* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
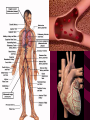
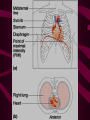
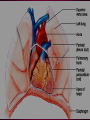
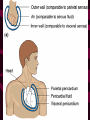
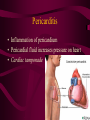
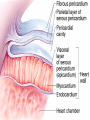
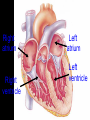
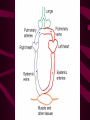
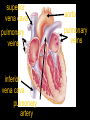
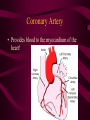
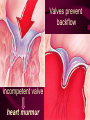
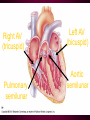
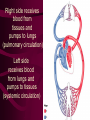
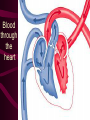
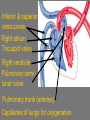
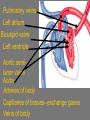
Cardiovascular System Chapter 42 IB Biology Biological Function of Cardiovascular System • TRANSPORT! – Maintains constant flow of : • • • • • Nutrients Hormones Respiratory Gases Wastes Enzymes to /from tissue cells! 3 Major Components of CV System 1. Blood 2. Blood Vessels 1. Arteries / Arterioles 2. Veins / Venules 3. Capillaries 3. Heart Heart Anatomy 250-300 grams--size of fist Located in mediastinum Rests on diaphragm 2/3 left of midline Shifts toward right shoulder Apex points to left hip Protective Features of the Heart PERICARDIUM • Layered membrane surrounding heart • Fibrous pericardium – Tough, superficial layer • Serous pericardium – Thin, deep layer subdivided into: • Parietal layer: lines underside of fibrous pericardium • Epicardium: lines external surface of heart • Pericardial cavity: btwn parietal layer and epicardium filled with fluid! Pericarditis • Inflammation of pericardium • Pericardial fluid increases pressure on heart • Cardiac tamponade Heart Anatomy 3 Layers of Heart Wall 1. Epicardium: Superficial Layer Composed of CT 2. Myocardium: Intermediate Layer Composed of Muscle 3. Endocardium: Deep Layer Composed of Endothelium Internal Heart Anatomy FOUR CHAMBERS 2 ATRIA (Right Atrium, Left Atrium) Entry Chambers 2 VENTRICLES (Right Ventricle, Left Ventricle) Exit Chambers Right atrium Right ventricle Left atrium Left ventricle So what’s the big deal about a four chambered heart? EFFICIENCY What leads to the heart’s efficiency? ATRIOVENTRICULAR SEPTUM wall that creates a physical separation between right and left sides of heart (Interatrial septum + Interventricular septum = Atrioventricular Septum) AV SEPTUM How does the AV septum lead to efficiency? Creates two hearts in one! Maintains separation between oxygenated blood (high O2 / low CO2 ) and deoxygenated blood (low O2 / high CO2 ) Oxygenated blood always on left side! Deoxygenated blood always on right side! Mixing of Blood Occurs! Mixing of Blood Prevented! FOUR MAJOR BLOOD VESSELS ATTACHED TO HEART 1. VENA CAVA major vein of body 2. AORTA major artery of body 3. PULMONARY ARTERY 4. PULMONARY VEIN superior vena cava pulmonary veins inferior vena cava pulmonary artery aorta pulmonary veins Coronary Artery • Provides blood to the myocardium of the heart! Arteries vs. Veins ARTERY Always conducts blood AWAY from the heart! Usually carries oxygenated blood VEIN Always conducts blood TOWARD the heart! Usually carries deoxygenated blood Heart Valves • Flaps that open/close passageways for blood through the heart 2 Major Types of Valves: 1. Atrioventricular (AV) Valves Found between atria and ventricles Right AV Valve = Tricuspid Valve Left AV Valve = Bicuspid Valve / Mitral Valve Chordae tendinae / papillary muscles • Open/close AV valves • Prevent valves from opening backwards Valves prevent backflow incompetent valve heart murmur 2. Semilunar Valves found between ventricles and blood vessels leading out of the heart Right Valve = Pulmonary Semilunar Valve Left Valve = Aortic Semilunar Valve Right AV (tricuspid) Pulmonary semilunar Left AV (bicuspid) Aortic semilunar 31 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Circulation: blood flows to/from body tissues Pulmonary Circulation: blood flows to/from lungs Coronary Circulation: blood flows to/from heart muscle The Heart’s Assignment… …maintaining blood flow through ALL circulatory pathways of the body! Right side receives blood from tissues and pumps to lungs (pulmonary circulation) Left side receives blood from lungs and pumps to tissues (systemic circulation) Pathway of Blood Through the Heart Heart acts as double pump (Rt side/left side) Both pumps act in unison Deoxygenated blood returns to heart through vena cava Right side pumps blood to lungs Oxygenated blood returns to heart through pulmonary veins Left side pumps blood to body Blood through the heart Inferior & superior vena cavae Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary semilunar valve Pulmonary trunk (arteries) Capillaries of lungs for oxygenation Pulmonary veins Left atrium Bicuspid valve Left ventricle Aortic semilunar valve Aorta Arteries of body Capillaries of tissues--exchange gases Veins of body