* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics Visual Glossary and Atlas
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
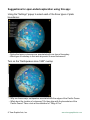
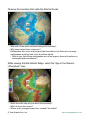
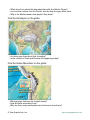
Plate Tectonics Visual Glossary and Atlas ########## ########## ########## ########## ########## Available for iOS and MacOS, this glossary and atlas app provides an excellent supplement to your Earth science curriculum. ################################ ################################ ############################## ############################## ¯ How to use this app in your classroom In addition to providing a comprehensive list of terms, definitions, illustrations, and animations related to plate tectonics, the app can also be used as a tool for inquirybased exploration of the Earth’s surface, tectonic plates, plate boundaries, ocean floor features, geography, etc. The app has many geographical locations labeled and described so that the app can be used for geography lessons as well. The "Settings" button allows the selection of different surface maps and the visibility of overlays. Also, there is a "Help" button with an overview of how to use the app. Concepts that can be reinforced using this app: • • • • • • The different types and characteristics of plate boundaries. The basic locations and frequency of different types of plate boundaries. Earthquakes and volcanoes are associated with certain types of plate boundaries. Where and how mountains form. Seafloor spreading occurs at mid-ocean ridges (which are plate boundaries). Maps convey information about actual locations on Earth’s surface. • Identifying locations using latitude and longitude coordinates (using the 15° overlay grid). • How the composition of Earth’s interior relates to the driving force of plate tectonics. • Hot spots and plate movement and their role in island, seamount, and volcanic development. © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com Higher-order thinking skills supported by this app: • Analyzing data to determine the characteristics of different types of plate boundaries. • Classify and describe the characteristics of the different types of plate boundaries. • Determine which boundary types have the greatest earthquake or volcanic hazards. • Observe evidence of seafloor spreading and draw conclusions about the movement of tectonic plates. • Write about scientific theories such as plate tectonics and support conclusions with scientific evidence. • Incorporate the definitions contained in the glossary into written evidence. • Visualize data in 3D that is traditionally represented in 2D. Using the glossary list: The glossary list allows individual terms to be selected (tapped) to reveal their definition. Within each definition are links to other terms or to locations. Tap the icon for each term to see the definition and image or animation on the globe. Tapping a "pin" or "volcano" icon spins the globe to a location and describes the geology there. The description may include a photo, illustration, or animation. When a definition is displayed on the globe, tapping links within the definition will present new definitions on the globe. © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com Suggestions for open-ended exploration using this app: Using the "Settings" popup to select each of the three types of plate boundaries: • Notice that many volcanoes are associated with one type of boundary. • What type of boundary is that and why would it cause volcanoes? Turn on the "Earthquakes since 1900" overlay: • Why are these major earthquakes associated with the edges of the Pacific Ocean. • What about the location of volcanoes? Do they align with the boundaries of the Pacific Ocean? Take a look at the definition for "Ring of Fire." © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com Observe the boundary that splits the Atlantic Ocean: • Why aren't there more volcanoes along the boundary? • Why does Iceland have volcanoes? • Earthquakes also occur at divergent plate boundaries, but these are not major earthquakes and they tend to be at shallow depths. • Why do you think these earthquakes are not as large as those at transform or convergent plate boundaries? While viewing the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, select the "Age of the Oceanic Lithosphere" map: • What does this map tell you about this boundary? • What do the colors mean? • Where is the youngest ocean floor located? the oldest? © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com • What does it say about this boundary that splits the Atlantic Ocean? • Look at other oceans, like the Pacific, and see how the ages differ there. • Why is the Mediterranean dark purple? Any ideas? Find the Himalayas on the globe: • Are there any clues about their formation? • Is the collision of India and Eurasia still happening today? Find the Andes Mountains on the globe: • What geologic features are located nearby? • How did these mountains form? • Why are there many earthquakes and volcanoes found here? © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com Find the Hawaiian Islands on the globe: • Why are volcanoes found here? • How are the present-day islands different than the Hawaiian Seamounts? • Can you find similar examples at other locations on the globe? Turn off all layers and boundaries and explore the surface of the Earth: • Describe what you see. Draw conclusions about: • the depth of the oceans, • the heights of mountain ranges, • the locations of volcanoes, • and where big earthquakes are located. • Describe what the colors mean on the "physiographic" map (the default surface map). © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com Tap any of the "pin" icons in the List of Terms: • Think about the features at each pin location and their relationship to plate boundaries and/or plate motion. • Describe what’s happening at that location in your own words. Choose a location with an active hot spot (such as Tristan da Cunha): • Discuss the formation of hot spots, their relation to volcanic islands, and what happens when plates move over them. • What happens when the hot spot is on a divergent plate boundary? • Is there another location like Tristan da Cunha? Explain your reasoning. © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com Find the Yellowstone Hot Spot on the globe: • Describe the geological activity here (hint: see Yellowstone Caldera). Find the term "Tsunami" in the list. Tap on the image icon to view the definition on the globe. Scroll down within the definition to find the locations of significant tsunamis and tap each one. • What are the similarities and differences between them? • Why did they cause so much damage? Select specific plates in the glossary list (i.e. African plate): • Describe why and how each plate is changing size and location (see the term "Spreading rate" for more information). Compare and contrast the Mariana-type subduction zone to the Peru-Chiletype subduction zone. © Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. www.tasagraphicarts.com