* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Napoleon - World Civ at DHS with Mrs. Thomsen
Reign of Terror wikipedia , lookup
Causes of the French Revolution wikipedia , lookup
French Revolutionary Wars wikipedia , lookup
War of the Fifth Coalition wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Amiens wikipedia , lookup
Germaine de Staël wikipedia , lookup
Hundred Days wikipedia , lookup
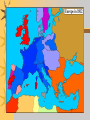
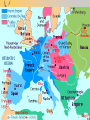
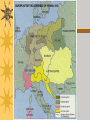
Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte to the Congress of Vienna Basics 4 Vocab Three estates – France’s 3 social classes: the clergy (1st), the nobility (2nd), and everyone else (3rd) Bourgeoisie – the middle class and highest level of the 3rd estate Estates-General – France’s legislative, law-making, body in which each estate had one vote National Assembly – Revolutionary legislature formed when the 1st & 2nd estates locked the 3rd estate out of the Estates-General Tennis Court Oath – Oath taken by the National Assembly to not leave until there was a new French Constitution More Basics 4 Vocab Bastille – Parisian prison that was destroyed July 14th 1789 as crowds searched for weapons and gunpowder to protect themselves from the French Army Sans-culottes – working class revolutionaries who pushed for a republic and wanted to end the monarchy Jacobins – middle class lawyers and intellectuals who were in favor of a republic Émigré – clergy and nobles who fled France and revolutionaries with tales of mob violence that frightened many European monarchs Last slide of Basics 4 Vocab Suffrage – the right to vote Robespierre – leader of the Committee of Public Safety, a Jacobin, he took control of the French Revolution and began the Reign of Terror Reign of Terror – September 1793 – July 1794 which tried about 300,000 individuals and executed 17,000 “enemies of the revolution” Nationalism – feelings of pride and love for one’s country Area of Concern France Poland Saxony German Confederacy Lowlands Italy Finland French and Dutch Colonies Slave Trade Holy Alliance What else?? Description of decision Napoleon a Rising Star 1795-At 25 – hero of the Republic of France 1796-At 26 – “the General” led victories over enemy forces 1799-At 30 – control of France’s Military – coup d’etat (blow of state) • Used his troops and influence to take over the government of France A leader at last… Coup led to a victory over anti-French powers – Britain, Austria and Russia 1800- vote of the people (plebiscite) – all real power given to Napoleon • vote overwhelmingly in favor of Napoleon Stability and Order Napoleon wanted: – Strong central government – Strong Economy 1. Equality in Taxation 2. Effective tax-collection 3. National Bank – End of Corruption • Wanted to keep some of the same changes that were made during the Revolution Napoleonic Code Code of Laws – Would end many injustices – promoted order But… – Women lost many rights – Freedom of Press and Speech limited – Restored slavery in the French colonies Emperor Napoleon crowns himself and wife- December 2nd 1804 Colonies started to revolt Revolutionary ideas start to spread around the world – Reached the people of St. Domingue (Haiti) • Demanded that they be given the same freedoms as the French people – What other “colonial” event does this sound like? • They were denied and civil war erupted – Slaves under Toussaint L’Ouverture led a rebellion and seized the colony! Continued… Napoleon decides to back out of the Americas – Sells Louisiana Territory • $15 million to President Jefferson and the US – What did he gain? • Money to conquer Europe • Punishment for the British Napoleon starts to lose power Battle of Trafalgar – British fleet separates the French • French CANNOT defeat the British, now what? Does not have an heir – Divorces his wife, marries into the Austrian family to create an alliance • Napoleon II is born Continental System – Tries to starve out the British Russia The BIG mistake: Who? The BIG mistake: What? Napoleon attacks the only rival left on the mainland of Europe The BIG mistake: HOW? Over 600,000 men! The BIG mistake: Russia retaliates! Why is this effective? The BIG mistake: What is Napoleon’s next move? Wait in Moscow for the Russians to surrender Do they?? NO! Napoleon is defeated! Running low on supplies Soldiers start dying What happens after? Napoleon withdrawals his army – 600,000 to start – 28,000 at the end of the attack!! Napoleon – Leaves his army – Attempts to rebuild in France – Other European powers unite to defeat him in 1813 Exile—Return—Exile Exiled to the small island of Elba (Italy) – Why not just kill him? Napoleon escapes and for 100 days returns to be Emperor of France but is defeated at Waterloo (1815) – Monarchy temporary restored, people fear “the old days” Re-exiled to St. Helena (South Atlantic) Died in 1821 of a stomach ailment Peace—Congress of Vienna The five “great” powers of Europe – Austria, Russia, Prussia, Britain and France (under a new King) – How to deal with Europe after Napoleon’s Empire is dismantled? The two big goals: Return the royal families to their rightful thrones 1. – Any democratic movement was a threat! Prevent another war—Balance of Power 2. – If one power attacks another the rest will join against the attacker Nationalism Devotion and loyalty to a nation Why is nationalism considered a side effect of the French Revolution, Napoleon’s rule, and the Congress of Vienna? Hero Tyrant Add a 1 paragraph summary to the end of your notes! Area of Concern France Poland Saxony German Confederacy Lowlands Italy Finland French and Dutch Colonies Slave Trade Holy Alliance What else?? Description of decision