* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9/13/07 Math 31 Handout: Section 3
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
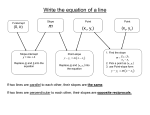
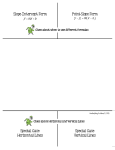
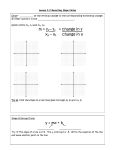
Math 125 Exam 1 Checklist and Focus Problems Homework Due: Chapters 1, 2, 3 (except 2.4 and 3.4) Calculators NOT allowed for this exam Section 1.1 Focus Problems: From the exercises at the end of each section 11th Edition! (Warning! I choose these problems based on the level for the exam. The 10th edition may not reflect the same types of problems.) 21 Key notes 1.2 1.3 47, 65, 79 81 11 37, 41, 47 65, 73 1.4 39 43, 45 2.1 21, 29 59 23, 33, 41 2.2 3, 7, 9 Know the following sets of numbers and how they relate to each other: Natural numbers Whole numbers Integers Rational numbers Irrational numbers Real numbers Know the decimal representations of rational numbers (terminates or repeats) Know the decimal representation of irrational numbers (does not terminate, does not repeat) Be able to perform operations on real numbers: Add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers, fractions, decimals Division by zero is undefined Work with positive exponents Work with square roots (know all square roots of perfect squares up to 225 Use the order of operations to simplify expressions Simplify algebraic expressions Know the commutative, associative, distributive properties Solve linear equations and know how to check your answers (by substituting answer back into original equation) Solve equations with fractions (clear denominators first) Special cases: Equations which have solution set “all real numbers” Equations which have “no solution” solution set is the empty set Solve formula for specified variable 1 2.3 2.5 7, 11 17 39 49, 55 13, 17, 29 37, 39 2.6 21, 23, 27 35, 45 2.7 9, 69 33, 41, 71, 73 93, 103 101 3.1 9 35 45, 49 3.2 25, 31 23 67, 69 Write algebraic expressions Set up, solve, and answer application problems Remember to define your variable Remember to answer with the correct units of measurement and use a complete sentence. Solve interest and mixture problems See Handout on Word Problems Solve linear inequalities, write solution set using interval notation, and graph on number line Note: the only time the inequality direction is reversed is when you multiply or divide by a negative number Special cases: If variable is eliminated in the process and the resulting statement is true (such as 0 < 2), then the solution is all real numbers , If resulting statement is false (such as 5 < 3), then there is no solution, solution set is Know the difference between “and” and “or” Find solution set to compound inequalities Solve compound inequalities, write final solution set using interval notation, and graph Know definition of absolute value (distance of a number from 0) Solve absolute value equations Solve absolute value inequalities Be careful, sometimes the solution set is , or Remember, first step is to isolate the absolute value. See Summary Box on page 113, and Caution Box on page 115. Know what an ordered pair (x, y) means and how to plot it on a rectangular coordinate system. Know the Quadrants (I, II, III, and IV). Know: x-intercept is the point on the line that crosses the x-axis, yintercept is the point that crosses the y-axis. Coordinates of x-intercept is (x,0); y-intercept is (0, y). Determine the intercepts from an equation: letting y = 0 gives the x -intercept, letting x = 0 gives the y - intercept. Graph a line by using x and y intercepts Identify the equations of a vertical and horizontal line, and graph them: x = a is a vertical line, y = b is a horizontal line. Know the formula for slope. Know how to find the slope of a line, given two points. Know what each type of slope looks like: positive slope, negative slope, zero slope, undefined slope Be able to identify the slopes of a horizontal line and a vertical line: A horizontal line has slope = 0. A vertical line has undefined slope. Using slopes, determine if lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. Note: slopes of parallel lines are the same; slopes of perpendicular lines are opposite reciprocals of each other 2 3.3 31 21 35, 61 45, 47 69, 71, 73 85 3.5 9, 11 27, 29, 31 3.6 5, 15, 19 23 31 37 45 51 Know the standard form of the equation of a line Know the slope-intercept form of the equation of a line. Know how to use the slope-intercept form to determine the line’s slope and y-intercept, solving for y if necessary. Graph a line using slope and y-intercept Be able to write down the equation of a line given its slope and yintercept. Example: Write down the equation of a line passing through (0, -5) with slope 8. Answer: y= 8x – 5 Know the point-slope form of the equation of a line. Know how to write the equation of a line using the point-slope form, then rearrange to get the slope-intercept form or the standard form Be able to write down the equation of a line given information about the line and its relationship to another line. Solve application problems. See Handout on 3.3, Know the definition of a function. Be able to distinguish whether a relation is a function or not a function. Know what the vertical line test says, and use it to determine whether a graph represents a function. Be able to determine the domain and range of a relation. Given a set of ordered pairs Given a graph Understand function notation f(x) for equations for ordered pairs for graphs Write equations of lines using function notation. Graph and give domain and range of a linear function. (Note that a horizontal line has range which is a single number). 3