* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Public Lecture - Size of the Universe
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
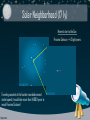
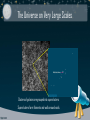
SIZE OF THE UNIVERSE James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC “Somewhere, something incredible is waiting to be known.” -Carl Sagan Measuring Distance • Base unit = meters (m) and kilometer (km) – Used to describe “smaller” distances (ie: Earth to Moon) • Astronomical Unit (AU) = 1.496 x1011 m – AU is the average Earth-Sun distance – Used to measure solar system distances • Light year (ly) = 63240 AU – The distance light travels in one year! – Used to measure distances between nearby stars • Parsec (pc) = 3.26 ly – Used to measure galactic distances – Kiloparsec (1000 pc) and Megaparsec (1,000,000 pc) used for extragalactic distances Distance is a Measure of Time • All information comes in the form of light – Max light speed = 300,000 km/s • Farther away an object is (spatial distance), the more time light has taken to reach us • Celestial objects are not observed as they are, but rather as they were 16 x 16 m 1 mile x 1 mile 100 miles x 100 miles Diameter of the Earth 12,756 km Earth-Moon Distance: 384,000 km Sun-Earth Dist.: ~150,000,000km (or 1 AU) Solar System (approx. 100 AU) (Almost) Empty Space Around Our Solar System: 10,000 AU Solar Neighborhood (17 ly) Nearest star to the Sun: Proxima Centauri, ~4.2 light years Traveling constant at the fastest recorded manned rocket speed, it would take more than 114,000 years to reach Proxima Centauri! Extended Solar Neighborhood (1,700ly) Diameter of Milky Way ~100,000 ly Local Group of Galaxies Distance to the nearest large galaxies: several million light years The Universe on Very Large Scales Clusters of galaxies are grouped into superclusters. Superclusters form filaments and walls around voids. How big is the Universe? • The Milky Way is one of about 100-500 billion galaxies • Each galaxy is estimated to contain approximately 100-400 billion stars • Estimated number of stars – Low: 10 billion, billion = 10 sextillion – High: 200 billion, billion = 200 sextillion • That’s a lot of stars! Scientific Notation • Compact manner in which very large numbers are made manageable – For example: 5.9742 x 1024 kg = 597,420,000,000,000,000,000 kg Name (U.S.) Number Scientific Notation How long would it take to count to this number from 0 One 1 100 1 second Thousand 1,000 103 17 minutes Million 1,000,000 106 12 days Billion 1,000,000,000 109 32 years Trillion 1,000,000,000,000 1012 32,000 years (longer than any civilization on Earth) Quadrillion 1,000,000,000,000,000 1015 32 million years (longer than humans on Earth) How big is the Universe? • Postulate: The Universe has as many stars as grains of dry sand on all of Earth’s beaches. • How many grains of dry sand are there on all of Earth’s beaches? 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑠 ≥ 𝑆𝑎𝑛𝑑? Calculating Grains of Sand • One grain of dry sand measures approximately 0.5 mm – 20 mm of side-by-side sand would create 1 centimeter (< 0.5 in) • To estimate the amount of sand on all of Earth’s beaches – Must estimate the average volume of a sandy beach and the average amount of coastlines which are beaches – Estimated to be 700 trillion cubic meters of beach • or about 2.5-10 sextillion grains of sand At the low end, there are just as many, if not more stars in the universe than grains of sand on all of Earth’s beaches! FOR ASTRONOMY NEWS + EVENTS… Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC LSSC.edu/faculty/james_martin Thank You for Attending!