* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slides - Prof. Emily Block
Development economics wikipedia , lookup
Race and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Ethnoscience wikipedia , lookup
Discrimination based on skin color wikipedia , lookup
Industrial and organizational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Multiliteracy wikipedia , lookup
Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory wikipedia , lookup
Multiculturalism wikipedia , lookup
Structural inequality wikipedia , lookup
Nations and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural differences in decision-making wikipedia , lookup
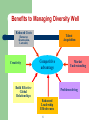
Diversity 1 What is Workforce Diversity? Race Gender Age Workforce diversity Disability Ethnicity Culture Education Religion A Definition of Workforce Diversity Workforce diversity is the varied perspectives and approaches to work that employees bring into the workplace. These differences in perspective and approach have many sources, including: – – – – – Training and Education Job Function Past Work Experience Age Gender, Race/Ethnicity Diversity Management versus EEO Equal employment opportunity means treating people fairly and equitably and taking actions that do not discriminate against people in protected classes on the basis of some illegal criterion. Diversity management places a much heavier role on recognizing and appreciating differences among people at work and attempting to accommodate those differences to the extent that is feasible and possible. Why We Should Care About Diversity Legal Reasons Business Reasons – – – – – Diversity of the Labor Pool Costs of higher turnover & absenteeism, and discrimination lawsuits Inability to attract, retain, and promote diverse employees puts you at a competitive disadvantage You’re not mobilizing your best people Diversity creates organizational value 5 Benefits to Managing Diversity Well Reduced Costs Talent Acquisition (Turnover, Absenteeism, Lawsuits) Creativity Competitive advantage Build Effective Global Relationships Market Understanding Problem-solving Enhanced Leadership Effectiveness 6 What are the Causes of Lack of Diversity? Demand Factors Assumptions about differences in behaviors as a function of demographic differences – – – – Attitudes and behaviors toward “different” others – – Hiring decisions Compensation decisions Promotion decisions Transfer decisions “Old Boys” Network – women omitted from “informal” structure Male managers “protect” women Discrimination 7 What are the Causes of Lack of Diversity? Supply Factors Lack of Role Models – – – Job Segregation Leaves Some Groups Unprepared Attitudes and behaviors toward women – Application and job transfer decisions Tokenism Lack of career mentoring opportunities Discrimination and harassment discourage other’s participation Work – Life Issues – – Women are more likely to raise children and be care-givers Failure to accommodate religious / cultural differences 8 Barriers to Selecting a Diverse Workforce We like people who are like us (similarity is the single most important basis of interpersonal attraction and liking) We all unconsciously rely on cognitive “shortcuts” that can lead to biased selection decisions: – Implicit personality theory – Stereotyping – Halo effect These shortcuts are most likely to be activated in situations where we have to process a lot of new information (e.g., interviews) 9 How Do You Manage Diversity? Be committed and provide leadership Create policies and structures that accommodate the differences between demographically different employees Invest in training ALL your employees – – – Provide training – particularly to demographic minorities Make employees aware of subtle discrimination Provide behavioral advice, education, & socialization to minorities Remove structural barriers – – – – Assign coaches and mentors Be aware of how you make job assignments Pay attention to the numbers and “relative” numbers Change the social norms. 10 As if it were not complicated enough… We all have multiple identities. Some examples: – – – – – – – Gender Race/Ethnicity Age Occupation/Major Organizational Membership Formal Roles (e.g., Manager) Social Roles (e.g., Son) At any moment in time one of these identities is more salient than the others. The situation determines which of these identities is most salient. We All Have Multiple Identities Because we all have multiple identities, each of us contains, within ourselves, a diversity of perspectives and approaches. Thus, diversity in the workplace comes from both: – Differences BETWEEN individuals – Differences WITHIN individuals Hint: This is why I made you do the exercise twice Making Differences Matter The article by Thomas and Ely identifies three paradigms or models for managing diversity: – – – Discrimination and Fairness Access and Legitimacy Learning and Effectiveness What are each of these paradigms or models? Three Paradigms for Managing Diversity Discrimination and Fairness – – – The demographic makeup of the organization should reflect the demographic makeup of society. All employees should be treated equally and with respect An emphasis on sameness (“we are all essentially the same”) Three Paradigms for Managing Diversity Access and Legitimacy – – – In order to be successful, we must serve consumers from many countries and with many demographic backgrounds We need a demographically diverse workforce to serve our diverse markets. Diversity is a critical business issue. An emphasis on differences. Three Paradigms for Managing Diversity Learning and Effectiveness – – – – Both fairness and acknowledging differences are important The organization needs to do more than acknowledge differences, it needs to learn and create new opportunities from them. We are all on the same team with our differences not despite them. Focus on common goals Three Paradigms and Multiple Identities Discrimination and Fairness: eliminate or deny multiple identities Access and Legitimacy: highlight and focus on a single identity Learning and Effectiveness: learn from different perspectives provided by multiple identities To Move Toward Learning & Effectiveness: 8 Preconditions for Leadership …. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 18 Understand that a diverse workforce embodies different perspectives and approaches to work Be committed to a long process of learning and relearning Create a culture of an expectation of high standards of performance for everyone Create a culture that stimulates personal development Create a culture that encourages openness Create a culture that makes workers feel valued Have a well-articulated and widely understood mission Have a relatively egalitarian, non-bureaucratic structure