* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUIT LAB
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
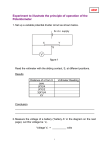
Name SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUIT LAB Purpose: To discover the difference between series and parallel circuits using the knowledge of current all ready gained. Also to become acquainted with the digital multi-meter as a diagnostic tool. To do: Go to each station and follow the directions below. Answer each question fully. Station A - Series circuit. 1) Unscrew one light bulb. Describe and explain what happens to the other light bulbs using words like current and voltage? 2) Set the multimeter to volts and touch the leads on either side of each light bulb in the circuit. Also touch either side of the power supply posts. Record the voltage below. Voltage Current light bulb 1 light bulb 1 - 4.0 amps light bulb 2 light bulb 2 - 4.1 amps light bulb 3 light bulb 3 - 3.9 amps battery battery - 4.0 amps 4) How does the voltage drop across each light bulb compare to the voltage drop across the battery. 5) How does the current through each light bulb compare to the current through the battery? 6) Draw a circuit diagram of the series circuit you used in this part of the lab. Name Station B - Parallel circuit 1) Unscrew one light bulb. Describe and explain what happens to the other light bulbs using words like current and voltage? 2) Set the multimeter to volts and touch the leads on either side of each light bulb in the circuit. Also touch either side of the power supply posts. Record the voltage below. Voltage Current light bulb 1 light bulb 1 - 1.4 amps light bulb 2 light bulb 2 - 1.3 amps light bulb 3 light bulb 3 - 1.3 amps battery battery - 4.0 amps 4) How does the voltage drop across each light bulb compare to the voltage drop across the battery. 5) How does the current through each light bulb compare to the current through the battery? 6) Draw a circuit diagram of the parallel circuit you used in this part of the lab. Station C - Unknown circuit 1) Unscrew one light bulb. Describe and explain what happens to the other light bulbs using words like current and voltage? Name 2) Set the multimeter to volts and touch the leads on either side of each light bulb in the circuit. Also touch either side of the power supply posts. Record the voltage below. Voltage light bulb 1 Current light bulb 1 - 4.0 amps light bulb 2 light bulb 2 - 2.0 amps light bulb 3 light bulb 3 - 2.0 amps battery battery - 4.0 amps 4) How does the voltage drop across each light bulb compare to the voltage drop across the battery. 5) How does the current through each light bulb compare to the current through the battery? 6) Draw a circuit diagram of the circuit you used in this part of the lab. Questions 1) Explain the difference between a series and a parallel circuit in terms of current and voltage? 2) In a series circuit do the voltages or the amps add up? 3) In a parallel circuit do the voltages or the amps add up? 4) Which circuit would you rather have in your house and why? 5) Draw a circuit below that has 3 parallel resistors and 4 series resistors connected to one battery. Name Circuit Diagram Cheat Sheet R Battery Symbol 1 Wires Simple Circuit R 1 R 2 Series Circuit R 1 R R 2 R 3 Parallel Circuit R 1 R R 2 4 A Series - Parallel Circuit R 3 4