* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Understanding Our Environment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
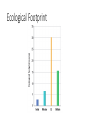
Understanding Our Environment What is Environmental Science? •Environmental Science is the study of the air, water, and land surrounding an organism or a community Goals of Environmental Science • Understand and solve environmental problems • To do this scientist must study • How our actions alter our environment • The use of natural resources Many Fields of Study • Environmental science is an interdisciplinary science, which means it involves many fields of study • Ecology, the study of interactions of living organisms with one another and their environment, is important to the foundation of environmental science Hunter-Gatherers • Humans have changed the environment by hunting, growing food, and settling • Hunter gathers are people that obtain food by collecting plants and hunting wild animals or scavenging the remains. • Hunter gathers have affected their environment by: • Native American tribes hunted bison • Native Americans set fires to burn the prairies and prevent growth of trees Agricultural Revolution • Agriculture is the raising of crops and livestock for food or other products. • Started in many areas over 10,000 years ago • Allowed populations to grow at unprecedented rate • Changed the food we eat • Many habitats were destroyed as grasslands, forest, and wetlands were replaced with farmland • Caused soil loss, floods, and water shortages Industrial Revolution • Involved a shift from energy sources such as animals and running water to fossil fuels such as coal and oil • Increased efficiency of agriculture, industry, and transportation • Quality of life was improved • Increased sanitation, nutrition, and medical care • Introduced new environmental problems • Pollution and habitat loss • 1900s, societies began using artificial substances • We now have plastics, artificial pesticides, and fertilizers • Many of these made life easier, but caused environmental problems Population Growth • The industrial revolution, modern medicine, and sanitation all allowed the human population to grow faster than it ever had before • Producing enough food for large populations has environmental consequences • Habitat destruction • Pesticide pollution • Scientist think the population will double in the 21st century What are the Main Environmental Problems? •Resource Depletion •Pollution •Loss of Biodiversity Supply and Demand • The Law of Supply and Demand is a law of economics that states as the demand for a good or service increases, the value of the food or service also increases. Ecological Footprints • Ecological footprints are calculations that show the productive area of Earth needed to support one person in a particular country. • Estimates: • Land used for crops, grazing, forest products, and housing • Ocean area used to harvest seafood • Forest area needed to absorb the air pollution by fossil fuels Ecological Footprint