* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COCHLEAR IMPLANTS
Speech perception wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
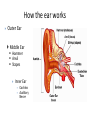
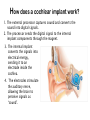
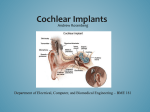
COCHLEAR IMPLANTS INSERVICE How the ear works Outer Ear Middle Ear Hammer Anvil Stapes Inner Ear Cochlea Auditory Nerve A Conductive Hearing Loss~ • This happens when there is a problem with a part of the outer or middle ear. • Most kids with conductive hearing loss have a mild to moderate hearing loss. • Sometimes it is temporary because medical treatment can help. • Causes are: ear infections, wax buildup, fluid buildup, problem in ossicular chain, childhood diseases, congenital abnormalities A Sensorineural Hearing Loss~ • This happens when the cochlea is not working correctly because the tiny hair cells are damaged or destroyed. A sensorineural hearing loss means the nerve that carries the messages from the cochlea to the brain is damaged. • Sensorineural hearing impairment is almost always permanent and a kid's ability to talk normally may be affected. • This loss is often severe to profound. • Causes are: birth trauma, head trauma, severe infections/illnesses, noise, lack of oxygen, hereditary, ototoxic drugs SIMULATIONS Listening demos of acoustic simulations of hearing loss http://www.betterhearing.or g/sound/index.cfm Listening demos of acoustic simulations of cochlear implants http://www.utdallas.edu/~loiz ou/cimplants/cdemos.htm How does a cochlear implant work? 1. The external processor captures sound and converts the sound into digital signals. 2. The processor sends the digital signal to the internal implant components through the magnet. 3. The internal implant converts the signals into electrical energy, sending it to an electrode inside the cochlea. 4. The electrodes stimulate the auditory nerve, allowing the brain to perceive signals as “sound”. ???? Do You Remember ???? • • • • • • Where does the cochlear implant go? Name three parts of the cochlear implant. What is another name for programming? How long until it is turned on? How long until it is fully on and ready? What is the patient’s responsibility? External Processor SURGERY 2-4 hours Surgeon drills an area in temporal bone and then into the mastoid bone Drills a hole into the cochlear Implant under skin and inside skull thread wires with electrodes into the cochlear (spiral) Close are and apply dressing Dizzy for several days HOW IT WORKS Audiologist Electrodes are tested and turned on. Patient identifies loudest volume tolerated. Measures softest and loudest sounds electrode can transmit. Processor matches sounds to different electrodes to create digital version of sound. Limited number of electrodes for thousands of hair cells Pick up sounds after a few programming sessions. Indentify and interpret the new sounds. Programming (mapping) takes several months.