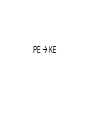* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy Unit Review - Powers Physical Science
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy Unit Review 1. A material that does not conduct heat well is called a(n) Insulator 2. The total potential and kinetic energy of the particles in an object is called Thermal energy 3. When generators are spun by turbines, they Produce electricity 4. Heat, like work, is an energy transfer measured in Joules 5. Heat is transferred from one particle of matter to another without the movement of matter itself in a process called Conduction The total energy of all the particles in a substance is called Thermal energy 7. Kinetic energy increases as Both mass and velocity increase 8. Examples of kinetic energy Something that moves •A ball rolling down the street 9. The energy associated with motion is called Kinetic energy 10. The rate at which energy is transferred is called Power 11. The movement of thermal energy from a warmer object to a cooler object is called heat 12. A change from one form of energy into another Energy transformation 13. When you rub your hands together on a cold day, you use friction to convert Mechanical thermal energy 14. The transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves is called Electromagnetic energy 15. Something that stores chemical energy is Food you eat a match a battery 16. Unlike kinetic energy, potential energy is Stored energy 17. Energy is measured in units called Joules 18. Any temperature on the Kelvin scale can be changed to Celsius by Subtracting 273 19. A measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles in an object is called Temperature 20. The law of conservation of energy states that when one form of energy is converted into another Energy is not created or destroyed 21. A pole-vaulter first converts kinetic energy into Elastic potential energy 22. Visible light is an example of Electromagnetic energy 23. How would you calculate an object’s mechanical energy? ME = KE+PE 24. Absolute zero is shown as 0 on which scale? The Kelvin scale 25. Water freezes at 32 degrees on which temperature scale? Fahrenheit 26. Moving water can be used to produce electricity because Most energy can be transformed into other forms of energy 27. The ability to do work is called energy 28. Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom is called Nuclear energy 29. When fossil fuels are burned, their chemical potential energy is converted into Thermal energy 30. What is the freezing point of water in degrees Celsius? What is the boiling point of water in degrees Celsius? Freezing point = 0 degrees Boiling point = 100 degrees 31. Heated air moves from baseboard heaters to the rest of a room in a process called Convection 32. The type of energy stored by fossil fuels such as coal is Chemical potential energy 33. Potential energy that depends on height is called Gravitational potential energy 34. No more energy can be removed from matter at 0 Kelvin 35. What type of conversion is taking place when natural gas is used to heat water? Chemical Thermal 36. Niagara Falls is a good example of PE KE 37. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object is Mechanical energy 38. What type of energy does a spinning turbine have? Mechanical 39. Heat transfer occurs from warm objects to colder ones