* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduc%on to Animals - Warren County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
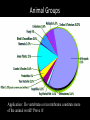
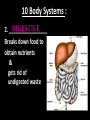
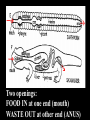
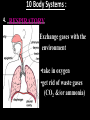
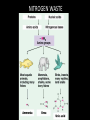
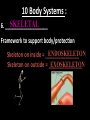
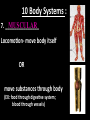
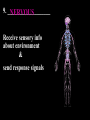
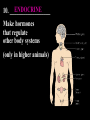
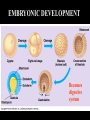
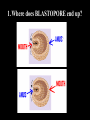
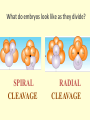
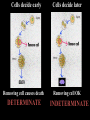
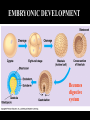
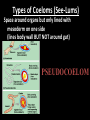
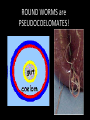
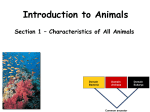
Introduc)on to Animals Focus Ques)ons: 1)What characteris)cs do all animals share? 2) What are the major body systems an animal has? 3) Which type of diges)ve system is advantageous? Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods Vertebrates-‐ Animals with backbones Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Animal Groups Application: Do vertebrates or invertebrates constitute more of the animal world? Prove it! Characteris:cs of ALL Animals: 1. Are ____________________ EUKARYOTES cells have nucleus & membrane bound organelles HETEROTROPHIC 2. Are ____________________ get food from consuming other organisms MULTICELLULAR 3. Are ____________________ made of many cells SPECIALIZATION 4. Show __________________ different kinds of cells do different jobs Characteris:cs of ALL Animals: MOVE (at some point in life cycle) 5. _____________ for food, find mates, escape danger DNA 6. Contain _____________ which carries the gene:c code REPRODUCE 7. ____________________ Make offspring Most have sexual reproduc:on (few asexual) 10 Body Systems : 1. _____________________ INTEGUMENTARY OUTSIDE BODY COVERING (fur, skin, scales, feathers) Covers and protects, ID, prevents heat & water loss 10 Body Systems : DIGESTIVE 2. _________________ Breaks down food to obtain nutrients & gets rid of undigested waste NO OPENINGS: Food enters through skin Only one opening: FOOD IN and WASTE OUT through same opening Two openings: FOOD IN at one end (mouth) WASTE OUT at other end (ANUS) Two openings: Most efficient If food flows only one direction it allows for organ specialization (Different parts can start to do different jobs) 10 Body Systems : 3. __________________ CIRCULATORY Transports nutrients/oxygen to body cells Carries carbon dioxide/nitrogen waste away from cells Circulatory fluid can be: inside blood vessels = _________ CLOSED loose inside body spaces = _OPEN ______ 10 Body Systems : 4. ___________________ RESPIRATORY Exchange gases with the environment • take in oxygen • get rid of waste gases (CO2 &/or ammonia) 10 Body Systems : 5. ___________________ EXCRETORY • Get rid of nitrogen waste made by cells • Help with HOMEOSTASIS by maintaining water/ion balance (_________________________) OSMOREGULATION NITROGEN WASTE : AMMONIA _________________ Most TOXIC Must be removed QUICKLY Needs MOST water to dilute _________________ Made from ammonia by liver UREA Less toxic than ammonia Can be stored if diluted with water (Needs less water to dilute than ammonia) URIC ACID LEAST TOXIC _________________ Can be stored if diluted with water (Needs LEAST amount of water to dilute) NITROGEN WASTE ALL WASTE is NOT THE SAME! DIGESTIVE WASTE WHERE ITS MADE? left over from undigested food Body system used? Handled by digestive system In what form? Feces NITROGEN WASTE made by cells from break down of proteins Handled by excretory system ammonia, urea, or uric acid 10 Body Systems : SKELETAL 6. ___________________ Framework to support body/protec:on ENDOSKELETON Skeleton on inside = _______________ Skeleton on outside = _EXOSKELETON ______________ 10 Body Systems : MUSCULAR 7. _______________ Locomo:on-‐ move body itself OR move substances through body (EX: food through diges:ve system; blood through vessels) 10 Body Systems : 8. _REPRODUCTIVE ____________________ -‐ Produce offspring by combining gene:c material from 2 parents = _SEXUAL _________________________ REPRODUCTION Produce offspring using genetic material from only 1 parent =_____________________________ ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION 10 Body Systems : INDIRECT DEVELOPMENT ______________ immature LARVA looks different than adult _DIRECT _________ DEVELOPMENT young are smaller versions on adults Sperm and egg join fertilization outside female s body = _External __________________ Sperm and egg join inside female s body = ____________________ Internal fertilization 9. ___________________ NERVOUS Receive sensory info about environment & send response signals ENDOCRINE 10. __________________ Make hormones that regulate other body systems (only in higher animals) Kinds of Symmetry No symmetry Radial symmetry Bilateral symmetry ASYMMETRY ___________________ No symmetry Doesn t maker how you cut it; you never get 2 iden:cal halves. Radial Symmetry _______ Get 2 iden:cal halves in several direc:ons. Bilateral Symmetry ___________ If divide animal down the middle you get 2 mirror images BUT only divides equally in ONE direc:on Focus Ques)ons: • How can embryology help us classify organisms? • What is a blastopore? • What characteris)cs are shared by protostomes? And deuterostomes? EMBRYOLOGY 1. Where does BLASTOPORE end up? 2. What do embryos look like as they divide? 3. When do cells decide what they will be? EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT Becomes digestive system 1. Where does BLASTOPORE end up? What do embryos look like as they divide? SPIRAL CLEAVAGE RADIAL CLEAVAGE When do cells decide what they will become? Cells decide early Removing cell causes death DETERMINATE Cells decide later Removing cell OK INDETERMINATE ANIMALS PROTOSTOMES DEUTEROSTOMES Blastopore becomes MOUTH Blastopore becomes ANUS Decide later (INDETERMINATE) RADIAL cleavage Decide very early (DETERMINATE) SPIRAL cleavage ALL INVERTEBRATES except ECHINODERMS ALL VERTEBRATES (Fish, amphibians, birds, reptiles, mammals) plus ECHINODERMS EMBRYOLOGY __________________ Echinoderms are the excep:on to the rule ! They are INVERTEBRATES but their embryos act like DEUTEROSTOMES _________________________ EMBRYONIC DEVELOPMENT Becomes digestive system Focus Ques)ons: 1) What are the 3 germ layers, and what do they develop into? 2) Describe the internal structure of animals that have a pseudocoelem or eucoelom. 3) Which type of coelom is advantageous? All animals except sponges, jellyfish, anemones have 3 germ layers in their embryos Endoderm Digestive system, respiratory muscle, excretory, bones, Mesoderm circulatory Outer skin, brain, Ectoderm nervous system Types of Coeloms (See-‐Lums) No cavity (space) around organs ACOELOM = without space FLATWORMS are ACOELOMATES! Types of Coeloms (See-‐Lums) Space around organs but only lined with mesoderm on one side (lines body wall BUT NOT around gut) PSEUDOCOELOM ROUND WORMS are PSEUDOCOELOMATES! Kinds of Coeloms (See-‐Lums) EUCOELOM: Body cavity (space) lined on BOTH sides by mesoderm EUCOELOM = TRUE COELOM = COELOM EUCOELOMATES ALL VERTEBRATES & SOME INVERTEBRATES ALL ANIMALS you will dissect this year are EUCOELOMATES! 3 Types of Coeloms ACOELOM ectoderm mesoderm endoderm EUCOELOM PSEUDOCOELOM Advantages o f h aving a C OELOM (body space): Provides space for internal organs In animals without a skeletonFluid in coelom space can act as a HYDROSTATIC skeleton In animals without blood vesselsFluid in coelom space can circulate nutrients and oxygen to cells WHY is a EUCOELOM the best? Digestive organ muscles and body wall muscles come from MESODERM in different places so organism can digest food and move at same time. Which way is up? DORSAL (top) ANTERIOR head end POSTERIOR tail end VENTRAL (underneath) CEPHALIZATION ________________ Concentra:on of nervous :ssue and sensory organs in anterior end of an organism (head area)