* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Physiology
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
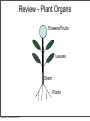
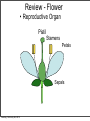
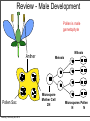
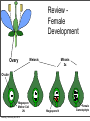
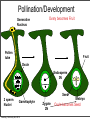
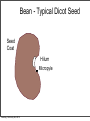
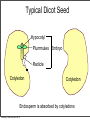
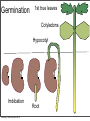
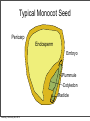
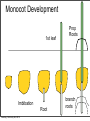
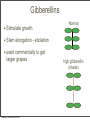
Plant Physiology Biology 2 Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Reminders Exam 2: March 6, 2013 Assignment 1: March 4, 2013 Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Review - Plant Organs Flowers/Fruits Leaves Stem Roots Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Review - Flower • Reproductive Organ Pistil Stamens Petals Sepals Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Review - Male Development Pollen is male gametophyte Anther Pollen Sac Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Mitosis Meiosis Microspore Mother Cell 2N Microspores Pollen N N Review Female Development Ovary Meiosis Mitosis 3x Ovule Megaspore Mother Cell 2N Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Megaspore N Female Gametophyte Pollination/Development Generative Nucleus Ovary becomes Fruit Pollen tube Fruit Ovule Endosperm 3N 2 sperm Nuclei Seed Gametophyte Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Zygote 2N Embryo Ovule becomes Seed Bean - Typical Dicot Seed Seed Coat Hilum Micropyle Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Typical Dicot Seed Hypocotyl Plummules Embryo Radicle Cotyledon Cotyledon Endosperm is absorbed by cotyledons Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Germination 1st true leaves Cotyledons Hypocotyl Imbibation Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Root Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Typical Monocot Seed Pericarp Endosperm Embryo Plummule Cotyledon Radicle Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Monocot Development 1st leaf Imbibation Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Root Prop Roots branch roots Fruit • Flowering Plant Organ containing seed(s) • Forms from ovary Endocarp Seed Mesocarp Exocarp Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Pericarp Simple Fruit • Derived from a single ovary • Fleshy Fruits – moist at maturity • Dry fruits – dry at maturity Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Simple Fleshy Fruits peach tomato Drupe-stony endocarp Berry-soft endocarp avocado walnut Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Dry Fruits Legumesplits along 2 seams Grainfruit fused to seed Tuesday, February 26, 2013 NutDoes not split Compound Fruits • Derived from a many ovaries 1 flower - many pistils Multiple flowers e.g. raspberry e.g. osage orange Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Fruit Function - Seed Dispersal Wind Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Animals Plant Physiology Study of function How things work e.g. what controls growth e.g. what controls flowering and fruiting Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Photoperiodism Response to day length Long Day Plants - flower photoperiod > critical length. Short Day Plants - flower photoperiod < critical length. Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Short Day (Long Night) Plants Fig 26.18 Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Circadian Rhythms Daily movements Prayer Plant leaves horizontal in day vertical at night Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Sunflower flower turns to face sun throughout day/ Phytochrome plant photoreceptor Red Light Fig 26.16 Far red Light Inactive •photoperiodism •seed germination •circadian rhythms Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Active Hormones • chemicals made in minute amounts • transported to target region • affect growth Auxin Cytokinins Gibberellins Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Abscisic Acid Ethylene Auxins • • Generally stimulates growth Cell elongation Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Phototropism • • Movement relative to light. Auxin elongates cells on dark side Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Gravitropism • Bending relative to gravity. • Auxin causes elongation on one side - gravitropism Tuesday, February 26, 2013 + gravitropism Apical Dominance • Auxin inhibits axillary bud growth Remove tip No auxin, Buds grow Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Auxin • Promotes root formation Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Herbicides • • • Weed killers synthetic auxins overstimulates Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Agent Orange • • • • Used in Vietnam 2,4-D, 2,4-T Deforest Stop agriculture Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Gibberellins • Stimulate growth Normal • Stem elongation - etiolation • used commercially to get larger grapes Tuesday, February 26, 2013 high gibberellin (shade) Cytokinins • stimulate cell division • interacts with auxin • used in tissue culture Tuesday, February 26, 2013 Ethylene • Fruit ripening (starch to sugar, green to color) • Abscission - leaf loss H H C Tuesday, February 26, 2013 C H H Abscisic Acid • • • • Growth inhibiting hormone “stress hormone” Promotes bud and seed dormancy Closes stomata Tuesday, February 26, 2013 The End Tuesday, February 26, 2013