* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tina`s 12 Lead Class Notes
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
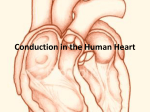
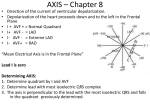
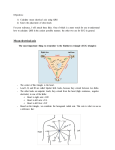
Basic 12 Lead EKGs Review Pathological Q-waves are greater than 0.04 seconds in duration and/or at least one-third the amplitude of the R-wave. U-waves (if seen) should be low and have the same deflection as the T-wave. S-T segment J-point is located at the end of the QRS where the T-wave begins. It should be isoelectric. If it has a deflection, either positive or negative, to be significant, it should be greater than 1 mm. QRS axis determination Lead I aVF Normal + + RAD + LAD + Indeterminate Left ventricular hypertrophy is indicated when the amplitude of the S-wave of V1 plus the R-wave amplitude in V5 is greater than or equal to 35 mm. Vessels involved in acute MI—bring heart to this class to show where they are Anterior MI—LAD Lateral MI—Left circumflex Inferior MI—RCA or sometimes left circumflex Involves left ventricle, but RV and RCA are involved in 30 – 50% of inferior MIs Use NTG and MSO4 with care because too much vasodilation can cause hypotension Give this patient fluid to maintain normal blood pressure Myocardial infarction and ischemia Type of infarct Associated leads Inferior II, III, aVF Septal V1, V2 Anterior V3, V4 Low lateral V5, V6 High lateral I, aVL Reciprocal leads I, aVL None None II, III, aVF II, III, aVF Acute MI is marked by S-T elevation and is often accompanied by reciprocal S-T depression. Recent MI (24 hours to one week) has minimal S-T elevation, frequent T-wave inversion, and Q-waves beginning to form. Reciprocal changes are minimal or absent. Old MI (greater than one week) has pathological Q-waves and occasional T-wave inversion. Ischemia is caused by a lack of oxygenated blood to an area of the heart and shows diffuse S-T depression with deep T-wave inversion. Acute MI and ischemia EKGs Pages 246, 250, 258, 260, 262, 266, 268, 272, 274, 276, 278, 280, 292, 306, 308, 310, 312, 314 Run 12 leads Q 5 minutes, if you’re suspicious that something may be going on. Remember to keep scene time to a minimum.