* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Trench Warfare in WWI
History of the United Kingdom during the First World War wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
American entry into World War I wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War I wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War I wikipedia , lookup
History of Germany during World War I wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War I wikipedia , lookup
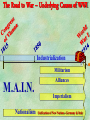
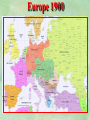
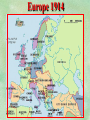
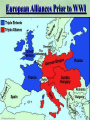
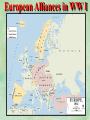
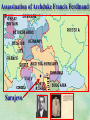
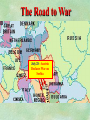
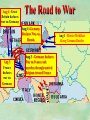
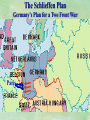
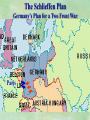
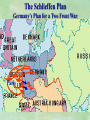
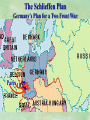
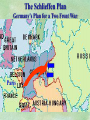
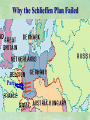
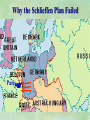
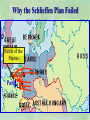
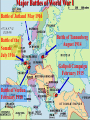
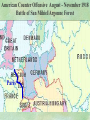
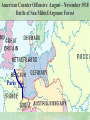
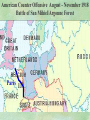
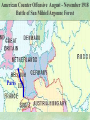
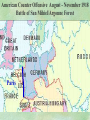
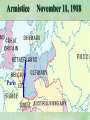
THE GREAT WAR 1914-1918 “The War to End all Wars” The Road to War – Underlying Causes of WWI Industrialization Militarism M.A.I.N. Nationalism Alliances Imperialism Unification of New Nations – Germany & Italy Europe 1900 Europe 1914 Underlying Causes of World War I Militarism Most European countries began drafts. Germany began building a navy to rival Britain. Britain increased its navy to stay ahead. Other nations joined in the arms race to keep up and to showcase their military advances. Industrialization encouraged mass production of new weapons and war technologies. Underlying Causes of World War I Alliances Dual Alliance (1879) – Secret defensive alliance between Germany and Austria-Hungary which guaranteed mutual support if either was attacked by Russia. Triple Alliance (1882) - Italy joined the secret Dual Alliance because of anger toward France. Franco-Russian Alliance (1894) - Russia and Germany break relations. France joined Russia in a secret alliance. Triple Entente (1907) - Britain joined France and Russia in an alliance to counter the Triple Alliance . European Alliances Prior to WWI European Alliances in WW I Underlying Causes of World War I Imperialism European countries fought over territory in Africa and Asia Germany entered the race for empire after its unification, particularly in Africa. The Congress of Berlin (1878) preserved an uneasy peace between European imperialist powers because of Bismarck’s diplomacy. Underlying Causes of World War I Nationalism Unification of Germany and Italy caused a shift in the balance of power National rivalries led to policies of expansion. Intense patriotism fanned the flames for war. Balkan States wanted independence from Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman Empires. Russia and Austria sought stronger influence in the Balkans. Underlying Causes of World War I International Anarchy Newspapers caused resentment and encouraged violent acts of protest No strong international organizations existed to settle disputes Political Assassinations destroyed stability 1881 - Alexander II of Russia killed by bomb 1898 - Empress Elizabeth of stabbed to death 1901 - US President William McKinley assassinated by anarchist Immediate Cause of World War I Assassination of Austrian Archduke Francis Ferdinand and his wife • On June 28, 1914, the heir to the Austrian throne Francis Ferdinand and his wife were assassinated by a young Serbian nationalist in Sarajevo. • The assassination sparked a chain reaction which would plunge Europe and other nations into the world’s first global war. Assassination of Archduke Francis Ferdinand Sarajevo The Road to War July 26, 1914 - Austria gets a guarantee of support from Germany and issues an ultimatum to Serbia. Its demands that Serbia: • Stop all anti-Austrian propaganda • Dismiss all anti-Austrian government officials • Allow Austria into Serbia to investigate the assassination July 27, 1914 - Serbia receives a promise of support from Russia and rejects the ultimatum July 28, 1914 - Austria declares war on Serbia The Road to War July 28 - Austria Declares War on Serbia The Road to War August 1, 1914 - Russia begins to mobilize along German border. Germany declares war on Russia August 3, 1914 - Germany declares war on France. They begin marching through neutral Belgium toward France. France declares war on Germany. August 4, 1914 - Great Britain, which had pledged to protect Belgium’s neutrality, declares war on Germany. Aug 4 - Great Britain declares war on Germany The Road to War Aug 1 -Germany Declares War on Russia Aug 3 France declares war on Germany Aug 3 - Germany declares War on France and marches through neutral Belgium toward France Aug 1 - Russia Mobilizes Along German Border The Road to War August 14, 1914 - China declares war on Germany August 24, 1914 - Japan declares war on Germany November 1, 1914 - Russia declares war on the Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans join Germany and Austria. Bulgaria later joins. They become known as the Central Powers. April 26, 1915 - Italy joins Great Britain, France, Russia, Belgium, and over 30 other countries. They become known as the Allied Powers. Central Powers • Germany • Austria-Hungary • Bulgaria • Turkey (Ottoman Empire) Allied Powers •Great Britain •France •Italy •Russia •Japan •United States (1917) & over 30 other countries Europe Prepares for War Europe Prepares for War Europe Prepares for War Europe Prepares for War Europe Prepares for War Europe Prepares for War Europe Prepares for War THE GREAT WAR Early German Strategy The Schlieffen Plan Lure France into attacking Alsace and Lorraine on the French/German border with minimal German troops defending. Send overwhelming force through Belgium and capture Paris Sweep back to the east entrapping French forces in a vice between two German armies Defeat France then move troops to the Eastern Front to fight Russia. The Schlieffen Plan Germany’s Plan for a Two Front War Paris The Schlieffen Plan Germany’s Plan for a Two Front War Paris The Schlieffen Plan Germany’s Plan for a Two Front War Paris The Schlieffen Plan Germany’s Plan for a Two Front War Paris The Schlieffen Plan Germany’s Plan for a Two Front War Paris Why the Schlieffen Plan Failed Paris Why the Schlieffen Plan Failed Paris Why the Schlieffen Plan Failed Battle of the Marne Paris The war becomes stalemated after the Battle of the Marne and both sides begin to dig in. Trenches stretched for 300 miles from Switzerland to the English Channel. Trench warfare results because of technological advances in weapons. Trenches TECHNOLOGY & WAR Technology turned WWI into an Industrial War. Military tactics were unable to stay up with the changes in technology. Communications, transportation, munitions … New weapons changed the tactics of warfare and led to a stalemated “war of attrition” TECHNOLOGY & WAR Machine guns - led to trench warfare and a stalemated war. TECHNOLOGY & WAR Poison Gas - First used by Germany in 1915 despite treaties outlawing it. Suffocated and blinded victims. TECHNOLOGY & WAR Tanks - Developed by British in 1916. Eventually helped break the stalemate. TECHNOLOGY & WAR Airplanes - First used for reconnaissance and later for primitive bombing. TECHNOLOGY & WAR Submarines (U-Boats) - Unrestricted Submarine Warfare led to American entry in 1917. Total War World War I was the first “total war” in which all of the resources of a nation were put into the war effort. Many citizens were targeted or became victims of the war effort Women – were forced to work in munitions plants and factories and to tend to agricultural duties Governments began rationing of food and other supplies to provided enough for the men on the front Governments began censoring and controlling news accounts to build support for the war on the home front. Trench Warfare in WWI Trench Warfare in WWI Trench Warfare in WWI Trench Rats Many men killed in the trenches were buried almost where they fell. If a trench subsided, or new trenches or dugouts were needed, large numbers of decomposing bodies would be found just below the surface. These corpses, as well as the food scraps that littered the trenches, attracted rats. One pair of rats can produce 880 offspring in a year and so the trenches were soon swarming with them. "Rats came up from the canal, fed on the plentiful corpses, and multiplied exceedingly. While I stayed here with the Welch. a new officer joined the company and, in token of welcome, was given a dug-out containing a spring-bed. When he turned in that night he heard a scuffling, shone his torch on the bed, and found two rats on his blanket tussling for the possession of a severed hand." Trench Warfare in WWI Trench Rats …there were rats as big as cats". ....They were so big they would eat a wounded man if he couldn't defend himself." These rats became very bold and would attempt to take food from the pockets of sleeping men. Two or three rats would always be found on a dead body. They usually went for the eyes first and then they burrowed their way right into the corpse. One soldier described finding a group of dead bodies while on patrol: "I saw some rats running from under the dead men's greatcoats, enormous rats, fat with human flesh. My heart pounded as we edged towards one of the bodies. His helmet had rolled off. The man displayed a grimacing face, stripped of flesh; the skull bare, the eyes devoured and from the yawning mouth leapt a rat." Trench Warfare in WWI Trench Foot and Amputations Trench Warfare in WWI Children on the Front Officer (to a boy of 13 who has given his age as 16): "Do you know where boys go who tell lies?" Applicant: "To the Front, Sir." George Maher, who was only 13 at the time, claims that Lewis was too short to see over the edge of the trench. "The youngest was 12 years old. A little nuggety bloke he was, too. We joked that the other soldiers would have had to have lifted him up to see over the trenches. the Top No Over Man’s Land Trench Warfare in WWI Trench Warfare in WWI Poison Gas Poison Gas Deaths: 1914-1918 Country NonFatal Deaths Total British Empire 180,597 8,109 188,706 France 182,000 8,000 190,000 United States 71,345 1,462 72,807 Italy 55,373 4,627 60,000 Russia 419,340 56,000 475,340 Germany 191,000 9,000 200,000 AustriaHungary 97,000 3,000 100,000 Others 9,000 1,000 10.000 Total 1,205,65 5 91,198 1,296,85 3 An estimated 91,198 soldiers died as a result of poison gas attacks and another 1.2 million were hospitalized. The Russian Army , with 56,000 deaths, suffered more than any other armed force. Death in the Trenches German Notice Placed in American Newspapers in April 1915 IMPERIAL GERMAN EMBASSY, Washington, D.C. 22nd April 1915 NOTICE! TRAVELLERS intending to embark on the Atlantic voyage are reminded that a state of war exists between Germany and her allies and Great Britain and her allies; that the zone of war includes the waters adjacent to the British Isles; that, in accordance with formal notice given by the Imperial German Government, vessels flying the flag of Great Britain, or any of her allies, are liable to destruction in those waters and that travelers sailing in the war zone on the ships of Great Britain or her allies do so at their own risk. Sinking of the Lusitania May 7, 1915 Sinking of the Lusitania May 7, 1915 • 1959 People on Board. • Sank 8 Miles of the Irish Coast. • 1198 Men, Women, and Children died including over 120 Americans. • Turned Public Opinion against Germany. • Instrumental in bringing America into the war in 1917. Sinking of the Lusitania May 7, 1915 American Entry Into the War Major Battles of World War I Battle of Jutland May 1916 Battle of the Somme July 1916 Battle of Tannenberg August 1914 Galipoli Campaign February 1915 Battle of Verdun February 1916 American Entry Into the War The Zimmerman Telegram American Entry Into the War American Entry Into the War American Entry Into the War The United States Declares War against Germany on April 1, 1917 President Woodrow Wilson asks Congress for a Declaration of War April 1, 1917 American Counter Offensive August - November 1918 Battle of San Mihiel/Argonne Forest Paris American Counter Offensive August - November 1918 Battle of San Mihiel/Argonne Forest Paris American Counter Offensive August - November 1918 Battle of San Mihiel/Argonne Forest Paris American Counter Offensive August - November 1918 Battle of San Mihiel/Argonne Forest Paris American Counter Offensive August - November 1918 Battle of San Mihiel/Argonne Forest Paris Armistice Paris November 11, 1918 Armistice! November 11, 1918 - 11:00 AM “The Eleventh Hour of the Eleventh Day of the Eleventh Month” Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points Major Points Right to self-rule Right to free trade Free Access to the seas by all nations An international peace keeping body “League of Nations” The Treaty of Versailles The Hall of Mirrors in the Palace of Versailles The Treaty of Versailles The Big Four George Clemenceau – France David Lloyd George – Great Britain Vittorio Emanule Orlando – Italy Woodrow Wilson – United States The Treaty of Versailles What Resulted? • Wilson wanted all countries to share equally in peace “Peace without Victory” • The other countries wanted revenge on Germany • • • • Germany was required to accept all blame for the war. Required to pay $33 Billion in reparations to the Allies. Germany was forced to disarm its military. A demilitarized zone (the Rhineland) set up between Germany and France. • Redrew the map of Europe from land of Central Powers. • The seeds of future war were sewn with the harsh terms of the treaty and the humiliation of Germany.