* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar terminology - Haydonleigh Primary School
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Contraction (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
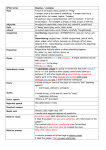
UPDATED Grammar Terminology at Year 6 This list of grammatical terms, produced at the request of some Somerset schools, is drawn from the pilot grammar test for year 6, the draft KS2 programme of study and the updated sample materials (December 2013). Terminology Notes noun, adjective, verb, adverb, pronoun, See word class chart for a definition of each of these terms. preposition, conjunction, determiner, Children should be able to identify these in sentences and insert appropriately where missing in a sentence. article Many teachers use the term ‘connective’ as a global term for any linking word within or between sentences. This is a convenient term in practice but children should also know the word conjunction as defined on the word class chart. adverbial Children should be able to identify or add in an adverbial (i.e. an adverb/adverbial phrase/adverbial clause). e.g. Suddenly, he opened the door. / With care, he opened the door. / Whistling quietly to himself, he opened the door. tense – present, past, future Children should be able to change a sentence from a given tense to another. statement/command/exclamation/question Children should understand that a sentence can be any of these. active and passive Children should be able to change a sentence from active to passive and vice versa. passive tense/passive verb punctuation and punctuation mark Children need to know not just the names of punctuation marks but the terms ‘punctuation’ and ‘punctuation mark’. speech marks /inverted commas/direct and Many teachers use the term ‘speech marks’, but children should also know the term ‘inverted commas’. indirect speech They should be able to change direct speech into indirect speech and vice-versa, as well as being able to punctuate dialogue correctly. full-stop, capital letter, question mark, Children should be able to identify these punctuation marks, understand their function and insert them in unpunctuated text. exclamation mark, comma, bullet point, Note that, according to current guidance, the use of semi-colons is not expected before level 6. apostrophe, dash, hyphen, colon, semicolon, ellipsis apostrophe for contraction and possession Children should be able to change words into a contracted form and vice versa. e.g. I will be there - I’ll be there. the terms omission and contraction Children should know how to use the apostrophe to show possession. singular and plural Children should be able to change words from singular to plural and vice versa. consonant and vowel Children should know that the determiner ‘a’ or ‘an’ will depend on whether there is a vowel or a consonant at the beginning of a word. phrase, clause and subordinate clause, Children should be able to identify the main and subordinate clauses in sentences as well as the subordinating connective complex sentence; subordinating connective that links them. They should know that a clause contains a verb, but a phrase does not. prefix and suffix Children should be able to transform words from one word class to another using prefixes and suffixes. e.g. changing the adjective ‘happy ‘ to the noun ‘happiness’; changing words into their opposites by adding a prefix. synonym and antonym Children should be able to suggest words which mean the same as, or the opposite of, a given word. Standard English; double negative; Children should understand Standard English usage. e.g. I did it, not I done it. They should understand that subject and verb subject/verb agreement must agree. e.g. We were... not We was... They should understand that a double negative is incorrect usage. e.g. I didn’t do nothing. They should know the correct usage of I and me. e.g. My brother and I went to school; Between you and me...