* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio Lab: Flower Dissection
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
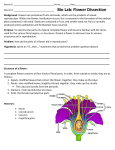
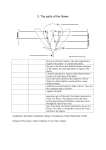
Botanist 1: ______________________________________ Date: _____________________________ Period: ______ Botanist 2: ______________________________________ Bio Lab: Flower Dissection Background: Flowers are premature fruits and seeds, which are the products of sexual reproduction. Within the flower, fertilization occurs; this is essential to the formation of the embryo plant contained in the seed. Seeds are contained in fruit, and neither seed nor fruit is normally produced unless pollination and fertilization have occurred. Procedure (Be sure to answer all questions using your best writing skills): 1. Locate the outermost layer of flower parts. This is the calyx, which is composed of sepals. Note: Some flowers’ sepals are the same color and size as the petals. Carefully remove the sepals. a. On your data table: Record the number of sepals, attach one with tape to the proper box, and describe its function. 2. Identify the corolla; these are the petals that form the next layer of flower parts. Carefully remove each petal. a. On your data table: Record the number of petals, attach one with tape to the proper box, and describe its function. b. Do the sepals and petals resemble each other in size and color? Explain. Purpose: To examine the parts of a typical complete flower and become familiar with the terms used for the various floral organs, or structures. Dissect a flower to discover how its various structures aid in reproduction. Problem: How do the parts of a flower aid in reproduction? Hypothesis (Write an “If…,then…” statement that answers the problem question above): ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ What term is used for the entire floral envelope (calyx and corolla)? _________________________ d. Why are these two parts referred to as “accessory parts”? __________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________ Structure of a flower: ______________________________________________________________________________________ e. A complete flower contains all four kinds of floral parts. In order, from outside to inside, they are as follows: 1. Sepals: Modified leaves that protect the flower; together, they make up the calyx. 2. Petals: Also modified leaves, brightly colored; together, they make up the corolla. • The calyx and corolla form the entire floral envelope called the perianth. 3. Stamens: Male reproductive structure made of the anther and filament. 4. Pistil (Many fused CARPELS): Female reproductive parts. What is the function of these two parts? __________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Are your flower parts represented by multiples of 3, 4, or 5? ________________________________ f. Circle one, is your flower a: Monocot Dicot g. Now locate the stamens. These male flower parts should now be exposed. Carefully remove the stamens with forceps. On your data table: Record the number of stamens, attach one with tape to the proper box, and describe its function. LABEL the anther and filament. How does number of stamens compare with the number of parts in the calyx and corolla? h. Materials: • • • • • c. ______________________________________________________________________________________ Flower Pencil Forceps (tweezers) Magnifying glass Tape (I will come around and hand this out) ______________________________________________________________________________________ (Pistil = Many carpels fused together) 3. The female flower parts remain. Most flowers have several carpels fused together, forming a structure called the pistil. On your data table: Record the number of pistil(s), attach one with tape to the proper box, and describe its function. LABEL the carpel(s), pistil, stigma, style, and ovary. a. How do the number of female flower parts compare with other parts of the flower? ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Data Table (It is okay if the structures don’t fit perfectly in their box – they can overlap a little): Flower Part # of parts Attach one of each part below Description of function Analyze and Conclude (Be sure to answer all questions using your best writing skills): 1. Do flowers usually contain more stamens or carpels? Why do you think this is? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Sepal _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does the position of the anthers relative to the position of the stigma suggest about how this flower is pollinated? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Petal _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________________________________ (Label the anther and filament) _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ Stamen Using the description of the stigma from the data, suggest reasons for its appearance as it relates to its function. _________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the necessity of having a stigma supported by a style? _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ (label the stigma, style, and ovary) _________________________________________________________________________________________ Pistil(s) For the next two questions locate a microscope set‐up by your teacher – DO NOT TOUCH THE SETTINGS!!!!! 5. Take a look at the prepared slide of a ranunculus stem (vascular tissue). What type of plant is this? (circle one) a. Monocot b. Dicot 6. Take a look at the ovary cross section: What is the name of the structure that is being pointed to? ____________________________________ 7. Looking at the cross section of the ovary, how many seeds would be produced? __________________