* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download VUS 6 SLAVERY ISSUES 1. Drew a line through the Louisiana
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
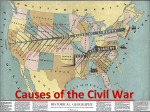
VUS 6 SLAVERY ISSUES 1. Drew a line through the Louisiana Purchase and prohibited slavery in the territories north of the line (36-30) except Missouri. Missouri enters the Union as a slave state and Maine as a free state: Missouri Compromise of 1820 2. Compromise of 1850 allowed what state to enter as a free state: California 3. What were the provisions of the Compromise of 1850 (also known as the California Compromise)? • • California entered the Union as a free state the new Southwestern territories acquired from Mexico (Mexican Cession – CC NUAN) would decide on their own (popular sovereignty). 4. To allow the people in the territories to decide whether to allow slavery: popular sovereignty 5. Provisions of the Kansas-Nebraska Act: a. repealed the Missouri Compromise line b. gave people in Kansas and Nebraska the choice whether to allow slavery in their states or not (“popular sovereignty”) 6. Which territory had a civil war over slavery: Kansas (Bleeding Kansas). The Kansas-‐ Nebraska Act produced bloody fighting in Kansas as pro-‐ and anti-‐slavery forces battled each other. It also led to the birth of the Republican Party that same year to oppose the spread of slavery. VUS 7 CIVIL WAR 1. Led to the secession of Southern states: Election of Lincoln 2. Causes of Civil War: • • • • • • • Sectional disagreements and debates over tariffs, extension of slavery into the territories, and the nature of the Union (states’ rights) Northern abolitionists versus Southern defenders of slavery United States Supreme Court decision in the Dred Scott case Publication of Uncle Tom’s Cabin by Harriet Beecher Stowe Ineffective presidential leadership in the 1850s A series of failed compromises over the expansion of slavery in the territories President Lincoln’s call for federal troops in 1861 3. The spark that started the Civil War: Ft. Sumter 4. Emancipation Proclamation is issued after this Union victory (which was the deadliest battle of the war): Battle of Antietam 5. The Emancipation Proclamation freed the slaves in states under rebellion (not in boarder states). 6. What battle is considered the turning point? Gettysburg 7. Identify the two sides that were fighting: Union (North) vs. Confederacy (South) 8. To end the Civil War, Lee surrendered to Grant at: Appamattox, Virginia 9. “Four score and seven years ago our fore-fathers…” Gettysburg Address 10. Lincoln wanted to preserve the Union 11. Assassinated Lincoln: John Wilkes Booth 12. Radical Republicans played a major role in the impeachment of: Lincoln 13. The South was divided into 5 military districts, state govt’s approved by Lincoln and Johnson were abolished, and new, stricter requirements were adopted for readmittance to the Union in the Reconstruction Act of 1867 14. What were the provisions of the Compromise of 1877? a. in return for support from Southern Democrats in the electoral college vote, the Republicans agreed to end the military occupation of the South (the Southern Democrats had to support the Republican candidate for president, Rutherford B. Hayes) b. former Confederates who controlled the Democratic Party before the Civil War regained power c. it opened the door to the “Jim Crow Era” and began a long period in which African Americans in the South were denied the full rights of American citizenship. 15. Laws put into place in the South legalizing segregation: Jim Crow laws 16. Describe the three Civil-Way Amendments? • • • 13th Amendment (1865): Slavery was abolished permanently in the United States. 14th Amendment (1868): States were prohibited from denying equal rights under the law to any American. 15th Amendment (1870): Voting rights were guaranteed regardless of “race, color, or previous condition of servitude” (former slaves). 17. Name tow Civil War Generals who did not want the South to be punished? Grant and Lee VUS 8 POST-RECONSTRUCTION 1. Before 1871 immigrants came from what areas? Northern and Western Europe 2. After 1871 immigrants came from what areas? Central and Southern Europe and Asia 3. The process of absorbing new culture, many immigrants were resistant to this: Assimilation (took place in public schools) 4. What served an essential role in the assimilation of immigrants into American society? Public schools 5. What did the Chinese Exclusion Act, Gentlemen’s Agreement, and Immigrant Restriction Act of 1921 do? Restricted immigration 6. Supreme Court ruled that “separate but equal did not violate the 14th Amendment” Plessy v. Ferguson (1898) 7. Mass movement of African Americans to Northern cities in search of jobs and to escape discrimination: Great Migration 8. This movement used government to reform problems created by industrialization. Progressive Movement 9. Gov’t controlled by the people, guaranteed economic opportunity through gov’t regulation, and elimination of social injustices are all goals of what? The Progressive Movement 10. Roosevelt’s economic plan: Square Deal 11. Wilson’s economic plan: New Freedom 12. Labor Unions: American Federation of Labor (AFL), Kights of Labor, American Railway Union (ARU), International Ladies’ Garment Workers Union 13. Labor Strikes: Pullman Strike, Haymarket Square Riot, Homestead Strike 14. AFL leader: Samuel Gompers 15. ARU leader: Eugene V. Debs 16. Accomplishments of Unions: higher wages, 8 hour day, safer working condtions 17. Female African-American newspaper editor and muckraker who used her newspaper to speakout against lynching? Ida B. Wells 18. What muckraker wrote about the meat packing industry? Upton Sinclare Name of book. The Jungle 19. What act provided free public land to any settlers willing to live on and work the land: Homestead Act 20. Reasons for economic growth after Civil War: Industrialization in the north and midwest and immigration 21. When government takes a “hands-off” approach to regulation business: Laissez Faire 22. Believed in a gradual approach to ending segregation: Booker T. Washington 23. Believed in equality immediately and started the NAACP: W.E.B. DuBois 24. Two leaders of Women’s Suffrage Movement: Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony 25. Amendment gave women right to vote: 19th Amendment VUS 8 INVENTIONS/ INVENTORS 1. Cotton Gin: Eli Whitney What affect did it have on the South? Increased cotton production and the demand for more slaves. 2. Electricity: Thomas Edison 3. Telephone: Alexander Graham Bell 4. Mechanical Reaper: Cyrus McCormick 5. Airplane: Wright Brothers 6. New process for stronger steel: Bessemer Process 7. J.P. Morgan: Finance 8. John D. Rockefeller: US Oil 9. Cornelius Vanderbilt: railroads 10. Andrew Carnegie: US Steel