* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Kelly Marchant RN
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
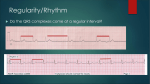
1. An abnormal p wave represents A. Irregular repolarization of the atria * B. Damaged atria C. Irregular depolarization of the ventricles 2. An EKG strip displays a P wave of 0.28 seconds. This rhythm is known as A. Normal Sinus Rhythm B. Bundle Branch Block * C. 1st Degree AV Block D. Ventricular Tachycardia 3. A normal QRS Complex usually measures * A. 0.06 -0.12 seconds B. 0.12- 0.2 seconds C. 0.2 -0.36 seconds D. 0.36- 0.44 seconds 4. An EKG wIth a QRS Complex of 0.20 seconds is representative of A. Normal sinus rhythm * B. Bundle Branch Block C. 1st Degree AV Block D. Ventricular tachycardia 5. A delayed impulse from the SA Node through the atria would measure A. 0.06 seconds B. 0.10 seconds C. 0.20 seconds * D. 0.28 seconds 6. A 3:1 A:V conduction ratio is present in what cardiac dysrhythmia? A. Atrial Fibrillation * B. Atrial Flutter C. Ventricular Fibrillation D. Ventricular Flutter 7. A patient is diagnosed with complete heart block. The most appropriate treatment for this patient would be… A. Administer 2L oxygen B. Increase dose of digoxin *C. Cardiac pacing D. Restrict IV fluid intake 8. A patient is noted to be in sinus bradycardia with a rate of 42 beats per minute with symptomatic hypotension. This condition would be best treated by A. Nitroglycerine B. Beta Blockers C. Aspirin *D. Atropine 9. An EKG is a measurement of * A. The electrical activity of cardiac muscle B. The contraction of cardiac muscle C. The strength of cardiac muscle D. All of the above 10. Your patient is complaining of palpitations. The patient’s EKG shows a heart rate of 120, regular rhythm, PR = 0.16, QRS complex = 0.08, and A:V conduction ratio is 1:1. The most appropriate nursing intervention to perform next would be A. Synchronized Cardioversion *B. Assess patient’s blood pressure C. Apply 2L oxygen by nasal cannula D. Administer Atropine 1mg IVP 11. A patient’s EKG demonstrates a rate of 35 and is in 2nd degree type II AV Block. The expected treatment for this patient would be A. Atropine 10 mg IVP B. Metoprolol 10 mg IVP C. Amlodipine 10 mg PO *D. Cardiac Pacemaker 12. During discharge teaching for a patient who was newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, the nurse recognizes the need for more teaching when the patient states A. I am starting on Warfarin to prevent blood clots *B. I should only take my Warfarin when I have chest pain C. Atrial fibrillation can lead to dizziness or low blood pressure D. I should take Warfarin at the same time every day 13. Under usual circumstances, after an impulse is generated in the SA node, it A. moves from left to right and top to bottom B. travels through the AV node to the Bundle Branches C. leads to cardiac muscle contraction *D. All of the above 14. 2nd Degree Type I AV Block A. Is also known as Wenckebach B. Is usually a temporary condition that is asymptomatic C. Has a pattern of a prolonged PR interval until a QRS complex is dropped *D. All of the above 15. A QRS complex that appears notched, and measures 0.16 seconds represents A. Normal ventricular depolarization B. Normal ventricular repolarization *C. A Bundle Branch Block D. An AV Block 16. PVCs (premature ventricular contractions) can be concerning because they can lead to *A. Ventricular tachycardia B. A Bundle Branch Block C. Complete Heart Block D. Ventricular bradycardia 17. Ventricular Tacchycardia can be caused by A. Coronary Artery Disease B. Digoxin Toxicity C. Left Ventricular Hypertrophy *D. All of the above 18. Your patient’s telemetry displays ventricular fibrillation. You assess the patient who is nonresponsive and with out a pulse or respirations. The most appropriate nursing intervention to perform would be A. A precordial thump *B. Defibrillation C. Chest compressions D. Administer 10 mg Atropine IVP 19. Ventricular fibrillation is concerning because A. It can lead to a life threatening arrhythmia B. The atrial and ventricular contractions are no longer coordinated *C. During this rhythm there is no cardiac output D. Conduction through the bundle branches is prolonged 20. A patient’s EKG in Lead II demonstrates a rate of 78, regular, PR 0.12 seconds, a QRS and 0.10 seconds, and an A:V conduction ratio of 1:1. Your analysis of this rhythm would be *A. Normal Sinus Rhythm B. Normal Sinus Rhythm with 1st Degree Av Block C. Normal Sinus Rhythm with 2nd Degree Av Block D. Normal Sinus Rhythm with Bundle Branch Block