* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Gastrointestinal Tract
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
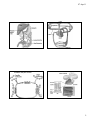
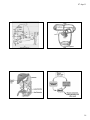
07-Apr-11 Digestion, Absorption and Transport The Gastrointestinal Tract Anatomy of the GI tract: – mouth – esophagus – stomach t h – small intestine – large intestine – rectum – anus Components of gastrointestinal tract The Gastrointestinal Tract Functions: Ingestion Transport p Secretion Digestion Absorption Elimination 1 07-Apr-11 Assisting Organs Salivary glands - saliva – Moisten food – Supply enzymes Liver – Produces bile Gallbladder – Stores and secretes bile Pancreas – Secretes bicarbonate – Secretes enzymes From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Mouth Tongue (Mixing) Teeth (Mastication) Digestion Physical movement – Peristalsis – Segmentation Chemical breakdown – Enzymes hydrolysis From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Mouth Enzymes Salivary amylase acts on starch Lingual lipase acts on fat Saliva Moistens food for enzymes activity and easier swallowing Esophagus – Transports food to stomach - bolus – Esophageal sphincter (upper & lower) 2 07-Apr-11 From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Epiglottis Esophageal sphincter From M to A: Digestion and Absorption From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Stomach Stomach Mechanical function – “Chewing” Esophegeal – Mixing Hydrochloric acid Prepares protein for digestion Activates enzymes “Disinfection” Sphincter Pepsin Begins protein Pyloric sphincter digestion Gastric lipase Some lipids digestion Gastrin (hormone) Stimulates gastric secretion and movement Intrinsic factor Needed for absorption of vitamin B12 3 07-Apr-11 The Small Intestinal Villi From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Small intestine: Pyloric Duodenum Sphincter (25 – 30 cm) Jejunum (120 cm) Ileum (150 cm) Assisting Organs: Liver & gallbladder Pancreas The Small Intestinal Villi and Microvilli Folds From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Pancreatic juices Bicarbonate Enzymes: – Trypsin and chymotrypsin Proteins – Amylases - Carbohydrates – Lipases - Lipids 4 07-Apr-11 From M to A: Digestion and Absorption pH of Digestive Tract Secretions How nutrients are transported? Absorptive mechanisms Facilitated diffusion Passive diffusion Active transport Small intestine - Absorption Folds, villi, and microvilli makes large absorptive surface Most nutrients absorbed Fat F Fatt-soluble l bl nutrients t i t go into lymph Other nutrients go into blood From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Large Intestine - Colon 5 07-Apr-11 From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Large intestine Nutrient digestion already completed Fermentation of undigested residues by bacteria: Production of vitamins K, B12, thiamin, riboflavin, ib fl i biotin, bi ti other th B’s B’ Gases Short chain fatty acids Antibiotics – protectant Lactic acid to control pH From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Large intestine Absorption Water Sodium, potassium, chloride Vitamin K and B group (produced by bacteria) Bile Waste Elimination Circulatory Systems Vascular system – Heart – Arteries A i – Capillaries – Veins 6 07-Apr-11 Circulation of Nutrients Excretion and elimination Lungs Excretes water and carbon dioxide Kidneys filter blood Excretes waste Maintains water and ion balance Summary of digestion and absorption 7 07-Apr-11 Circulatory Systems The Liver Vascular system – Portal vein – Hepatic vein Circulatory Systems Lymphatic system – Lymph – Thoracic duct Subclavian vein 8 07-Apr-11 Catabolic Enzymes Action 9 07-Apr-11 Waste Products Must Be Eliminated from the Body Substances such as fiber that are not absorbed from the intestine are eliminated from the gastrointestinal tract in the feces The waste products of metabolism are eliminated by the lungs, the skin, and the kidneys At the lungs, red blood cells release the carbon dioxide, which is i then th exhaled h l d into i t the th environment i t A significant amount of water is also lost from the lungs, by evaporation Some water, minerals, and byproducts breakdown are lost through the skin perspiration or sweat. But the kidney is the primary site for the excretion of water and the nitrogen nitrogen-containing byproducts of protein breakdown The amounts of water and other substances excreted in the urine are regulated so that homeostasis is maintained Digestion of a Sandwich Digestion of a Sandwich 10 07-Apr-11 Absorption – Modes of Transportation The Gastrointestinal Tract Complimentary organs Salivary glands Liver and gallbladder Pancreas Digestive Tract - Functions Physical Movement: Peristalsis Segmentation Chemical Breakdown: Enzymes Hydrolysis Other secretions 11 07-Apr-11 Secretions of Digestion Digestive Tract - Functions Stomach Chyme Pyloric sphincter Saliva – Salivary glands Water, salts, mucus, enzymes Muscular Action of Digestive Tract Stomach Muscles Esophegeal Sphincter Stomach mechanical action Pyrolic Sphincter 12 07-Apr-11 Digestive Tract - Functions Stomach Digestion factors: Hydrochloric acid (protein; enzymes activity; i i bacteria) b i ) Pepsin (protein digestion) Gastric lipase (Lipids) Gastrin (stimulate gastric secretion and movement) Muscular Action of Digestive Tract Absorption in the Small Intestine Villi – Microvilli – Capillaries and lacteals – Chylomicrons Crypts Muscular Action of Digestive Tract - Peristalsis Peristalsis Segmentation 13 07-Apr-11 Muscular Action of Digestive Tract - Segmentation From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Large intestine colon – Ileocecal valve – Appendix Rectum – Anus From M to A: Digestion and Absorption From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Small intestine – Digestion Bicarbonate neutralizes stomach acid Pancreatic and intestinal enzymes – Carbohydrates – Fat – Protein Sphincter contractions – Reflux (heart burn) 14 07-Apr-11 From M to A: Digestion and Absorption Liver – Bile - Emulsifier Gallbladder 15 07-Apr-11 16