* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 110 – Sections 2.1-2.3 2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
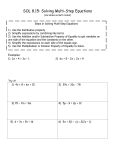
2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions Term – a number or the product of a number and variables raised to power. Math 110 – Sections 2.1-2.3 Numerical coefficient of a term is the numerical factor. Example 1. Identify the numerical coefficient in each term. Combining like terms: - Simplifying the sum or difference of like terms. • Like terms – have the same variables raised to the same power • Unlike terms – not like terms Example 3. Simplify each by combining like terms. a) 8 y − 12 y b) 13z 2 + 5z 2 c) 6 y − 3 x + 7 x Example 2. Determine whether the terms are like or unlike. a) 2 x, − 6 x b) 3 x 2 y 2 , -x 2 y 2 , 4 xy c) − 5ab, 6ba Note: In combining like terms, we can simply add numerical coefficients and multiply by common variable factors. Example 4. Simplify by combining like terms. a) − 7 xy − 2 + x + 3 b) 4z 2 − 5z c) − 1 x + 2x 4 Example 5. Find each product using the distributive property to remove parentheses. Removing parentheses by using the distributive property. 1 Example 6. Simplify the following expressions. a) 4( x − 2) − 3 x + 5 c) 9 − 5(6 y − 3) b) 3(2 x + 1) − (5 x − 2 ) Example 7. Write the following phrases as algebraic expressions and simplify if possible. a) Three times a number subtracted from 10 b) Five added to twice the sum of a number and seven. 2.2 Addition and Multiplication Properties of Equality Example 1. Solve for x. Linear Equation in one variable: Example 2. Solve for y. Addition Property of an Equality. Example 3. Solve for x. Multiplication Property of Equality We can multiply (or divide) both sides of an equation by any nonzero real number and the solution does not change. Example 5. Solve for x. Example 4. Solve: 2 Example 6. Solve for x. Writing Algebraic Expressions Example 9. a) The sum of two numbers is 50. If one number is x, write an expression representing the other. b) If x is the first of three consecutive integers, express the sum of the three integers in terms of x. Then simplify. Example 7. Solve for x. 2.3 Solving Linear Equations Example 1. Solve: 1. Multiply both sides by the LCD to clear the equations of fractions if they occur. 2. Use the distributive property to remove parentheses. 3. Simplify each side of the equation by combining like terms. 4. Get all variable terms on one side and all numbers on the other side using the addition property. 5. Get the variable alone by using the multiplication property. 6. Check the solution by substituting it into the original equation. Example 2. Solve: Example 3. Solve: 3 Example 4. Solve: Example 5. Solve: Example 6. Solve: Example 7. Three times a number, subtracted from two, equals twice the number, added to twenty seven. Find the number. 0.06 x − 0.10(x − 2 ) = −0.02(8) − 6(2 x + 1) − 14 = −10( x + 2) − 2 x 5(2 − x ) + 8 x = 3(x − 6) 4