* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download An overview of the Cold War
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
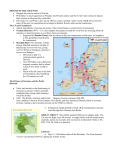
THE BEGINNING OF THE COLD WAR EQ: How can a war be ‘cold’? EQ: What were the Hotspots of the Cold War? WWII is over… Ready for peace? (p.384) After WWII, the USA and the USSR were the two world superpowers (to be powerful enough to influence events throughout the world). The USA was a capitalist society with a democracy. The USSR was a communist country with a dictatorship. Both wanted to be the most powerful nation in the world. Capitalist vs. Communist (p. 384-385) Capitalism Private ownership—People are free to live/work where they want The economy is based on people’s wants/needs Earn your worth—you get paid based on the work you do Social classes—upper, middle, lower Individual > Society (creativity > uniformity) Communism No private ownership—The government often tells people where to live and work The economy is based on government decisions Everything is shared— goods, wages, etc. No social classes—no poor, no rich Society> Individual (uniformity > creativity) The New Struggle (p.384) Even though the USA and USSR were Allies during WWII, they had a much different ideas of how government should be run. This began a war of words, not guns, but once it began it caused tension throughout the world. Countries were fighting to spread their type of government and beliefs to other countries. Now the question was, which would win? After WWII, Europe was split in two (p. 385) After WWII, the world changed! (p.385) Many countries became communist because they were under Soviet rule: - Czechoslovakia (1948) Poland (1947) Hungary (1947) China (1949) (see p. 390) Cuba (1959) North Korea (1945) - See also… p. 394-395 - - The domino effect (p. 390) The USSR had a lot of influence over many of the new communist countries (especially those in Europe). The USA was very worried that the USSR’s influence over these countries was making the USSR and communism more powerful. The USA did not want communism to spread any further – they were worried about the domino effect (one country becomes communist, then another, then another, etc.) “Cold War” (p. 384) The tension and rivalry between the USA and the USSR was described as the Cold War (1945-1990). There was never a real war between the two sides between 1945 and 1990, but there were often hotspots (times when war was very close). Both sides got involved in other conflicts in the world to either stop the spread of communism (USA) or help the spread (USSR). Iron Curtain (p. 385) In Europe, the separation of sides was labeled the “iron curtain” by Winston Churchill in 1946. The term represented the impassable barrier that separated free Europe from communist Europe. The communist countries were said to be “behind the iron curtain,” meaning they were cut off from the rest of the world. VIDEO http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?gui dAssetId=F28AB7D5-9526-4D86-99EF1053D8ACCA32&blnFromSearch=1&productcode =US (Stop at 11:51) Berlin, Korea, and NATO EQ: How can a war be ‘cold’? EQ: What were the Hotspots of the Cold War? Germany divided After World War II, Germany was divided into four zones, occupied by French, British, American, and Soviet troops. The capital city, Berlin, was also divided into four sectors. Soviet blockade: East Berlin West Germany East Germany West Berlin • In June of 1948, the French, British and American zones were joined into the nation of West Germany after the Soviets refused to end their occupation of Germany. Germany – divided (p.386) Germany and its capital were now split in two. Germany’s capital, Berlin, was located in East Germany, but West Germany still controlled a small part of it. West Germany and West Berlin were free. East Germany and East Berlin became communist. Berlin- also divided (p.386) The Soviets did not want the Western Allies in the capital city, so they cut off West Berlin from the rest of the world with a blockade (to prevent entry or outside communication). They blocked highways, railways, water routes, etc. and would not allow any food or fuel into the city. The Berlin Airlift (p.386, 388) President Truman decided to avoid the blockade by using airlifts (using planes to fly in food and other supplies) to supply the needy people of West Berlin. At times, over 5,000 tons of supplies arrived daily. British and American pilots did this for 11 months, and so the Soviets finally backed down and allowed land deliveries again. The Berlin Wall (p. 387) After the blockade ended, many people tried to escape the communist rule in East Berlin by sneaking over to West Berlin. In 1961, the East Berlin government and Soviets built a concrete wall to keep people from leaving. Sentries, soldiers hired to keep watch, with guns guarded the wall ready to shoot anyone that tried to sneak across. This wall, the Berlin Wall, became a real “iron curtain” in the city of Berlin, and it became one of the most wellknown symbols of the Cold War. The Berlin Wall, 1961 The Berlin Wall was built in 1961 to keep East Germans from escaping to West Germany. View of the Berlin Wall from the West http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Berlinermauer.jpg Where’s Korea? The Korean War (p.392) Like Germany, Korea was also divided in two parts after WWII. The USSR supported North Korea, and the USA supported South Korea. In 1950, North Korea, with the help of China, invaded South Korea in hopes of making the entire nation communist. The USA and United Nations sent soldiers to aid South Korea in their fight. The Korean War, 1950-1953 War = Stop to Communism? However, so many American soldiers were dying the war, that it soon became a controversy as to whether the USA should even be a part of the war or not. Dwight D. Eisenhower, a famous WWII general, promised the people that he would end the war if he was elected president. The people believed him and elected him as President in 1952. One year later, President Eisenhower was able to keep his promise. The North Korean troops were pushed back to North Korea, and a cease-fire was signed in 1953. South Korea was still independent. NATO (p. 386) Another way the USA tried to stop the spread of communism was through the formation of an alliance with other countries in 1949. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was formed. It stated, “The Parties of NATO agreed that an armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North America shall be considered an attack against them all.” List of current countries a part of NATO: http://www.nato.int/cps/en/natolive/nato_countries.htm All the countries a part of NATO