* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 6: Parts and Types of Triangles
Algebraic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
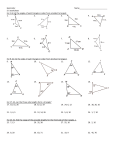
Lesson 6 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM U7 GEOMETRY Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ Lesson 6: Parts and Types of Triangles Learning Target: I can find the unknown angles and cite geometric justifications regarding angles in a triangle I can identify different types of triangles based on angles and sides Parts of a Triangle Each triangle has three __________ and three _______________. Each _______________ is where two sides meet. A pair of sides and the vertex define an ____________, so each triangle includes three _____________. Write "side" next to each side and circle the vertices on the triangle below. Each vertex is named with a ___________ letter. The sides can then be named with the letters of the two _____________ on either side of it. The triangle is named with a triangle symbol Δ in front followed by the three letters of its vertices. Label the vertices of the triangle at right with 𝑨, 𝑩, and 𝑪 Name the 3 sides of this triangle ______ ______ ______ Example 1. What is the name of the side shown in red? Lesson 6 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM U7 GEOMETRY Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ Example 2. What is the name of the side shown in red? Example 3 Which of the following are names of this triangle? Types of Triangles Isosceles: The ____________ angles of an Isosceles triangle (and sides opposite them) are _________________. Equilateral: Each angle/side of an equilateral triangle have __________ measures. Each interior angle of an equilateral triangle would have a measure of _________ degrees. Equilateral triangles are also called Equiangular ( when all angles are said to be equal) Scalene: The three angles/sides of a scalene triangle have _________________ measures. Right Triangle: A triangle that has one right angle Draw a picture Lesson 6 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM U7 GEOMETRY Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ Example 4. An isosceles triangle is _______________ an equilateral triangle. A. Sometimes B. Always C. Never Example 5. Write true or false for the following statements A triangle can have more than one right angle. An equilateral triangle is also an isosceles triangle Example 6. This triangle is classified as _______________________ . (Choose all that apply.) Triangle Sum Theorem In the past we have talked about how the interior angles of a triangle have a sum of 180°…..BUT WHY? In the diagram below, 𝑙 ∥ 𝑚. l m What is the value of∠ a? ______ Reason: __________________________________________________ What is the value of ∠ b? ______ Reason: __________________________________________________ What is the value of ∠ c? ______ Reason: __________________________________________________ Triangle Sum Theorem: 𝑚∠ 𝒂 + 𝑚∠ 𝑏 + 𝑚∠ 𝑐 = __________ The sum of the 3 angle measures of any triangle is ________. Lesson 6 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM U7 GEOMETRY Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ Example 1. Find the measure of the missing angle. Example 2. What is the measurement of the missing angle? Example 3. In 𝛥𝐴𝐵𝐶, if 𝑚∠𝐵 is 84° and 𝑚∠𝐶 is 36°, what is 𝑚∠𝐴? _________________ Example 4. Solve for w, v and t Give a reason for each answer: 𝒎∠𝒘 = _________ 𝒎∠𝒗 = _________ 𝒎∠𝒕 = _________ Example 5. Solve for 3, 4 and 5 Give a reason for each answer: 𝒎∠𝟑 = _________ 𝒎∠𝟒 = _________ 𝒎∠𝟓 = __________ Example 6. Solve for x Find the measure of ∠𝑄𝑅𝑃 𝑎𝑛𝑑 ∠𝑃𝑄𝑅 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 U7 GEOMETRY Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ Lesson 6: Parts and Types of Triangles Problem Set Directions: For #1-5, solve for the variable (s). Give a reason that justifies your response for each variable. Remember, you may need to solve for other unknown angles, before you can solve for the specific variable that is asked. For Activities 1, 2 and 3, solve for all unknown angles . Give a reason for each answer. 1. 2. 3. RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 U7 GEOMETRY Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ 4. Solve for x. 5. What is the measure of ∠B? 6. Solve for x and y in the diagrams. Explain why the equations you use to solve for x are appropriate and explain why they equations you used to solve for y are appropriate. Find the value of 𝑑 and 𝑘: 𝒅 = ________ 𝒙 = ________ Lesson 6 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM U7 GEOMETRY Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ Lesson 6: Parts and Types of Triangles Homework For activities 1 and 2 find the missing angle. Explain your reasoning 1. 2. 3. In the diagram of ∆𝐽𝐸𝐴 at right, 𝑚∠𝐽𝐸𝐴 = 90 and 𝑚∠𝐸𝐴𝐽 = 48. Line segment MS connects points M and S on the triangle, such that 𝑚∠𝐸𝑀𝑆 = 59. What is ∠𝐽𝑆𝑀 ? 4. The diagram at right shows ∆𝐴𝐵𝐷, with ⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗⃗ 𝐴𝐵𝐶 , ̅̅̅̅ 𝐵𝐸 ⊥ ̅̅̅̅ 𝐴𝐷, and ∠𝐸𝐵𝐷 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐵𝐷. If 𝑚∠𝐴𝐵𝐸 = 52, what is 𝑚∠𝐷 ?