* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title: Vision and hearing testing
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
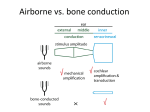
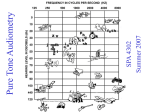
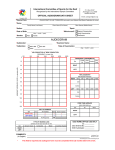
Title: Vision and hearing testing Teacher: Magdalena Gibas MD PhD, Coll. Anatomicum, 6 Święcicki Street, Dept. of Physiology I. Vision – examination of the visual system A. Examination of the visual acuity The most rewarding single test of ocular function is the evaluation of visual acuity. Reduced acuity will betray the presence of great variety of diseases as well as the need for refractive correction. Determination of visual acuity should be a part of every complete physical examination. 1. Distant acuity is measured with Snellen’s chart. a. The chart is read while standing at a distance of 20 feet=6m (5m in Poland). b. Visual acuity is expressed in a fraction — such as 20/20 vision (or 1.0;20/20=1.0). c. The top number refers to your distance from the eye chart, d. The bottom number indicates the distance at which a person with normal eyesight could correctly read the line patient reads. e. 20/20 (1.0) vision means that patient can see objects clearly from 20 feet away that a person with normal vision could see clearly from 20 feet away. f. However, if patient’s visual acuity is 20/50 (0.4), the line patient reads correctly at 20 feet could be read by a person with normal vision at 50 feet. 2. Measurement of near vision is relatively unimportant as a routine procedure except in patients complaining specifically of reading difficulty or in persons over 40 years of age. With increasing age the lens of the eye becomes less flexible, resulting in loss of accommodation for near vision, which interferes with reading. This condition is referred to as presbyopia. B. Examination of the color vision with Ishihara charts 1. The Ishihara charts are the plates on which are printed figures or numbers. The figures and numbers are made up of colors that are liable to look the same as the background to an individual who is color-blind. The plates are held 75 cm. from the subject and tilted so that the plane of the paper is at right angles to the line of vision. The numerals which are seen on plates are stated, and each answer should be given without more than three seconds delay. To explain the results of testing a specially designed table is used. C. Examination of the visual field The visual field of the eye is the portion of the external world visible out of the eye. The visual fields are mapped with an instrument called a perimeter. The process is refereed to as perimetry. Usually automated perimetry is performed (with computer). D. Ophtalmoscopic examination Physical examination should include careful study of the details of the posterior eye /fundus/ with an ophthalmoscope. It examines the back of the eye, including retina, optic disc, choroids and blood vessels. Doctor usually uses special eyedrops to dilate patient’s pupils, opening them wider. In addition to the detection of ocular disease this procedure will permit the diagnosis of serious systemic disorders. E. Keratoscopy – examination of cornea shape. F. Slit-lamp examination. 1.A slit lamp allows the doctor to see the structures at the front of patient’s eye using a microscope — called a slit lamp 2.Doctor uses this light to examine: cornea, iris, lens, and anterior chamber of the eye. II. Hearing A. Otoscopy – to observe tympanic membrane. Loss of hearing may be caused by otitis media (inflammation of middle ear), which requires otoscopy for complete diagnosis and appropriate treatment. B. Tunning fork tests - To distinguish between nerve and conduction deafness. WEBER RINNE SCHWABACH METHOD Base of vibrating tuning Base of vibrating Bone conduction of fork placed on vertex of tuning fork placed on patient compared with skull mastoid process untill that of normal subject subject no longer hears it, then held in air next to ear NORMAL Hears equally on both sides Conduction deafness (one ear) Sound louder in diseased Vibrations in air not ear because masking heard after bone effect of environmental conduction is over noise is absent on diseased side Nerve deafness (one ear) Sound louder in normal ear Hears vibration in air after bone conduction is over Bone conduction better than normal (conduction defect excludes masking noise) Vibration heard in air Bone conduction worse after bone conduction than normal is over, as long as nerve deafness is partial C. Audiometry. An audiometer is an electronic instrument used in medical clinics to test for hearing loss. An ear specialist uses it to chart an “audiogram”, by means of which certain defects in hearing can be detected. An instruction manual usually accompanies the audiometer. Test the audiotory acuity of several members of the class: Starting with high-piched sounds /8000 Hz/, determine the number of decibels required for the subject to first hear the sound. From “normal” values: plot the hearing loss /in decibels/ at frequencies from 8000 Hz in descending steps of 2000 Hz. Below 1000 Hz try 500, 250, and 125 Hz. Test right and left ears separately. When the plotted points are connected, you have an “audiogram” /see audiogram chart/. Audiogram. Name _______________________________________________________ Age _________ Sex _________ Date ____________Time _____________ Job location __________________________________________________ -10 0 HEARING LEVEL IN DECIBELS 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 250 500 750 1000 1500 2000 3000 4000 6000 8000 TONE FREQUENCY (Hz) Examiner________________________ Signature _____________________ Symbols: Ear Left Right Response X O Phone Blue Red