. This particular sensor is destructive by heat and humidity and makes lots of noise. ( This is the only sensor that disk for crank angle sensor revolve 1 revolution while crank shaft rotate 2 revolution. ) 2. Magnetic Sensor : If the electromagnetic power generated by coil is intercepted by revolution of a single-bodied camshaft with target wheel (normally outside of flywheel ), then the voltage is generated. The sensor is using this voltage for signal.. 3. Hall type sensor : The circuit is included in the sensor inside. This sensor electron The circuit included inside the sensor discharge the electron. The single bodied crank shaft with target wheel (normally outside of fly wheel ) disturbs discharging of electron and generate the voltage. This voltage is used for signal. Optical type Optical type Algorithm Magnetic type Magnetic type sensor signal This sensor is the most important sensor for the ECU. If sporadic engine stall happened , then suspect this sensor at first. 1. If the ECU detects fault on this signal, then the ECU stop “fuel injection and ignition 2. If the ECU could not detect fault signal, then normal component or not equipped component might be detected as a fault one. 5 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.1.2 The Methodology of Crank Angle Sensor Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Vehicle selection System(Engine / Transmission / ABS …)Crank Sensor Measuring Sensor repair info view. Normal value About sensor Data analysis 6 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.1.3 Crank Angle Sensor Trouble type and Analysis (1/2) Malfunction of Crank Angle Sensor (1/2) Troubles 1. The signal is always high or low. 2. The signal is intermittently missed. 3. The noise signal detection. 4. The signal is normal but ECU identify wrong crank angle signal. Cause of trouble Engine state 1. Malfunction of crank angle sensor or wiring circuit failure (Signal, Ground and Reference line) 2. Bad connection of wiring 3. Cut off noise or remove cause of noise from crank angle sensor 3.1 Shield crank angle sensor wiring. 3.2 Check whether spark plug is original part or not (Resistance range : 2.0 - 4.5K) 4. The counteraction of sensor maker should be required. 1. The engine is not started. 2. The engine vibration and stall are sometimes occurred. 3. The engine vibration and stall are sometimes occurred and display DTC of normal part or non existed part 4. The ignition timing is out of control range. Normal signal 7 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.1.3 Crank Angle Sensor Trouble type and Analysis (2/2) Malfunction of Crank Angle Sensor (2/2) Signal wave when trouble detection 1. Always constant signal 3. The noise signal detection 2. Intermittently signal missing 4. Signal is normal but ECU wrong identification Ignition timing from scanner is different with calculation from signal. 8 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.1.4 Crank Angle Sensor Field Service Example (1/2) 1.Field example of Crank angle sensor trouble:ECU wrong identification Trouble Cause of trouble Accent 2000MY vehicle is started with hesitation. ECU identified wrong crank angle signal and it led to wrong calculation of ignition timing. So, ECU started ignition with suction stroke. Related vehicles This phenomenon is frequently occurred with magnetic crank angle sensor. Accent 2000MY, Avante 1.5L/1.8L DOHC, Tiburon, Verna Signal view Ignition was BTDC 12deg on scanner but calculation from measured signal was ATDC 48deg. TDC position was identified from service information of Carman scan. 9 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.1.4 Crank Angle Sensor Field Service Example (2/2) 2.Field example of Crank angle sensor trouble:Intermittently signal missing Trouble Cause trouble HMC Sonata 2,3(1.8/2.0L DOHC MAP)vehicle : Vehicle is started with hesitation in cold ambient condition or don’t start. of Related vehicles Crank angle signal was abnormal due to power cut when key release. This phenomenon is frequently occurred with optical crank angle sensor(MELCO 52 pin ECU). New Sonata 2,3(1.8/2.0 DOHC), New grandeur etc. Signal view If you measure crank angle signal with above phenomenon, you can see abnormal crank signal.It result in injection cut off. 10 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.2 CAM angle sensor signal analysis 1.2.1 Introduction of cam angle sensor and principle(1/2) About Sensor CAM angle sensor is the sensor to indicate the TDC of each cylinders by ECU. This sensor is necessary to calculate injection phase. We can calculate TDC from the crank angle sensor but cylinder number. Therefore ECU recognize the TDC right after cam angle signal. ECU use the cam signal located between two long tooth. If the signal of cam is located inside the long tooth, then ECU detects it as a fault. TDC 19th TDC shown after CAM signal is the first TDC. Information from the signal of cam sensor : TDC of the1st cylinder 11 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.2.1 Introduction of cam angle sensor and principle(2/2) About Sensor Three mostly used cam angle sensor. 1. Optical Sensor : The sensor is used on a single-bodied cam shaft with a hole on the disk. The signal is recognized when the signal passes through the hole while the disk is revolving. This particular sensor is destructive by heat and humidity and makes lots of noise. ( This is the only sensor that disk for crank angle sensor revolve 2 revolution while crank shaft rotate 1 revolution. ) 2. Magnetic Sensor : If the electromagnetic power generated by coil is intercepted by revolution of a single-bodied camshaft with target wheel (normally outside of flywheel ), then the voltage is generated. The sensor is using this voltage for signal. 3. Hall type sensor : The circuit is included in the sensor inside. This sensor electron The circuit included inside the sensor discharge the electron. The single bodied crank shaft with target wheel (normally outside of fly wheel ) disturbs discharging of electron and generate the voltage. This voltage is used for signal Optical / hall type sensor signal Algorithm Magnetic type sensor signal In order to reduce the emission, injection should be finished before intake valve open. If the fuel is injected on the hot intake valve, then fuel is well vaporized and this helps good combustion. Therefore, cam signal is used to identify the cylinder number. In case of no spark time adjustment type,we can know it by comparing cam signal position with crank angle sensor. 12 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.2.2 The Methodology of Camshaft Angle Sensor Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Vehicle selectionSystem(ENG)CAM Part(F4 key) Measuring Remark : Since both A and B channels can be used at the same time, it is better to measure crank and cam angle signal simultaneously. Sensor repair info view Normal valve About sensor Data analysis 13 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.2.3 Camshaft Angle Sensor Trouble type and Analysis (1/2) Malfunction of Camshaft Angle Sensor(1/2) Trouble Cause of trouble Engine state Normal signal 1. The signal is always high or low. 2. The signal is intermittently missed(Invalid signal detection during 1 cycle). 3. The noise signal detection. 1. Malfunction of CAM angle sensor or wiring circuit failure (Signal, Ground and Reference line) 2. Check valve timing. If it is not proper, please adjust it. 3. Cut off noise or remove cause of noise from CAM angle sensor 3.1 Shield CAM angle sensor wiring. 3.2 Check whether spark plug is original part or not (Resistance range : 2.0 - 4.5K) 1. The engine problem is not occurred but GDI engine is not started. 2. CAM sensor error is intermittently detected with poor acceleration. 3. The engine vibration and stall are sometimes occurred and display DTC of normal part or non existed part 4. The ignition timing is out of control range and in case of LPG vehicle back-fire is occurred. Upper signal in picture is CAM signal and sine signal is crank signal. 14 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.2.3 Camshaft Angle Sensor Trouble type and Analysis (2/2) Malfunction of Camshaft Angle Sensor (2/2) Signal wave when trouble detection 1. Always constant signal 3. The noise signal detection Avante, XG use this signal 2. Intermittently signal missing (CAM signal detection in long tooth duration:This is normal with Avante XD) 15 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.2.4 Camshaft Angle Sensor Field Service Example Field example of CAM angle sensor trouble : Case of CAM signal delay Trouble Cause trouble Avante DOHC vehicle is not accelerated and CAM error is sometimes detected. of Related vehicles Ignition was retarded (about 9[deg]) due to wrong valve timing and CAM signal is detected just before long tooth. This phenomenon is occurred when CAM signal is identified before long tooth. Signal view CAM signal was identified before long tooth but distance between CAM signal and long tooth was not over 1 tooth. The valve timing was wrong adjusted as 1 tooth. < Reference > The valve timing can be fast or delay by tensioner moving when acce leration Before valve timing adjustment After valve timing adjustment 16 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.3 Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) signal analysis 1.3.1 Introduction of TPS and principle TPS About Sensor TPS is the sensor to know how much accelerate the acceleration pedal. If the line of this sensor is broken, then more than 4.7V or 2.1V of constant signal voltage can be produced depending on ECU internal circuit.. Sensor type Algorithm Wiper type is the mostly used signal sensing type by now. In order to response to the driver’s will quickly, fuel injection is controlled depending on the acceleration speed and pedal value. If the pedal value is more than 50%, then oxygen sensor feedback control is stopped to control the engine with more torque. In case of sensor failure, intake air sensor is substituted for TPS. Therefore, fast accel and decel can not be detected with sensor failure and hesitation can be occurred. 17 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.3.2 The Methodology of TPS Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. Carman scan Mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, - Vehicle selectionSystem(ENG)TPS Part(F4 key) Measuring Remark : As it is possible to use A,B channels at the same time, it is better to measure TPS and intake air flow simultaneously. Sensor repair info view Normal value About Sensor Data analysis 18 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.3.3 TPS Trouble type and Analysis (1/2) Malfunction of TPS (1/2) Trouble Cause of trouble 1. The signal is always high or low. 2. The signal is intermittently missed(Micro cut-off occurrence). 3. The noise signal detection. 4. Even if idle state, ECU does not identify it. 1. Malfunction of throttle position sensor or wiring circuit failure (Signal, Ground and Reference line) 2. Check ground line and connecting part. If there is something wrong, connect it correctly. If it is occurred again after repairing, ECU should be changed with latest version. (Many HMC vehicles have this problem) 3. Remove cause of noise 3.1 Shield sensor signal line. 3.2 Check whether spark plug is original part or not(Resistance range:2.0-4.5K) Engine state 1. The vehicle hesitation is occurred with acceleration. 2. Idle TPS adaptation value is less than TPS absolute value at normal idle and ECU doesn’t idle state even if real idle.Engine vibration is occurred with this phenomenon. 3. Emission is increased. 4. The vehicle hesitation and vibration are occurred with acceleration. Normal signal As can as possible, TPS signal should be compared with MAF sensor signal. And check whether TPS & MAF signal are increased at the same time when acceleration. 19 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.3.3 TPS Trouble type and Analysis (2/2) Malfunction of TPS (2/2) Signal wave when trouble detection 1. Always constant signal 3. The noise signal detection 2. Intermittently signal missing (Micro cut-off occurrence) 20 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.3.4 TPS Field Service Example (1/2) 1.Field example of TPS malfunction : Signal missing by micro cut off Trouble Cause trouble Accent 1.3L SOHC vehicle not only doesn’t identify idle state but also vibration and stall are occurred. The hesitation is occurred with acceleration and scanner doesn’t recognize idle state even if vehicle is real idle. of Related vehicle TPS signal is cut off. This phenomenon is occurred in HMC vehicle which TPS ground line is connected with ECU outside ( Accent 1.3/1.5L DOHC etc ) Signal view TPS signal is sometimes “0” with normal MAF sensor signal. 21 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.3.4 TPS Field Service Example (2/2) 2. Field example of TPS malfunction : Signal noise occurrence. Trouble The emission is increased so much in idle state with Coupe 2.0L vehicle. O2 sensor is normal feedback control but it is shifted to rich side. Cause of trouble Related vehicle As connecting TCU, TPS signal noise is so much detected. ECU identify noise as fast acceleration, so it result in over fuel enrichment. Vehicles which use same TPS wiring from TCU and ECU Signal view TPS signal noise is so much detected “0” with normal MAF sensor signal. Signal view 22 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.4 Intake Air Flow Sensor Signal Analysis 1.4.1 Introduction of Intake Air Flow Sensor and Algorithm About Sensor Sensor type Algorithm This is the sensor to see how much air flow is coming into the cylinder. It is very important to calculate injection time. If the line is broken, then there are occasions when output voltage is over 4.7V depending on internal circuit like TPS. Mostly used sensors by now are the MAP sensor ( Intake manifold pressure check ), MAF (Mass Air Flow :the resistance is changed when heated tip is cooled by inducted air )and Karman Vortex (This sensor monitors vortices generated as the intake air flows past vortex generators. Air flow is calculated by the frequency of ultrasonic waves that are changed depending on the amount of vortices. ) The fuel quantity is decided by the air flow and the injector opening time decides fuel quantity. The calculated fuel amount is compensated more precisely by oxygen sensor feedback compensation. In case of air flow sensor error, the substitute value is calculated by engine speed and TPS. 23 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.4.2 The Methodology of Air Flow Sensor Signal Measurement Carman scan Mode : Please How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Vehicle selectionSystem(ENG)MAP Part(F4 key) Measuring Remark : As it is possible to measure A,B channels, it is better to measure intake air flow and TPS simultaneously. Sensor repair info view Normal value About sensor Data analysis 24 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.4.3 Air Flow Sensor Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of Air flow sensor Trouble 1. The signal is always high or low. 2. The signal is intermittently constant. Cause of trouble 1. Malfunction of air flow sensor or wiring circuit failure (Signal, Ground and Reference line) 2. Check ground line and connecting part.If there is something wrong,connect it. Engine state 1. Engine is hard to start. Even if it is started, vehicle hesitation is occurred when acceleration 2. Intermittently vehicle hesitation or engine stall is taken place. Normal signal As can as possible, MAF signal should be compared with TPS signal. And check whether MAF and TPS signal are increased at the same time when acceleration. Signal wave when trouble detection As can as possible, MAF signal should be compared with TPS signal. And check whether MAF and TPS signal are increased at the same time when acceleration. 25 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.4.4 Air Flow Sensor Field Service Example Field example of Air flow sensor malfunction :Abnormally high signal (Sensor is normal but signal is high) Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Accent 2000MY vehicle is hard to start. Even if it is started, power is lack with acceleration and exhaust gas is black color. MAP signal is very high in idle state but scanner identify normal idle state. High MAP signal was detected because internal EGR was increased by exhaust pipe blocking. Due to that, ECU identify big air flow and exhaust pressure make high. It led to over fuel enrichment and poor acceleration due to lack of power. In case of MAP equipped vehicles,if exhaust pipe is blocked,this phenomenon is always occurred. MAP signal is increased proportion to exhaust pipe blocking status. Signal view Signal(1.9volt) is slightly higher than signal of no load racing(0.8 - 1.5volt) 26 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.5 Oxygen sensor signal analysis 1.5.1 Introduction of oxygen sensor and priciple About Sensor This is the sensor to compensate the fuel injection to get the stoichiometric air fuel ratio (14.6). The different voltage is generated depending on fuel richness ( oxygen richness ). According to this voltage variation, fuel injection is added or subtracted so that always relevant fuel is injected. Sensor type Mostly used sensor now is the Zirconia ( It generate the voltage from 0V to 1V by oxygen richness ), Titania ( It generate different resistance by oxygen richness ) and UEGO sensor ( It is used for lean burn engine and it generate different current by oxygen richness ). Titania and Zirconia sensors are classified with and without heater. Algorithm Oxygen sensor produce below 0.5V with rich oxygen( lean fuel) and over 0.5V with lean oxygen (rich fuel). Using this, ECU inject more fuel when oxygen sensor voltage is below 0.5V and reduce fuel as soon as voltage is over 0.5V. By continuing this control, supplied fuel is getting close to stoichiometirc air fuel ratio. This is the feedback control. In case of sensor failure, fuel is supplied by basic calculation. 27 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.5.2 The Methodology of O2 Sensor Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Vehicle selectionSystem(ENG)O2 sensor Part(F4 key) Measuring Remark : As it is possible to measure A,B channels, it is better to measure TPS too. Sensor repair info view Normal value About Data analysis 28 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.5.3 O2 Sensor Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of O2 sensor Trouble 1. The signal is always high or low. 2. The signal is intermittently constant 3. The switching is too fast. 4. The switching is too slow. Cause of trouble 1. Malfunction of O2 sensor or wiring circuit failure (Signal, Ground and Reference line) 2. Check ground line and connecting part.If there is something wrong,connect it. 3. A/F ratio distribution is unstable with individual cylinder (Fuel gas is induced from outside) 4. O2 sensor tip is poisoned or exhaust gas temperature is too low. Engine state 1,2 If acceleration pedal is worked before engine warm-up before, engine stall is occurred or power is lack. And also vehicle hesitation is taken place when fast acceleration. 3. Engine vibration is severe. In case of knock sensor equipped, power is lack and fuel economy make bad due to knock detection. 4. Engine stall is Sometimes occurred or exhaust gas is black with fast accel. Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection As can as possible, O2 sensor signal should be compared with TPS signal. And check whether O2 sensor signal is switched or not when acceleration. If signal is switched, O2 sensor is normal. 1. Always constant 2. Slow szwithing 3. Fast switching 29 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.5.4 O2 Sensor Field Service Example (1/2) 1. Field example of O2 sensor malfunction : Too fast signal switching Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Elantra 1.6 vehicle vibration is severe in idle state and heavy knocking is detected. O2 sensor signal is rapidly switched(Repeat high and low). Vibration and knocking is decreased after repairing hydro tappet but it is still remained. It is cleared as using synthetic oil. Most vehicles are related, especially it is so much taken place when low quality is used during long time. (In case of solid tappet equipped engine,if tappet is not adjusted,it is occurred) Signal view In case of too fast signal switching, it is due to abnormal tappet opening and canister closing etc. 30 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.5.4 O2 Sensor Field Service Example (2/2) 2. Field example of O2 sensor malfunction : Too slow signal response Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Accent 2000 MY vehicle hesitation or stall is taken place with acceleration after idling. At this time exhaust gas is black color and acceleration is poor. Due to insufficient O2 sensor light off, signal is low and ECU start feedback control at this time. ECU identify that fuel is lean with low signal and it result in over fuel enrichment. This phenomenon is frequently occurred with optical crank angle sensor (MELCO 52 pin ECU). Elantra, New sonata(1.8, 2.0L SOHC) etc. Signal view Signal is stayed around 0.4 volt when problem occurrence. If acceleration pedal is continuously worked, signal is bigger and bigger as below picture by exhaust temperature. < Counteraction > O2 sensor is exchanged with heated type.Signal and ground line make connection same as before. And heater line is connected with after main relay and always operated with engine start. After this working, spark plug should be changed with new one and drive with high speed(2hours) to remove carbon in combustion chamber. 31 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.6 Injector active signal analysis 1.6.1 Introduction of Injector and principle About Injector Injector type Algorithm The fuel quantity is decided by the air flow and the injector opening time decides fuel quantity. The injector open by electromagnetic power and close by spring force. Since the electromagnetic power is depending on battery power, injector opening time is compensated by battery power. The principles of opening ( open by electromagnetic power and close by spring force )are mostly same. But it is classified into orifice and pintle type by injection hole. If the signal of crank angle sensor has the noise or broken signal, ECU stop the fuel injection until it get normal signal of crank angle sensor. Therefore, engine can be unstable or stall. 32 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.6.2 The Methodology of Injector Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Actuator Injection Measuring . Sensor repair info view Normal value About sensor Data analysis 33 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.6.3 Injector Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of Injector Trouble 1. Injector is not opened. 2. Intermittently injector is not opened. 3. The clogging of injector. Cause of trouble Engine state 1. Wiring circuit failure (Power supply and Ground line) 2. Crank angle sensor noise detection 3. Carbon accumulation in combustion chamber or fuel filter problem by other materials. 1. Vehicle vibration is severe after start. 2. Vibration or engine stall is intermittently occurred. 3. Vehicle vibration is severe and engine sound is loud. Normal signal Peak voltage and injector opening time is equal to individual cylinder without acceleration pedal. In case of clogging of injector or taking out from engine, it can be checked by O2 sensor signal. Signal wave when trouble detection 1. Always constant 2. Injector is not opened 3. Clogging of injector 34 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.6.4 Injector Field Service Example (1/2) 1. Field example of Injector malfunction : Clogging of injector tip Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Coupe 2.0L DOHC (Camshaft modified vehicle): Checked O2 sensor signal due to severe engine vibration. O2 sensor signal switching is too fast. Valve overlap is too big (55 deg). Carbon make clogging of injector. Most vehicle which has big valve overlap and use injector exception pintle type make this phenomenon. Signal view Abnormal O2 sensor signal. It is due to abnormal A/F distribution with individual cylinder. Fuel is not supplied in a certain cylinder. Even if injector is clogged, injector signal is normal on scanner. 35 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.6.4 Injector Field Service Example (2/2) 2.Field example of Injector malfunction:Sometimes not opened injector Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Signal view New sonata (MAP sensor) vehicle vibration is intermittently occurred and engine stall. This is not taken place regularly. Abnormal crank angle signal is detected due to noise detection, so ECU cut off fuel injection . At this time problem is taken place. This phenomenon is occurred with optical or magnetic type crank angle sensor. O2 sensor signal is mainly below 0.5 volt(lean shift) but sometimes show above 0.5 volt(rich shift). We don’t know whether ECU identify noise detected crank angle signal. If injector is not opened, you can think that ECU identify noise signal. < Counteraction > Shield crank angle sensor signal line to prevent noise. 36 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.7 Ignition System Signal Analysis Refer to “Chapter 2 Application of Ignition Secondary Wave” 37 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.8 ISC valve control signal analysis 1.8.1 Introduction of ISC valve and principle About valve ISC ISC type valve ISC valve is the valve that bypass the air to keep constant engine speed when throttle valve is closed. ECU control only the opening of the valve and air is supplied by the under pressure in the surge tank.. Three mostly used type are DC type controlled by DC motor, Duty type controlled by duty and Step type controlled by the electromagnet ISC valve ISC valve Control line Control line Control line Control line Control line GND Duty control Control line Duty type (2 coil) Algorithm Step motor type The ECU compare the engine speed with target speed and open or close the valve when engine speed is lower or higher than target. This compensation is composed of proportional, integral and differential term- so called PID control.. Engine speed Engine speed Target speed ISC valve opening 38 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.8.2 The Methodology of ISC Valve Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Actuator ISC Measuring Sensor repair info view IAC valve Normal value IAC valve About sensor Data analysis 39 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.8.3 ISC Valve Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of ISC valve Trouble 1. ISC is not opened. 2. Intermittently ISC is not opened. 3. The closing stuck of ISC valve. Cause of trouble Engine state 1. Wiring circuit failure (Power supply and Ground line) or Malfunction of TR in ECU 2. Wiring is normal but valve is not operated by carbon or step loss etc. (Step loss : The difference between ECU control and actual opening duty) 3. Carbon accumulation in air flow path 1, Even if engine start is possible, it is stalled soon or severe vibration is occurred. (In case of BOSCH ISC, engine speed is stayed around 1500rpm) 2. If it is occurred with little opening,engine vibration or stall is taken place If it is occurred with big opening, engine is stayed with high speed. 3. As soon as engine is started, it is stalled. Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection ISC valve signal have difference according to which type is used. (Duty type / DC motor type / Step type) 1. Always constant 2. ISC valve stuck 3.ISC valve close stuck Although ISC valve is stuck with closed position ,signal is normal. So, it can be checked by actuator operation. “ Refer to chapter 5” 40 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.8.4 ISC Valve Field Service Example 1. Field example of ISC malfunction : Clogging of ISC valve pintle Trouble Trajet XG 2000MY stall is frequently occurred and engine start is hard. Cause of trouble Related vehicle Signal view Leaking oil from turbo is mixed with carbon. It led to block ISC valve pintle. This is often occurred with duty type ISC valve equipped vehicles, especially 1 coil type is more frequent. There is no problem in ISC signal, only ISC pintle is not operated. Carbon in pintle should be cleared. 2. Field example of ISC malfunction : ISC valve step loss Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Signal view Trajet XG 2000MY vehicle: If engine stall is occurred, it is frequently taken place. Step between ECU control and actual opening have big difference. At this time, ISC valve adaptation is abnormal and opening duty is not controlled properly. So, this phenomenon is taken place. This is occurred with step motor malfunction or aging vehicle(Above 50,000 km/h) without step motor equipped. There is no problem in ISC signal, only ISC pintle is not operated. ISC valve should be cleaned after disassembling. And reset ISC adaptation value and stay idle state more than 10 minute. This step loss is not cleared completely. Although it is repaired or exchanged with new one, it may occur later. 41 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.9 Temperature sensor signal analysis 1.9.1 Introduction of temperature sensor signal and principle About Sensor Sensor Type Coolant sensor is a sensor for detecting of how much engine is heated up and necessary to control injection/ignition/ISC valve depending on engine temperature. Because engine load is surely different depending on engine temperature. Intake air temperature sensor is used to calculate exact intake air flow and necessary for MAP sensor type. But it is often not to use it with MAF(Mass air flow )type. Some of MAP sensor include intake air temperature sensor inside and it is called TMAP sensor. Mostly used type is a thermistor type that increase the resistance with high temperature and decrease the resistance with low temperature. . Intake air temp. sensor Algorithm T_MAP sensor Coolant temp. sensor Intake air temperature sensor is a sensor for calculating intake air quantity more exactly. The coolant temp. sensor is to set different target of fuel(Air Fuel ratio)/target speed/ spark time in accordance with coolant temperature to compensate different engine load Target lambda area without feedback control depending on coolant temp Target ignition area depending on coolant temp. - idle status AF range Spark range Coolant Temp. 42 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.9.2 The Methodology of Temperature Sensor Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Sensor WTS Measuring Sensor repair info view Coolant sensor Coolant sensor Normal value Coolant sensor About sensor Data analysis 43 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.9.3 Temperature Sensor Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of Temperature sensor Trouble 1. Signal line open circuit (Temperature is below -30 deg.C ) 2. Signal line short to ground (Temperature is above 127 deg.C ) 3. Temperature signal change is too fast. Cause of trouble 1. Wiring circuit failure (Signal or Ground line open or shorted) 2. ECU internal circuit malfunction or temperature sensor position is not proper. Engine state 1. Poor acceleration or exhaust gas is black due to over fuel enrichment. It is returned normal after 10 minute. 2. Intermittently idle rpm is oscillating (800 - 1000rpm). Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection Temperature sensor signal have difference according to which type is used. (Duty type / DC motor type / Step type) 1. Always constant 2. Temp. signal rapidly change 44 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.9.4 Temperature Sensor Field Service Example Field example of Temp.sensor malfunction : Fast coolant signal change Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Signal view Accent 2000MY vehicle : Engine speed is oscillating from 800 to 1000rpm with idle state. Engine speed is oscillated by coolant temperature change due to ECU internal circuit malfunction. Idle engine speed is set with ECU data by coolant temperature in ECU. Siemens ECU(52 pin) has sometimes problem but other ECU may have this phenomenon. Engine speed is changed with coolant temperature oscillating. If actual coolant temperature is constant. The problem is still remained after TCO sensor change(3ea) but it is cleared after ECU change. If you want to measure temperature, please refer to “Chapter 4 Multi meter utilization” 45 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.10 Knock sensor signal analysis 1.10.1 Introduction of knock sensor and algorithm About Sensor Sensor type The knock sensor employ the piezoelectric element or silicon that produce the signal(voltage) when it gets pressure. If there is knocking in the engine, then vibration is transformed to pressure vibration and it produces voltage. According to this voltage, knocking is detected. It is difficult to distinguish the knock sensor type by means of sensor shape. element to detect vibration may be different. But the Knock sensor Algorithm The frequency of knocking signal is too fast(about 6 - 18Khz) to analyze it by ECU. Therefore, this signal is s ampled by hardware and knocking is detected. But the frequency of bad engine vibration can be overlapped with frequency of knocking. So, too much knocking can be detected by engine vibration. 46 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.10.2 The Methodology of Knock Sensor Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Sensor Knock Measuring Sensor repair info view Normal value About sensor Data analysis 47 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.10.3 Knock Sensor Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of Knock sensor Trouble Cause of trouble Engine state 1. Knocking signal is always constant (Signal line open or shorted) 2. Heavy knocking detection 3. Knock signal is normal but knock is not detected (Communication malfunction of knock signal in ECU) 1. Wiring circuit failure (Signal or Ground line open or shorted) or knock sensor malfunction 2. A/F is different with individual cylinder.(Refer to 2.6injector trouble) 3. ECU internal circuit malfunction (Should be changed ECU) 1.If ECU detect knock sensor error, ignition is retarded(6-12deg). It result in lack of power and bad fuel economy. If ECU don’t detect error,ignition is not retarded even if knocking is occurred. 2 Too much ignition retard(6-12deg) make lack of power and bad fuel economy 3.Same as NO.1 description. Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection Knock sensor signal have difference according to which type is used. (Duty type / DC motor type / Step type 1. Always constant 2. Heavy knocking detection Heavy knocking Abnormal : constant signal Normal signal Normal signal 48 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.10.4 Knock Sensor Field Service Example Field example of Knock sensor malfunction : Heavy knocking detection Trouble Trajet XG 2000MY vehicle: The power is lack with driving and fuel economy is bad. Cause of trouble Related vehicle Signal view Cylinder #1 intake valve is not opened properly due to malfunction of #1 rocker arm operation. It result in engine vibration and ignition retard by heavy knocking detection. So, ignition retard make lack of power and bad fuel economy. In case of knock sensor equipped vehicles, if engine state is unstable, it guess knocking detection. This signal can be also checked with O2 sensor signal. Knock signal with problem detection O2 sensor signal with problem detection Heavy knocking Normal signal Knock I.C exist in ECU. If it has malfunction, knocking detection is impossible. But ECU can detect whether it properly works or not. 49 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.11 Vehicle speed sensor signal analysis 1.11.1 Introduction of vehicle speed sensor and principle About Sensor Sensor Type Vehicle speed sensor is a sensor that check wheel speed per second to calculate vehicle speed. It measures speed of body of rotation that directly connected with driving shaft. Mostly used vehicle speed sensor are lead type (switch on and off at every revolution )/ magnetic type and hall type. VS sensor Rotor rotate with the cable connected to driving shaft A hole for cable connection Magnetic and hall type is same principle as crank angle sensor. VS sensor(lead switch type) Algorithm Vehicle speed is calculated by calculating how many voltage over the threshold(normally 1.0 - 2.5V) are generated at one second. If the noise signal is over the threshold, then it is recognized as vehicle speed. Vehicle speed signal is required for AT car to decide gear shifting level and for MT car to reduce the shock during fast acceleration by adjusting spark time and fuel depending on vehicle speed and gear level. ECU calculates the gear level using engine speed and vehicle speed. 50 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.11.2 The Methodology of Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. Carman scan Mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Sensor Vehicle Speed Measuring Sensor repair info view Vehicle speed Vehicle speed Normal value Vehicle speed About sensor Data analysis 51 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.11.3 Vehicle Speed Sensor Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of Vehicle speed sensor Trouble 1. Any vehicle speed sensor signal is not detected with driving. 2. Vehicle speed is much higher than actual speed. (Too much signal noise) 3. Even though vehicle stop, ECU identify vehicle speed. Cause of trouble Engine state 1. Wiring circuit failure (Signal or Ground line open or shorted) or vehicle sensor malfunction 2. Too much signal noise detection in vehicle speed sensor 1. Engine RPM is slightly high in idle state and it is oscillating. 2. In case of A/T vehicle, shift point is high gear position and it is shifted with 2 or 3 gear when take off. Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection Vehicle speed signal should be detected in driving. It should be always constant at vehicle stop. 1. always constant 2. Noise detection in VS signal 52 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.11.4 Vehicle Speed Sensor Field Service Example Field example of VS sensor malfunction : Signal noise detection Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Grandure XG V6 2.0L DOHC vehicle: Vehicle take off with 2 or 3 gear shifting. Acceleration is impossible and VS is displayed with 40 - 70 Km/H on scanner even if vehicle stop. Too much noise is detected in VS signal. ECU identify driving with high speed. All vehicles (Especially in case that ECU receive VS signal from TCU) Signal view VS signal with problem detection VS signal is not related to shape. Only check how many detect signal above 1.0 volt per 1sec. 53 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.12 EGR valve control signal analysis 1.12.1 Introduction of EGR valve and principle About EGR EGR type This is a valve to add exhaust gas into the cylinder and so the combustion temperature is reduced. Reduced combustion temperature results reducing of nitrous-oxide emission. Exhaust gas is supplied through this valve by under-pressure of surge tank. Mostly used one is mechanical type that the valve is opened by under-pressure of surge tank as soon as solenoid valve is opened. And the solenoid valve is opened by ON/OFF system or duty system. In case of EEGR(Electric EGR) type, the EGR valve is opened by electromagnetic power.. Electric EGR valve Algorithm Mechanical EGR valve EGR valve is opened within the range(2 - 7%) that is not to give big influence on engine operation. Opening value is controlled not to have big engine vibration. Therefore, in case of ON/OFF type, ON signal is activated in the area (engine speed & intake air flow )where no engine problem is found. With the EGR gas, ignition angle should be retarded about 4 - 8 degree If the EGR gas is provided into the cylinder, combustion temperature is reduced and it is effective on reducing of nitrous-oxide emission. 54 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.12.2 The Methodology of EGR Valve Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Actuator EGR valve Measuring Sensor repair info view EGR sensor / EGR valve Normal value EGR sensor / EGR valve About sensor Data analysis 55 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.12.3 EGR Valve Operation Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of EGR valve Trouble 1. Malfunction of valve operation 2. EGR valve closed stuck 3. EGR valve opened stuck Cause of trouble Engine state 1. Wiring circuit failure (Power supply or Ground line open or shorted) or EGR solenoid valve malfunction 2. EGR valve is stuck for a while or friction increase by over heating. 1. Severe engine vibration is occurred(Open stuck) or lean fuel control(MAP sensor type). 2. lean fuel control(MAP sensor type), fuel adaptation is increased to positive direction. Knocking is often taken place. 3 Severe engine vibration (Engine is hard to start or severe engine vibration after start) Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection EGR valve operation can be checked only if it is operated. So, it should be checked with working acceleration pedal. 1. Always constant EGR valve stuck is not checked with signal,indirectly it can be checked with O2 sensor signal. “Refer to O2 sensor chapter” 56 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.12.4 EGR Valve Field Service Example Field example of EGR valve malfunction : EGR valve closed stuck Trouble Cause of trouble Related vehicle Signal view Grandure XG V6 3.0L DOHC vehicle : Knocking is often taken place and intermittently fuel control is rich because fuel adaptation is increased to positive direction. EGR gas is not supplied in combustion chamber due to EGR valve closing stuck. At this time, ECU reduce fuel injection as much as EGR duty. So, injection is not sufficient and fuel adaptation is increased. And also knocking is occurred because ECU apply EGR activated ignition. This is occurred at EGR valve equipped vehicles with MAP sensor. MAF(Mass Air Flow:Hot Film Type)is also happened if ECU separately control EGR activated ignition. O2 sensor signal with problem detection EGR valve stuck is not checked with signal,indirectly it can be checked with O2 sensor signal. 57 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.13 Purge valve control signal analysis 1.13.1 Introduction of purge valve control and principle About valve Part type Fuel vapor gas from fuel tank is not emitted to the air but stored in the canister to follow the emission regulation. And then this fuel vapor gas is supplied to the engine via purge valve during engine running. Mostly used one is solenoid valve type that uses under-pressure of surge tank while valve is open. This is also divided into ON/OFF and duty type.. Purge solenoid valve Canister Algorithm Purge valve is opened in the limit area no to give big influence on engine operation. Opening amount is controlled no to have rpm drop by too much rich fuel caused by purge gas. Therefore, in case of ON/OFF type, ON signal is controlled to activate in the area ( engine speed, intake air flow )of no engine problem. If purge gas is supplied into the cylinder, mixture is getting richer. But as it is compensated by oxygen sensor, total fuel amount is same 58 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.13.2 The Methodology of Purge Valve Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be Carman scan Mode : Please used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Actuator Purge valve Measuring Sensor repair info view Canister purge solenoid Canister purge solenoid valve Normal value About sensor Data analysis 59 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.13.3 Purge Valve Operation Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of Purge valve Trouble 1. Malfunction of valve operation 2. Purge valve closed stuck 3. Purge valve opened stuck Cause of trouble Engine state 1. Wiring circuit failure (Power supply or Ground line open or shorted) or Purge solenoid valve malfunction 2. Purge valve is stuck for a while or friction increase by over heating. 1. Severe engine vibration is occurred when hot start(Open stuck) or over fuel enrichment control. 2. The smell of fuel gas is detected from vehicle. 3. Severe engine vibration is occurred when hot start(Open stuck) or over fuel enrichment control. Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection Purge valve operation can be only checked with driving. It should be always constant with vehicle stop. 1. Always constant Purge valve stuck is not checked with signal,indirectly it can be checked with O2 sensor signal. “Refer to O2 sensor chapter” 60 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.13.4 Purge Valve Field Service Example Field example of Purge valve malfunction : Purge valve opened stuck Trouble Coupe vehicle : Engine is hard to start when hot summer season. And fuel control is so rich with engine vibration after start. Cause of trouble Purge valve is stuck at closed position with hot condition. At this time, over fuel gas is supplied into engine when vehicle start and it lead to make hard vehicle start.Engine vibration is still remained until fuel gas is completely exhausted. Related vehicle Signal view This is frequently taken place with Siemens purge valve equipped vehicle. With BOSCH valve, it is sometimes occurred. O2 sensor signal with problem occurrence Purge valve stuck is not checked with signal,indirectly it can be checked with O2 sensor signal when fuel control is too rich. 61 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.14 Oxygen sensor heater control signal analysis 1.14.1 Introduction of oxygen sensor control and principle About sensor Oxygen sensor heater is a heater to heat up the tip of oxygen sensor. Since oxygen sensor activate when the sensor temperature is over 370degC, heater is needed to prevent delay of signal at low exhaust gas temperature. Sensor type There are oxygen sensor without heater too. Oxygen sensor without heater is used to reduce the cost. Algorithm In order to prevent sensor over-heating, heater control is stopped at high exhaust gas temperature area. In case of engine start, sensor might be cracked by heating due to water on the sensor. Therefore, heating is start after water is evaporated 62 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.14.2 The Methodology of O2 Sensor Heater Signal Measurement How to connect sensor : A and B channel can be used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. Carman scan Mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, - Scope meter Engine Sensor O2 sensor Measuring Sensor repair info view Normal value About Sensor Data analysis 63 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.14.3 O2 Sensor Heater Operation Trouble type and Analysis Malfunction of O2 sensor heater Trouble 1. Malfunction of valve operation (Power supply line is no problem but O2 sensor is not heated) 2. O2 sensor is not activated (Always OFF) Cause of trouble 1. O2 sensor heater damage 2. Wiring circuit failure (Power supply or Ground line open or shorted) Engine state 1,2 O2 sensor signal switching is too slow (Too slow light off) Intermittently exhaust gas is black and poor acceleration is detected and engine stall is occurred when fast acceleration. Fuel economy is bad. Normal signal Signal wave when trouble detection O2 sensor heater should be always “ON” if after start time is elapsed 40 sec (In case of duty type, it is “ON” above 95%) 1. Always constant If O2 sensor heater signal is “OFF” when idle, error is detected. 64 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 1.14.4 O2 Sensor Heater Field Service Example Field example of O2 sensor heater malfunction : Crack of tip Trouble HMC vehicles for US market : O2 sensor malfunction is many taken place in early winter season Cause of trouble O2 sensor heater should be operated after removing humidity around tip. But as soon as engine is started, O2 sensor is heated at the same time. It result in crack of O2 sensor tip. Related vehicle Signal view Vehicle which is manufactured before 1995 year (BOSCH O2 sensor:Frequently occurrence, Woojin O2 sensor:Sometimes occurrence) O2 sensor signal with problem occurrence O2 sensor signal is not switched (Always constant). 65 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 2. Application of Ignition Secondary Wave 2.1 General explanation & principle of Ignition secondary wave 2.2 Measuring method of Ignition secondary wave 2.3 Analysis of Ignition secondary wave 2.4 Field Examples 66 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 2.1 General explanation & principle of Ignition secondary wave The calculated time for ignition system by ECU are spark time and dwell time. The dwell time is to induct current to primary coil to get 60A and it is compensated by battery power. Dwell time is the power charging duration of primary coil. The longer dwell time is the higher current. That means, if this power charging duration of primary coil is long, then current is high and ignition energy (E = VA) is high so that combustion in the cylinder is stable with strong spark energy. But the problem is that electric energy is increase as current is increase. If it is too big then there will be a problem with endurance of ignition coil. So, with good endurance of ignition coil, we can increase dwell time, which gives high current. But, as it needs more money to increase endurance with current ECU that have power TR inside, current is controlled to a certain value (generally 6A) as fast as possible. Therefore eclectic current is changed very fast by dwell time and there is big difference of electric current by small dwell time change. Then what is a countermeasure of carmaker? 67 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor The countermeasure is to prevent over current, but there is no countermeasure for low current. Because over current can give damage on ignition coil or power TR while low current does not give big problem with small secondary voltage and small ignition spark. The reason why it is not a big problem is as following. The secondary voltage signal is almost similar at each engine operating conditions, but generation and destruction of instant high voltage is very various. Especially, it is depending on combustion chamber shape and engine operating conditions (temperature, airflow and mixture condition) and even with same conditions, it can not be regular. Therefore, in my opinion, to investigate engine condition with secondary voltage signal can give only few information such as problem of spark plug and coil wiring or decreasing of compression rate. If you want to understand the combustion condition exactly, you have to look at cylinder pressure. Some of electric control unit maker and carmaker’s research center use the sensor that equipped inside the spark plug to see cylinder pressure variation. Back to main subject, in fact, to say no problem with small ignition energy is dangerous. To say exact meaning, when engine is in idle at cold state (Coolant below -10C), energy of approximately 1J is required and energy of approximately 1 – 3mJ is required for warm-up engine with oxygen sensor feedback control. And more energy is required during acceleration or for rich mixture or for lean mixture. But normally required energy for warm-up engine is one-hundredths of cold engine. As carmaker make there ignition system to get enough energy at cold state, if there is no trouble with ignition system then there will be no big problem with low current at warm-up engine. Then what is the effect when we limit over current on ignition system? 68 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor If we limit the current then we can see that voltage increase by a step. This does not give any influence on engine (combustion condition), but ignition system has to consume more energy by itself. And this current size is depending on battery voltage. So, according to battery voltage, ECU gives different dwell time. As a reference, ECU has several power supply lines with different purposes and the line for battery voltage recognition is used to compensate battery voltage. What if battery voltage is changed due to high resistance or noise in the battery voltage line, which is connected to ECU? Then ignition sparks for each cylinder is irregular due to frequent changing of ignition enrage by irregular dwell time. This phenomenon happens more in hot summer with complex power supply wiring to ECU. Then what will be influence by this phenomenon? First, engine combustion is unstable due to unstable current flow. And this leads engine vibration. In case of knock sensor, engine vibration generates knock sensor signal and ECU detect this signal as knocking and retard spark time. < Reference> ECU analyzes knock sensor signal frequency to define real knocking frequency (generally 8-13KHz) from the engine. Yet, engine vibration due to different ignition power between each cylinder can be detected as knocking. How can the technician find out this condition that has very short difference of dwell time? It is difficult. But it can be suspected that dwell time is unstable when battery voltage from the power line that recognized by ECU is irregular. If engine vibration is severe with that condition, connect power line for voltage recognition to the ECU directly with one line. 69 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 2.2 Measurement of Ignition Secondary Wave How to connect Carman scan : A and B channel can be used simultaneously. The plus of probe(Red color) should be connected with signal line of sensor and the minus(black color) should be connected with ground line of sensor. Connection of Pick-up cable Carman scan Mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, - Vehicle Scope Automatic scope Ignition Measuring Connection of Ground wire Normal value Analysis of data 70 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 2.3 Analysis of Ignition Secondary Wave A. Measurement of Ignition primary wave. Ignition secondary wave shows discharging status according to the status of the cylinder. As it has a complicated relation with status of components and wires which control electrical energy at first coil, status of second coil which is induced by high voltage and status of mixed gas in the cylinders representing how much thermal electrons discharge while being discharged finally, To confirm whether status of supplying electrical energy to ignition system is good or not, it is desirable to check the current from first coil at each cylinder. To generate enough ignition energy at secondary voltage, there must be enough current at first coil. Although this current is different according to the sorts of the vehicle, generally 60.5A is considered as a standard. The point keeping in mind is despite this current is weak, ignition secondary wave may not have any problem. If air-fuel ratio in the normal temperature (over 20 °C) is closer to stoichiometric , Ignition by secondary voltage is possible with approximately 1/200~1/1000 energy of the ignition energy in the cold temperature (below -5°C). In case that the current flows weak , but ignition secondary wave has no problem, Ignition secondary wave must be confirmed whether it is normal state at rapid acceleration, cold temperature, both rich and lean of fuel condition. Ignition energy at normal temperature and stoichiometric condition : 1~2mJ Cold temperature and Rich fuel: approximately 1J 71 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor Checkpoint for current and primary ignition wave. 1)Distributor Less Ignition type < Measuring part > Measure flowing time and the current at checkpoint 1,2 <Checkpoint> Resistance of wire, status of components (checking components 1: internal ECU or external TR) 2) Distributor Ignition type <Measuring part> Measure flowing time and the current at checkpoint 1,2 <Checkpoint> Resistance of wire or a short, status of components (checking components 1: internal ECU or External TR, checking components 2: ignition coil) Most important point is dwell time(depends on battery voltage). If battery voltage is 13.5V the dwell time is 3.0~3.5msec. Cylinder by cylinder deviation(over 20%) check is required to know the normal or not. If the deviation is more than 20%, it means coil, power TR or wire has a problem.. Also check the ECU recognized battery voltage is stable(within 3V). Because the dwell time can be some difference depends on battery voltage. 72 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor B. Measurement of Ignition Secondary wave Ignition secondary wave means discharging to high voltage from electric energy at first coil. Especially ignition system in automobile, discharging time & discharging voltage level is affected more by status of the mixed gas in the cylinders and plug than electric energy from first coil. When secondary high voltage (approximately 20000~30000V) is induced instantly and flows, the flow means discharging, time is discharging time, Voltage is discharging voltage. When the secondary voltage generates, this energy separates carbon and hydrogen from constituent of fuel. <Ignition secondary wave: classification of each wave> While this constituent of fuel separates, electrons are generated. It’s called thermalelectron. Discharging voltage combusted normally from the cylinder is a voltage discharging through those thermal-electrons. Since level and time of the discharging voltage are affected by the temperature and shape (vortex) in the cylinder, air-fuel ratio of the mixture, and compression ratio, it is hard to fix absolute value. So it must be analyzed through comparing each cylinder. 73 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor Parts to confirm ignition secondary wave are as follows. 1) Distributor less type <Measuring parts> Measure flowing time and the current at checkpoint 1,2 <Checkpoint> Resistance of wire, status of components 2) Distributor Ignition type <Measuring part> Measure voltage secondary wave at checkpoint 1,2(plug wire at each cylinder) <Checkpoint> Resistance of wire or short, status components (checking components 1,2) of 74 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor . Comparing each cylinder (1) After a current flowed, if peak (voltage of surge) is low or discharging time is short and high: This means that electric energy through discharged thermal-electron isn’t discharging well,while molecule separates from fuel.Electric energy trying to ignite isn’t for fuel combustion , it’s kind of discharging phenomenon through plug ejja. So misfire occurs in the cylinder. A.Confirm the status of plug (attached carbon, clearance) When a peak voltage is generated, some parts of voltages flow on the attached carbon in the plug tip. So it gets weak to separate molecule. In case that discharging voltage flows through carbon to plug. B.Check plug wiring and status of coil In case that connection to plug and high voltage wire and coil status aren’t good , peak voltage becomes weak. Then electric energy to separate fuel molecule becomes weak because Thermal-electrons generated from fuel are little so that resistance discharges large state.. c.Check if the mixture ratio of fuel is too lean In case that fuel is lean, even more electric energy is needed to generate thermalelectrons separated from fuel molecule.thus peak voltage generated near stoichiometric with normal fuel isn’t enough to generate thermal-electron so that resistance dischargelarge state d.Check if the compression ratio is too high In case compression is high, far more electric energy is needed to generate thermal-electrons separated from fuel molecules. Thus peak voltage generated near normal compression ratio isn’t enough to generate thermal-electron so that resistance discharges large state. It isn’t for normal case. it’s for especially reorganized vehicle. Just do interpret that as theoretical aspect. In 4 cylinder engine , If one cylinder has some troubles, the troubles are made in two cylinders at the same time. Therefore when measuring wave with Carman scan, choose “one of NO1.and NO3.” or “ one of NO2. and NO4.” then measure 2cylinders at the same time. 75 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor (2)After a current flowed,if a peak(voltage of surge) is low and discharging time is long: Although electric discharge is well,it causes power reduction because discharging electric energy (spark) gets weak and long so that combustion timing of fuel gets long and flame spread leading to combust between fuel particles gets weak a. Check status of plug (clearance of tip is too small) b. Check compression pressure of cylinder is low c. Check the mixture ratio is too rich <Reference> More detail refers to chap 6.”6.3 uniform ignition energy to each cylinder. In 4 cylinder engine , If one cylinder has some troubles, the troubles are made in two cylinders at the same time. Therefore when measuring wave with Carman scan, choose “one of NO1.and NO3.” or “ one of NO2. and NO4.” then measure 2cylinders at the same time. 76 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor Ignition Energy Discharging Time For ignition, high voltage must be generated and sparked on ignition plug tip in cylinder But actually to combust fuel in cylinder, discharging must be done continuously for some time.Because spark from combusted fuel in cylinder must transfer flame to other surrounding fuel. If intake air is little (idle, deceleration), air playing a role on transferring flame and fuel mixture gets lack and compression ratio is low in cylinder so that there is high possibility to occur misfire. Actually in US regulation (OBD2: On Board Diagnostic2), if misfire rate is over regulation on exhaust gas, ECU recognizes as a malfunction It is written that “if intake air is little, misfire exempts from regulation So to speak, this means it admits air lack case is inevitable on air-fuel mixture transferring flame to the cylinder. But if enough secondary voltage keeps for some time (about 1,5msec), these misfire decreases. There is some product (CDI) making secondary voltage strong and discharging long time. The purpose of those products is on that. Compression pressure in according to ignition timing. cylinder Although the direct way to keep discharging time is to produce CDI, there is also indirect way to keep pressure in cylinder high. One of them is to retard ignition timing. 77 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 2.4 Field Service Example of Ignition Secondary Wave (1/3) 1. Field example of Ignition secondary wave : In case heat value of plug is too high Coupe 2.0L DOHC vehicle which platinum plug is equipped has poor performance when acceleration,black color of exhaust gas and engine start is hard in cold ambient condition. Trouble Cause trouble of Related Vehicle Combustion wasn’t well due to high heat-value Pt plug All vehicle equipped with too high heat-value Spark plug Signal View Big difference at wave between appropriate plug and high heat-value plug. (Discharging time is short with cold heat-value plug) < Reference > Since waves are different according to vehicle/ engine/ temperature of temperature, there were no absolute standard. It should be compared when it is normal condition. Pt plug equipped Comparison pt plug with appropriate one 78 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 2.4 Field Service Example of Ignition Secondary Wave (2/3) 2. Field example of Ignition secondary wave : In case too much noise is generated from plug Trouble New sonata (Map) Cranking isn’t well,After cranking engine disorder is severe. Cause of trouble Effected on ECU by being used no resistor plug, at ignition excessive noise was generated. Related Vehicle All vehicles equipped with no resistor plug (except using SIEMENS 55 pin ECU) Signal View Big difference at wave between appropriate plug (resistance:3.5~4.5 kohm) and no resistor plug. (After discharging, finishing is well) < Reference > Since waves are different according to vehicle/ engine/ temperature of temperature, there were no absolute standard. It should be compared when it is normal condition. No resistor plug Comparison no resistor plug and appropriate one 79 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 2.4 Field Service Example of Ignition Secondary Wave (3/3) 3. Field example of Ignition secondary wave : In case Compression ratio at cylinder is low Trouble Cause trouble Avante 1.5L DOHC Vehicle is a normal at cold engine condition, engine gets warmer, engine disorder happens. of Related Vehicle Signal view Since too much carbon was attached on intake valve stem, no problem at cold condition, but engine gets warmer stem expands so that compression pressure gets lower because stem can’t be closed well. All vehicles used too much fuel annex to raise octane value, probability is high. One of two ignition secondary wave discharging time is long and discharging voltage is low. < Reference > Since waves are different according to vehicle/ engine/ temperature of temperature, there were no absolute standard. It should be compared when it is normal condition. Pressure in cylinder is low 80 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 3. Multi-meter Utilization 3.1 Repair by measuring current 3.2 Repair by measuring pressure 3.3 Repair by measuring temp. 81 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 3.1 Repair by measuring current 3.1.1 Measuring of Large current ( 1 - 600 A ) How to connect Carman scan : Carman scan mode : Please perform Can be used by B channel, connect cable for following procedure on the screen measuring large current to main line (battery ). -Vehicle scope Oscilloscope Measure Connection of Current cable Explanation of current probe Measure Compression pressure Check compression leak at each cylinder Cranking current Check status of battery charging 82 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 3.1.2 Measuring of Small current ( 50mA - 100 A ) How to connect Carman scan : Can be used by B channel, connect cable for small current to each component power supply line. Connection of current cable Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, -Vehicle scopemeter Oscilloscope Measure Explanation of current probe Measure Ignition primary current Check Ignition system(Status of Power supply) Component operating current Check operating status of each component 83 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 3.2 Repair by measuring pressure 3.2.1 Measurement of vaccum : 760mmHg - 0 (From atmospheric pressure to vaccum 1bar) 3.2.2 Measurement of pressure : 0 - 500 psi (From atmospheric pressure to 35 bar) How to connect Carman scan : A and B channel can be used simultaneously. After connecting adapter to pressure line(measuring part), connect cable to converting module. Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, -Vehicle scopemeter Multimeter PressureMeasure. Measuring of vaccum : check MAP sensor and master back Measuring of pressure: check fuel pump,regulator 84 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 3.3 Repair by measuring Temp. (Can be measured from -50°C to 1000 °C ) How to connect Carman scan : Both Channel A and Bcan be used. After installing thermo couple, connect cable to converting module. Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen , -Vehicle scopemeter MultimeterTemperature Measurement of Temp. : Intake air Temp, Coolant Temp, Exhaust Gas Temp. 85 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 4. Application of Simulation Function 4.1 Operating Sensor 4.2 Operating Actuator 86 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 4.1 Operating Sensor 4.1.1 The Methodology of operating sensor with Carman scan If Service data from Carman scan is strange, sending signal to the sensor directly, Check whether a problem of line or a problem of component. How to connect Carman scan : Can be used by B channel, connect cable to sensor Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, -Vehicle scopemeter simulation operating with (+), (-) key (+)---->signal line, (-)-----> GND (body of vehicle) DRIVING ??? 87 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 4.1.2 The flow of operating sensor with Carman scan With this function, being able to distinguish exact cause between sensor and wire which is causing any abnormal engine running or fault. Sending signal by Carman scan Connector without sensor Sending signal Abnormal E/G running No Yes Fault code ? Monitoring service data expected as a cause No Yes Abnormal Service data ? No Yes Sending signal by Carman scan Disappeared fault code ? Sending signal by Carman scan No Yes Disappeared abnormal service Data ? Yes Disappeared abnormal E/G running ? No Yes Sensor problem Wire problem Sensor problem Other cause 88 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 4.2 Operating Actuator 4.2.1 The Methodology of operating actuator with Carman scan Although there is some problem at state of engine, No trouble code is showed at actuator system,(namely, No problem at actuator power but it is suspicious of operating well), Check it directly if actuator operates well. How to connect Carman scan : Can be used by A channel. connect (+) at cable for sensor to component operating line(-) Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, Vehicle scope meter Actuator Operating with ‘driv’, ‘stop’key. Connection cable to operating line DRIVING ?!? 89 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 4.2.2 The flow of operating actuator with Carman scan With this function, being able to distinguish exact cause between actuator and wire which is causing any abnormal engine running or fault. Sending activation signal by Carman scan Actuator without connector Sending activation signal Abnormal E/G running No Yes Fault code ? Monitoring E/G running phenomenon No Yes Any actuator related to problem ? Yes Sending activation signal by Carman scan Sending activation signal by Carman scan Disappeared fault code ? No No Yes E/G running is changed ? Yes Disappeared abnormal E/G running ? No Yes Actuator problem Wire problem or actuator stick Actuator problem Other cause 90 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 5. Application of Special Maintenance 5.1 Compression pressure at each cylinder 5.2 Battery charging status 5.3 Check if actuator is stuck 91 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 5.1 Compression pressure at each cylinder How to connect Carman scan : Can be used by B channel, connect cable for large current to main line (Battery). Connection current cable Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, -Vehicle scopemeter OscilloscopeMeasure Explanation of current probe View compression pressure Measure with CAM signal, first peak is NO1.Cylinder it shows explosion oder of engine. By comparison of height, compare pressure of each cylinder. 92 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 5.2 Battery charging status How to connect Carman scan : Can be used by B channel, connect cable for large current to main line (Battery) Connection current cable Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, -Vehicle scopemeter Oscilloscope Measure. Explanation of current probe View Cranking Current Comparing the first peak current with CCA, if the value of peak is below 70% of CCA value, Judging “Battery charging status ” is lack. 93 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 5.3 Check if Actuator operates well How to connect Carman scan : Can be used by A channel, connect cable for sensor(+) to component operating line(power), (-)to GND. Carman scan mode : Please perform following procedure on the screen, -vehicle scopemeter Actuator operating ‘Driv’, ‘stop’ key Connecting cable to operating line DRIVING Check if RPM increases proportionally, when duty gets larger by Carman scan PRO. After disconnection of ISC probe. 94 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 6. Carman scanUtilization chart (1/3) Signal analysis of ENGINE/TCU/ABS related sensor Each function and explanation ● : Judgment ○ : Possible △:Partially possible Blank : Confirmation impossible or unnessary Function of HI-SCAN Pro 1 SCAN DATA Input signal to ECU: Crank angle sensor / Cam angle sensor / TPS / Intake air flow sensor / O2 sensor / Intake air temperature sensor / Coolant temperature sensor / Vehicle Speed sensor / battery recognition vlotage / Ground recognition / Knock sensor / I Explanation of function Poor sensor ● ● ○ ○ ○ ○ Intermittent trouble Signal modulation Noise occuring Poor wire View communication with ECU 1.1 Trouble codes 1.2 Data value when trouble occurs View details of trouble when trouble occurs 1.3 Internal ECU calculation DATA View calculating value internal ECU 1.4 Operation status monitoring 1.5 Simulation Checking status of OBD2 operation 2 Scopemeter Comparing operating sign with scan data Measuring signal wave directly Measuring signal and operating status directly 2.2 Analysis of wave checking if abnormality exists comparing with normal wave 2.3 Explanation of wave 2.4 Analysis of Data 2.5 Data store 2.7 Operating Component Operating actuator directly Measuring ignition secondary wave directly 3.2 Analysis of wave checking if abnormality exists comparing with normal wave Comparing compression at each cylinder 4.1.2 Cranking test △ △ △ △ ○ ○ ○ Measuring status of each wiring & components Measuring consuming status of electrical energy(current) View conversed compression pressure at each cylinder Measuring status of battery charging status indirectly Measuring current flowing on ignition coil Measuring current to operating components 4.2 Measuring pressure Measuring pressure of engine vaccum & fuel pump etc. 4.3 Measuring Temperature Measuring temperature 4.4 Measuring frequency Measuring frequency of duty signal 4.5 4.6 Measuring duty pluse width Measuring proportion of duty signal ON 5 PC SCAN ○ Explanation of wave 4.1.4 Measuring Operating curent 4.7 Measuring resistor ○ Sending & watching wave after storing 4.1.3 Measuring current at coil Measuring duty ○ Measuring wave inducting to ignition secondary coil 3.1 Measuring wave 4.1 Measuring current ○ Operating component directly Changnig signal of sensor with optional value 4 Function of Multimeter ○ Sending & watching wave after storing 2.2.2 Operating Actuator 3.3 Eaplanation of wave 3.4 Wave store ○ Explanation of wave Analysis & explanation of MIN/MAX/Average value 2.2.1 Operating sensor 3 Ignition Secondary wave △ (For US only) View operating value of troubled component 2.1 Measuring wave 4.1.1 A wire snap / a short circuit △ △ △ △ Measuring time of frequency operated by duty Measuring resistor components at each wiring & ○ Realization of SCANNER function from PC 5.1 SCAN Data 5.2 Simulation View communication with ECU 5.3 Store Data and Wave Sending & watching wave after storing 5.4 Function of scope Measuring wave directly Operating components directly 95 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 6. Carman scanUtilization chart (2/3) Actuator related Each function and explanation ● : Judgment ○ : Possible △:Partially possible Blank : Confirmation impossible or unnessary Function of HI-SCAN Pro 1 SCAN DATA Components operated by ECU : Injector / ISC valve/ Purge valve / O2 sensor heater / EGR valve Explanation of function View details of trouble when trouble occurs 1.3 Internal ECU calculation DATA View calculating value internal ECU 1.4 Operation status monitoring 1.5 Simulation Checking status of OBD2 operation 2.1 Measuring wave 2.2 Analysis of wave 2.3 Explanation of wave 2.4 Analysis of Data 2.5 Data store 2.7 Operating Component Measuring signal and operating status directly Measuring consuming status of electrical energy(current) View conversed compression pressure at each cylinder Measuring status of battery charging status indirectly ○ ○ ○ ○ △ △ ○ ○ ○ △ ○ ○ ○ ○ ● ● ○ Measuring pressure of engine vaccum & fuel pump etc. Measuring frequency of duty signal 4.5 4.6 Measuring duty pluse width Measuring proportion of duty signal ON Measuring time of frequency operated by duty Measuring resistor components at each wiring & ○ Realization of SCANNER function from PC 5.1 SCAN Data 5.2 Simulation View communication with ECU 5.3 Store Data and Wave Sending & watching wave after storing 5.4 Measuring wave directly Function of scope ○ Measuring current flowing on ignition coil 4.4 Measuring frequency 5 PC SCAN ○ Measuring status of each wiring & components Measuring temperature 4.7 Measuring resistor ○ Explanation of wave 4.3 Measuring Temperature Measuring duty ○ Sending & watching wave after storing 4.1.4 Measuring Operating curent Measuring current to operating components 4.2 ○ Measuring wave inducting to ignition secondary coil checking if abnormality exists comparing with normal wave Measuring pressure △ Operating component directly 3.2 Analysis of wave 4.1.3 Measuring current at coil ○ Sending & watching wave after storing Measuring ignition secondary wave directly 4.1.2 Cranking test ○ Explanation of wave Analysis & explanation of MIN/MAX/Average value 3.1 Measuring wave Comparing compression at 4.1.1 each cylinder ○ checking if abnormality exists comparing with normal wave Operating actuator directly 4.1 Measuring current ● Measuring signal wave directly Changnig signal of sensor with optional value 4 Function of Multimeter ● Comparing operating sign with scan data 2.2.2 Operating Actuator 3.3 Eaplanation of wave 3.4 Wave store Poor wire View operating value of troubled component 2.2.1 Operating sensor 3 Ignition Secondary wave Component trouble Intermittent trouble Operating modulation View communication with ECU 1.1 Trouble codes 1.2 Data value when trouble occurs 2 Scopemeter A wire snap / a short circuit Operating components directly 96 Carman scanFor EMS PROfesor 6. Carman scanUtilization chart (3/3) Etc Each function and explanation ● : Judgment ○ : Possible △:Partially possible Blank : Confirmation impossible or unnessary Function of HI-SCAN Pro 1 SCAN DATA Watching Watching Checking compression charging status status of pressure at of battery actuator stuck eachcylinder Watching Measuring Receiving pressure of temperature general cmpression of each part technical advice /vaccum Receiving professional technical advice to treat trouble Explanation of function View communication with ECU 1.1 Trouble codes 1.2 Data value when trouble occurs View details of trouble when trouble occurs 1.3 Internal ECU calculation DATA View calculating value internal ECU 1.4 Operation status monitoring 1.5 Simulation Checking status of OBD2 operation 2 Scopemeter View operating value of troubled component Comparing operating sign with scan data Measuring signal wave directly 2.1 Measuring wave Measuring signal and operating status directly 2.2 Analysis of wave checking if abnormality exists comparing with normal wave 2.3 Explanation of wave 2.4 Analysis of Data 2.5 Data store 2.7 Operating Component Explanation of wave Analysis & explanation of MIN/MAX/Average value Sending & watching wave after storing Operating component directly 2.2.1 Operating sensor Changnig signal of sensor with optional value 2.2.2 Operating Actuator Operating actuator directly 3 Ignition Secondary wave ○ Measuring ignition secondary wave directly 3.2 Analysis of wave checking if abnormality exists comparing with normal wave 3.3 Eaplanation of wave 3.4 Wave store 4 Function of Multimeter 4.1 Measuring current Comparing compression at each cylinder 4.1.2 Cranking test 4.1.3 Measuring current at coil ○ Measuring wave inducting to ignition secondary coil 3.1 Measuring wave 4.1.1 having remote help Explanation of wave Sending & watching wave after storing Measuring status of each wiring & components Measuring consuming status of electrical energy(current) View conversed compression pressure at each cylinder Measuring status of battery charging status indirectly △ △ ○ ○ Measuring current flowing on ignition coil 4.1.4 Measuring Operating curent Measuring current to operating components 4.2 Measuring pressure Measuring pressure of engine vaccum & fuel pump etc. 4.3 Measuring temperature Measuring Temperature Measuring frequency of duty signal 4.5 Measuring duty 4.6 Measuring duty pluse width Measuring proportion of duty signal ON 5 PC SCAN ○ ○ 4.4 Measuring frequency 4.7 Measuring resistor ○ Measuring time of frequency operated by duty Measuring resistor components at each wiring & Realization of SCANNER function from PC 5.1 SCAN Data 5.2 Simulation View communication with ECU 5.3 Store Data and Wave Sending & watching wave after storing 5.4 Function of scope Measuring wave directly ○ ○ Operating components directly ○ 97