* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forest Management
Survey
Document related concepts
Fire ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Conservation movement wikipedia , lookup
Tropical rainforest wikipedia , lookup
Operation Wallacea wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
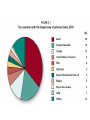
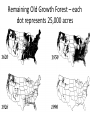
Forest Management: Issues with harvesting trees for wood-based products Area of forest Ecosystems • About one half of the forests that covered the earth are gone • Each year another 16 million hectares disappears • Today, forests cover ~1/4 of world’s total land area Some definitions… • Ecological (or ecosystem) services: Natural services or natural capital that support life on the earth and are essential to the quality of human life • Economic services: resources and opportunities available that support the functioning of the world’s economies Importance of Forests • • • • • • • • Ecological services: Support energy flow and nutrient cycling Reduce soil erosion Absorb and release water slowly Purify water and air Influence local and regional climate Store atmospheric carbon Provide numerous wildlife habitats • Forests remove _____ from and add _____ to the atmosphere. a. oxygen . . . carbon dioxide b. nitrogen . . . oxygen c. carbon dioxide . . . sulfur dioxide d. carbon dioxide . . . oxygen e. nitrogen . . . carbon dioxide Importance of Forests • • • • • • • • Economic Services: Fuelwood Lumber Pulp for paper Mining Livestock grazing Recreation Jobs • Which of the following is not an economic service provided by forests? a. purification of water and air b. fuelwood c. lumber d. mining e. jobs Types of Forests • Old-growth: uncut or regenerated forest that has not been seriously disturbed by human activities or natural disasters for at least several hundred years – <10% - 22% of world’s forest From Scientific American… • According to a study done in 2008, “Old growth forests in the U.S. Pacific Northwest as well as Canada and Russia consume 8-20% of the global terrestrial carbon sink, or roughly 440.9 million tons of carbon per year” • We release 1.8 billion tons through deforestation and crop-clearing a year… Remaining Old Growth Forest – each dot represents 25,000 acres • Second-growth • A stand of trees resulting from natural succession (the return of species to an area that has been disturbed) • Tree farm or plantation: • Farm of trees – all roughly the same age and generally one or two species that are harvested by clear-cutting as soon as they are commercially valuable How are trees harvested? • Selective cutting: harvesting intermediate-age or mature trees singly or in small groups – Reduces crowding, disease, encourages growth of younger trees • Clear cutting: Removes all trees in an area • Strip cutting: clear cutting a strip of trees with the corridor narrow enough to allow natural regeneration within a few years Which of these methods do you think is the most damaging and why? • Selective Cutting • Clear Cutting • Strip Cutting • Certified Sustainably Grown Timber must a. eliminate dead trees within the forest b. must include a minimum number of roads within the forest system c. ensure that cutting has not exceeded longterm forest regeneration d. All of the above. e. None of the above. Clear cutting in Washington Issues with Deforestation • • • • • • • Decreased soil fertility due to erosion Runoff of eroded soil into aquatic systems Extinction of species with specialized niches Loss of habitat Regional climate change from clearing Release of CO2 into the atmosphere Acceleration of flooding Cattle pasture in the Brazilian Amazon Solutions We can use forests more sustainably by emphasizing: Economic value of ecological services. Harvesting trees no faster than they are replenished. Protecting old-growth and vulnerable areas. Figure 10-12 An example of the 3 lenses of true sustainability • Less than 1.5% of original tree cover remains intact • Why???? Deforestation in Haiti • Haiti is still ranked as the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere – 80% live below the poverty line, 54% in abject poverty • Haiti’s electricity sector only covered 10% of its population in 2006 • Wood became and continues to be the principal energy source in Haiti - accounting for 70% of energy consumption • Deforestation leads to erosion – an estimated 6,000 hectares of soil lost each year to erosion (1 ha = 10,000 m2 = 2.47105 acres) • Also exposure to natural disasters – hurricanes, landslides, etc. • MIT researcher Amy Smith has been working with Haitians in developing a way to make charcoal for cooking from the waste fibers of sugar cane • Burns cleaner than wood charcoal • Saves trees, reduces lung disease and premature deaths Managing Forests • Forests on federal and state lands are managed according to multiple use doctrine – i.e. land is available for recreation and maintains a healthy forest ecosystem in the midst of forest harvest • Good news: Forests in the US cover more area than they did in 1920 – Considered to be the great environmental story of the US – US timber companies and conservation organizations are working together to protect large areas of forest – Every year more wood is grown in the US than cut – Protected forests make up about 40% of total forest area Forest Management Cont. • Fire management – controversial • Are all forest fires bad??? • Fire suppression can lead to highly destructive crown fires from the accumulation of brush and smaller trees • Also, many species need fires to survive – Ex: Several species of pine trees release their seeds only after the fire heats its cone to melt their waxy seals – Blazing star, wild lupine, sandplain gerardia (endangered species) also need fire to reproduce – Fires return nutrients quickly to the soil (oak trees rely on this) – Also help open up and maintain meadow habitats and grasslands • Solutions: • Controlled burns or prescribed fires : start small, contained surface fires to clear out brush • Allow fires in public lands to burn as long as the fires do not threaten human structures and life • Healthy Forests Restoration Act: (2003) allows timber companies to cut down economically valuable trees in 71% of the total area in national forests in return for clearing away smaller brush • Many fire scientists believe this will actually encourage large fires as timber companies remove the larger fire resistant trees and leave behind slash piles and smaller trees/brush